Jacksonian Democracy
advertisement

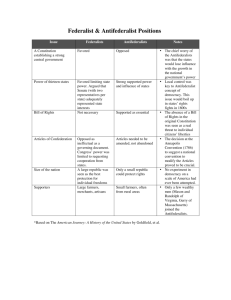
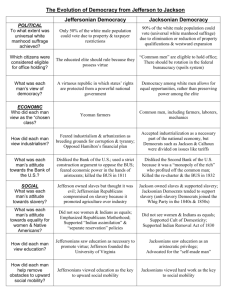
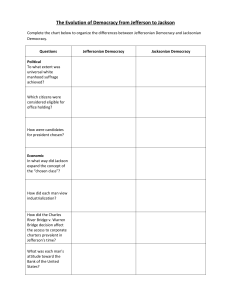
Jacksonian Democracy Jacksonian Democracy compared with Jeffersonian Democracy Jefferson • Believed that capable, well-educated leaders should govern in people’s interests. • Reelected chiefly an agricultural society. • Limited democracy mainly to its political aspects. Andy’s turn Jackson • Believed that the people themselves should manage governmental affairs. • Reflected an agricultural and industrial society. • Expanded democracy to include social and economic aspects Political aspects of the Jackson Era • 1. Democracy in the states. (qualifications, elected vice appointed officials, term lengths.) • 2. Democracy in Presidential elections. Down with “King Caucus”. Conventions instead. • 3. Democratic view of the Presidency. The veto, South Carolina challenge, refusal to enforce Marshall decision regarding the Cherokee. • 4. Spoils system. “To the victory belong the spoils.” Encouraged turnover and this protected against built-in aristocracy. Economic aspects of the Jacksonian Era • 1. Cheap land. 80 acres for as little as $1.25 an acre. Squatters rights. • 2. Growth of Trade Unions. Located mainly in large cities. Sectional Issues The Northeast Bank Supported Internal improvements Supported Territorial Expansion Opposed Liberal land policy Opposed Expansion of Slavery Opposed the South Protected Tariff Favored Sectional Issues The West Protective Tariff Supported the North Second Bank of the US Opposed Internal improvements Favored Liberal Land Policy Supported Territorial Expansion Supported the South Expansion of Slavery Utilzed free labor Sectional Issues The South Protective Tariff Opposed the North Second Bank of the US Opposed Internal Improvements Opposed Federal expenditures Liberal Land Policy Divided More land v. Western Influence Territorial Expansion Favored Expansion of Slavery Favored