Heat in Changes of State
advertisement

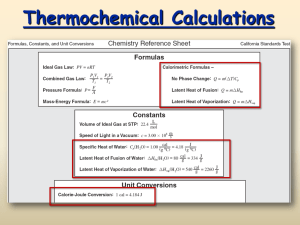
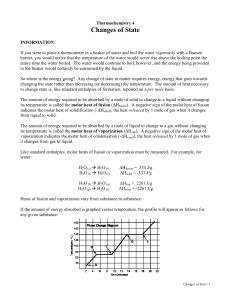
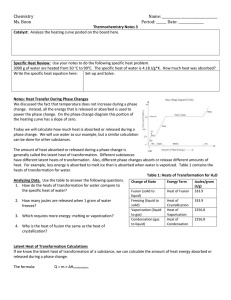
Heat in Changes of State Section 17.3 Standards 7.c. Students know energy is released when material condenses or freezes and is absorbed when material evaporates or melts. 7.d. Students know how to solve problems involving heat flow and temperature changes, using known values of specific heat and latent heat of phase changes. Heats of fusion and solidification All solids absorb heat as they melt to become liquids Molar heat of fusion: the heat absorbed by one mole of solid substance as it melts to a liquid (ΔHfus) Molar heat of solidification: the heat lost when one mole of liquid solidifies (ΔHsolid) Heat of fusion and solidification The quantity of heat absorbed by a melting solid is exactly the same as the quantity of heat released when the liquid solidifies. OR ΔHfus = ΔHsolid Figure Problem 15 Problem 16-18 Heat of vaporization and condensation Molar heat of vaporization: the amount of heat necessary to vaporize one mole of a given liquid (ΔHvap)) H2O (l) H2O (g) Δhvap = 40.7 kJ/mol Molar heat of vaporization and condensation Molar heat of condensation: the amount of heat released when 1 mol of vapor condenses (ΔHcond) The quantity of heat absorbed by vaporizing a liquid is exactly the same as the quantity of heat released when the vapor condenses ΔHvap = -ΔHcond H2O (g) H2O (l) ΔH = -40.7 kJ/mol Heating curve Answer questions a, b, and c. Sample Problem #19 Questions 20-22 Molar Heat of Solution During the formation of a solution, heat is either released or absorbed Molar heat of solution: the enthalpy change caused by dissolution of one mole of substance Sample Problem Problems #23-25 TO DO In Class: Pg 25 #27-31, Pg 27 #5556 HW: Pg 25 #17-20