bone_muscle_exam
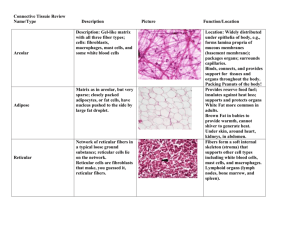
advertisement

Name: _____________________________________ Period: __________________ Date: ________________ Connective Tissue Exam 1. ________ Hyaline Cartilage is defined as a. closely packed but very thing and fine collagen fibers making it tough but flexible b. numerous and very conspicuous elastic fibers that make it extremely resilient and flexible c. dominated by course, readily visible bundles that are interwoven. 2. ________ Fibro Cartilage is defined as a. closely packed but very thing and fine collagen fibers making it tough but flexible b. numerous and very conspicuous elastic fibers that make it extremely resilient and flexible c. dominated by course, readily visible bundles that are interwoven. 3. ________ Elastic Cartilage is defined as a. closely packed but very thing and fine collagen fibers making it tough but flexible b. numerous and very conspicuous elastic fibers that make it extremely resilient and flexible c. dominated by course, readily visible bundles that are interwoven. 4. ________ Cartilage found in the larynx is the a. Elastic b. Fibro c. Hyaline 5. ________ Cartilage found in the epiglottis is called a. Elastic b. Fibro c. Hyaline 6. ________ Cartilage found in the outer ear is called a. Elastic b. Fibro c. Hyaline 7. ________ Cartilage found in the sternum is called a. Elastic b. Fibro c. Hyaline 8. ________ Cartilage found in the synovial joints is called a. Elastic b. Fibro c. Hyaline 9. ________ Cartilage found in the intervertebral discs is called a. Elastic b. Fibro c. Hyaline 10. ________ Cartilage growth is slow due to a. life cycle of chondrocytes b. amount of nutrients needed for new cartilage not found in normal diet. c. rate of waste removal and input of needed nutrients due to avascular conditions. d. Constant movement of cartilage does not give proper healing time.. 11. ________ All of the following are functions of the skeletal systems except: a. Blood Cell Production in bone marrow. b. Storage of minerals and lipids. c. With the use of muscles, act as a lever. d. Energy production. 12. ________ Mature bone cells are known as a. osteoblast b. osteocytes c. osteoprogenitor cells d. osteoclast 13. ________ Cells that actively deposit bone matrix before maturing are called a. osteoblast b. osteocytes c. osteoprogenitor cells d. osteoclast 14. ________ Bone stem cells who give rise to osteoblast to repair bone are called a. osteoblast b. osteocytes c. osteoprogenitor cells d. osteoclast 15. ________ Bone cells that remove bone matrix when nutrients are needed a. osteoblast b. osteocytes c. osteoprogenitor cells d. osteoclast 16. ________ Joints that are immovable and found in the bones of the skull a. synarthrosis b. amphiarthroses c. diarthroses d. ellipsoidal 17. ________ A synovial joint that is find between the carpals and tarsals is the a. saddle joint b. ball-and-socket joint c. pivot joint d. gliding joint 18. ________ Shoulder is considered a a. gliding joint b. hinge joint c. ball-and-socket joint d. pivot joint 19. ________ Allows for pronation and supination of the palm a. Pivot joint b. Gliding joint c. Saddle joint d. Ellipsoidal joint 20. ________ Hinge joint is found in the a. Shoulder socket b. Knee c. Elbow d. A & C e. B & C 21. ________ Humans have a(n) a. Exoskeleton b. Endoskeleton c. Cartilaginous skeleton Cardiac Straited Smooth 22. ________________________ Muscles that are found in the gut and blood vessels 23. ________________________ Muscles found in the heart for pumping blood are called 24. ________________________ Muscles found in the leg or arm are called 25. Explain in as much detail as you can the contraction of a muscle (you may utilize drawings to help your explanation). 26. Explain the differences between force / work / power. 27. What is the origin and insertion of a muscle? How does this help with flexion or extension? 28. What is the role of connective tissue (cartilage) in the body (3 things)? 29. Explain in detail why is cartilage slow to heal in comparison to other types of tissue? 30. List and briefly describe the five primary functions of the skeletal system. Bonus 31. Bone tissue is composed primarily of two basic elements, collagen and calcium phosphate. What characteristics do they give to bone tissue?