Chapter Four: The Periodic Table
advertisement

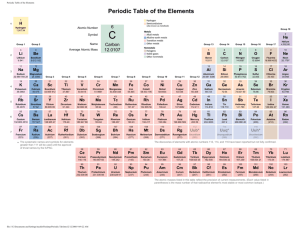
Chapter 6.1, 6.3 The Periodic Table Day One Thursday October 27th ORGANIZATION OF THE ELEMENTS The Elements • As scientists learned more about the elements, they organized them in different ways…think about how a grocery store is organized. – Organized by the properties of the elements • So who came up with this wonderful Periodic Table of Elements? Antoine Lavoisier • Made a list of all of the known elements at the time of the late 1700s. • Industrial Revolution played a major role in the advancement of chemistry. • Once we started using the same method for determining atomic mass, scientists could begin trying to understand the relationships among the elements. Organizing Elements Activity • How did you arrange the elements? – Trends in color (periods and groups) – Trends for mass (periods and groups) – Where would you put Fuchsia gas? Range for the mass? – Properties for the element that would fill the last remaining gap in the table? Xn Ad Bp Rx Tu Qa Pd Lq Cx Ax The wavelength decreases across the period and color becomes lighter down the group. The mass increases across the period and down the group. Cx does not fit the period trend for mass, but it fits in the third column with other green brittle solids. Ph would fit in the third period, first column based on color and stated trends. The mass would be between 99-106g. The remaining gap would be a yellow-colored liquid with a mass most likely between 70g-82g. John Newlands 1865: English Chemist • Arranged the known elements according to properties and in order of increasing atomic mass • He noticed that all elements in a given row had similar properties and this pattern repeated every eight elements (Law of Octaves) – Patterns like this occur periodically (periodic table) Dmitri Mendeleev 1869: Russian Chemist • Invented the first Periodic Table (my hero!) • Organized the 63 known elements according to their properties and predicted elements not yet known to exist. • Periodic Law: repeating physical and chemical properties change periodically with their atomic # • Two interesting things came from this: 1. Gaps 2. Elements did not necessarily fit according to atomic mass Mayer • Worked at the same time as Mendeleev, but didn’t get his work published quick enough to get credit for it. • Demonstrated connection with element properties and atomic mass. Henry Mosley • Discovered the problems with Mendeleev’s arrangement of the periodic table. • Discovered that atoms contain a unique # of protons called the atomic #. • Rearranged the elements in order of atomic # -which gave way to periodic patterns of the properties. The Periodic Table • Organized in rows and columns – Rows = PERIODS – Columns = (GROUPS or FAMILIES) • Each box is for all of the information for a single element. – Contains the name, symbol, atomic #, and atomic mass. • Elements in groups 1,2, and 13-18 have a much larger range of chemical/physical properties. They often get called main group or representative elements. • Groups 3-12 are referred to as transition elements. • www.learn360.com – Power of the Periodic Table Page 49 Name of Group Alkali Alkaline Earth Halogen Noble Transition Location on the Periodic Table Main Characteristics Day Four Tuesday November 4th FAMILIES DISCUSSION METAL/NONMETAL & ELECTRON CONFIGURATION NOTES Discussion of Families Lab • Let’s look at Mg, Ca, Ba. – What family are they in? – Do you notice any trends with reacting with chemicals? • Let’s look at Cl, Br, I. – What family are they in? – Do you notice any trends with reacting with chemicals? Based on what we observed, which pairs of elements would you expect to behave similarly? Scandium and Lawrencium Potassium and Hydrogen Neon and Krypton Actinium and Thorium Rhodium and Silver Neon and Carbon Selenium and Polonium Germanium and Lead Characteristics of Metals/ Nonmetals • Conducts electricity • Malleable (bends without breaking) • Reacts with Acid • Doesn’t conduct • Brittle • Doesn’t react with acid Where are they located? BAtMAN!!!!! Day Five Wednesday November 5th METAL/NONMETAL LAB M/NM & FAMILIES LAB W-UP Recording Data for Metal/Nonmetal Lab . 1. ( ) shiny 2. ( ) dull 3. (-) malleable 4. ( +) reacts with acid Conductivity 4. ( ) bright light 5. ( ) dim light 6. (X) no light Day Nine and Ten Tuesday November 11th and Wednesday November 12th POSTER ON ELEMENTS