AY 2013-2014 (doc)
advertisement

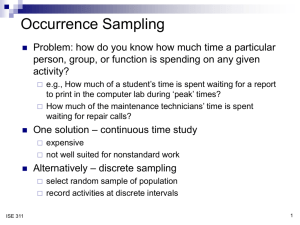
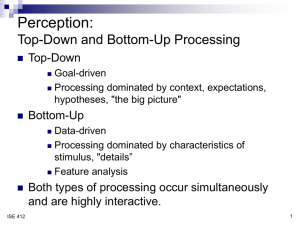
SJSU Annual Program Assessment Form Academic Year 2013-2014 Department: Industrial & Systems Engineering Program: Industrial & systems Engineering College: Engineering Website: http://ise.sjsu.edu/ - Check here if your website addresses the University Learning Goals. Program Accreditation (if any): ABET through 2018 Contact Person and Email: Minnie H. Patel Minnie.patel@sjsu.edu Date of Report: March 1, 2014 Part A 1. List of Program Learning Outcomes (PLOs) a b c d e f g h i j k Have an ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science and industrial and systems engineering. Have an ability to design and conduct experiments, as well as to analyze and interpret data. Have an ability to design a system, component, or process to meet desired needs within realistic constraints such as economic, environmental, social, political, ethical, health and safety, manufacturability, and sustainability Have an ability to function on multi-disciplinary teams. Have an ability to identify, formulate and solve engineering problems. Have an understanding of professional and ethical responsibility. Have an ability to communicate effectively. Have the broad education necessary to understand the impact of engineering solutions in a global, economic, environmental, and societal context Have a recognition of the need for, and an ability to engage in, life-long learning. Have the knowledge of contemporary issues. Have an ability to use the techniques, skills, and modern industrial and systems engineering tools necessary for industrial and systems engineering practice. x x x Social and Global Responsibilities Applied Knowledge Intellectual Skills Broad Integrative knowledge PLO/ULG a. Disciplinary Knowledge b. Proficiency with experiments c. Design d. Multidisciplinary teamwork e. Problem solving f. Ethics g. Communication skills h. Broad impacts of engineering i. Life-long learning j. Contemporary issues of engineering k. Modern Tools Specialized knowledge 2. Map of PLOs to University Learning Goals (ULGs) x x x x x x x x x x x x 3. Alignment – Matrix of PLOs to Courses Each ISE course coordinator applied Bloom’s Taxonomy of learning levels (Table 3.1) to characterize the expected level of learning for each course topic. Table 3.1 – Bloom’s Taxonomy Bloom’s Taxonomy Remembering Understanding Applying Active Description Verbs Retrieving, recognizing, and recalling relevant knowledge from long-term memory. . Constructing meaning from oral, written, and graphic messages through interpreting, exemplifying, classifying, summarizing, inferring, comparing, and explaining. Carrying out or using a procedure through executing, or implementing. Level of Learning + ++ Analyzing Evaluating Creating Breaking material into constituent parts, determining how the parts relate to one another and to an overall structure or purpose through differentiating, organizing, and attributing. Making judgments based on criteria and standards through checking and critiquing. Putting elements together to form a coherent or functional whole; reorganizing elements into a new pattern or structure through generating, planning, or producing. +++ Matrix mapping of course topics to Program Outcomes Each ISE course coordinator applied Bloom’s Taxonomy of learning levels (Table 3.1) to characterize the expected level of learning for each course topic. The Table 3.2 summarizes program learning outcomes mapped to each course in the program at appropriate leaning levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy. Table 3.2 – ISE Program – Outcome Mapping Matrix Outcome Mapping Matrix – 2010/11 Program Outcome: a b c d e f g h i j k + + + + + Required Courses (Engineering Core) Engr. 10 + ME 20 + CmpE 46 Or 30 ++ + ++ Engr. 100W ++ ++ EE 98 + MATE 25 + ISE 102 ++ +++ ++ ++ + + ++ ++ +++ +++ CmpE 131 ISE 105 +++ +++ ++ ISE 115 +++ +++ +++ ++ ISE 120 ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ISE 130 +++ ++ ++ + ++ ++ ++ ISE 131 ++ ++ ++ +++ +++ ++ ++ ISE 135 ++ ++ ++ ++ +++ ++ ISE 140 ++ +++ +++ ++ +++ ++ ++ ++ ISE 142 ++ ++ +++ +++ +++ ++ +++ + + +++ ++ +++ +++ ++ ++ +++ +++ ++ +++ + +++ ++ ++ ++ ++ +++ ++ +++ ++ ++ ++ ++ +++ + ++ + +++ ++ ISE 151 ISE 155 ++ ISE 167 +++ ++ ++ ISE 170 +++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ +++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ +++ +++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ Capstone Courses ISE 195A ISE 195B +++ +++ ++ +++ +++ Elective Courses ISE 112 ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ +++ ISE 114 +++ ++ +++ ++ +++ +++ ISE 164 + ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ME 110 + Skill level 1 or 2 in Bloom’s Taxonomy ++ Skills relevant but not presently assessed Skill level 3 or 4 in Bloom’s Taxonomy +++ Skill level 5 or 6 in Bloom’s Taxonomy The Outcome Mapping Matrix in Table 3.2 above indicates across the ISE curriculum, each outcome is addressed many times at all levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy. The table also points out the contributions of the Engineering Core and Technical Writing course to the achievement of program learning outcomes. 4. Planning – Assessment Schedule See Table 4.1 summarizing performance criteria for each program learning outcome, corresponding courses used to assess and evaluate student outcomes, and semester in which data are collected and results analyzed every two years. However, we do assess the outcomes using the senior exit exam every year and analyze every two years. The last time the data for each performance criterion listed in Table 4.1 was collected and analyzed in Fall 2012 and Spring 2013. Currently the outcomes of the data analysis results are being implemented for improvement of learning. The next time the student outcomes will be assessed in Fall 2014 and Spring 2015 and implemented in Fall 2016 and Spring 2017. Thus we have an assessment cycle for performance criteria with an alternating data collection and analysis period of one academic year and an implementation of assessment data analysis results in the following academic year period. Table 4.1: Student Outcome and Corresponding Performance Criteria along with the Course Numbers ABET Outcome a An ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science, and engineering Performance Criteria Assessment Solve statistical decision making engineering problems (Apply knowledge of mathematics) ISE 130 Solve management decision making engineering problems ISE 170 F S X X (Apply knowledge of math, science, and engineering) b c An ability to design and conduct experiments, as well as to analyze and interpret data An ability to design a system, component, or process to meet desired needs within realistic constraints such as economic, environmental, social, political, ethical, health and safety, manufacturability, and Solve engineering economic problems (Apply knowledge of mathematics) ISE 102 X Solve statistical decision making engineering problems (Analyze and interpret data) ISE 130 X Design experiments and collect, analyze, and interpret data to solve engineering problems ISE 135 X Collect, analyze, and interpret data in simulation studies ISE 167 X Design and plan process, facilities ISE 195B X sustainability d An ability to function on multi-disciplinary teams Develop a strategic and management plans ISE 195B Collaboration and conflict management: team development, interpersonal style, conflict management, participation ISE 151 X Team Communication: ISE 151 X ISE 151, X ISE 140 X Formulate and solve engineering economic analysis problems ISE 102 X Demonstrate improvement of process strategies, cycle time, and WIP reduction ISE 140 X Formulate and solve operations research/management decision making problems ISE 170 Demonstrates an ability to make informed ethical choices ISE 151, 105 X Demonstrates knowledge of professional code of ethics ISE 151, ISE 195A X X Active listening, feedback, influencing others, sharing information Team decision making: Defining a problem, innovation and idea generation, judgment/ using facts, reaching consensus Team performance on a multidisciplinary project e f g An ability to identify, formulate, and solve engineering problems An understanding of professional and ethical responsibility An ability to communicate effectively Communicate in small teams, writing and in variety of other ways ISE 120 X X X h i j Understanding of the impact of engineering solutions in global/societal context Recognition of the need for, and an ability to engage in lifelong learning Knowledge of contemporary issue Develop technical writing skills ENGR 100W X Demonstrates effective technical presentations and writing senior design report ISE 195A and ISE 195B Evaluate society context of poor quality ISE 131 X Demonstrate approaches to improve quality ISE 131 X Demonstrate the impact and benefits of moving to a leaner production system ISE 140 Develop green system solutions ISE 195B Learn to use a ProModel, and excel for solving operational problems ISE 140 Learn to use MINITAB and Microsoft Excel to for solving statistical quality problems ISE 131 Research and present on contemporary topics ISE 195A X Research and analyze new IE topics ISE 195A X Use of current financial data/parameters to solve engineering decision-making problems ISE 102 X Develop an understanding of the "state of the art" of service management thinking ISE 142 X Remember/recognize the benefits of a well-defined and integrated supply chain and the technical benefits and impact of an ERP system ISE 155 X Research and present contemporary ISE 195A X X X X X X X topics k Ability to use the techniques, skills and modern engineering tools necessary for engineering practice Learn to use LINDO optimization software to do sensitivity analysis ISE 170 Learn to use a simulation software PROMODEL to do the analysis of the existing systems/processes ISE 167 X X The senior exit oral and written exam data collected during academic year 2012-2013 and 20132014 will be analyzed in summer of 2014. The results will be implemented in 2014-2015. 5. Student Experience The PLOs are posted on the ISE webpage. Here is a link http://ise.sjsu.edu/content/bs-ise-studentoutcomes. The students’ feedback is considered in defining and improving program objectives via alumni survey. The program learning outcomes are then revised accordingly since they map to program objectives. Thus students’ feedback is considered indirectly. Part B 6. Graduation Rates for Total, Non URM and URM students (per program and degree) <These numbers can be obtained for your program from the IEA website at http://www.iea.sjsu.edu/ under Retention/Graduation. URM stands for Under-Represented Minorities. In some cases, the number of students who choose to report their ethnicity is too small to compute a reliable number, so please check if this is the case before interpreting. The university targets for first-time freshmen 6-yr graduation rates set by the Chancellor’s Office are 51.6%, 47.8%, and 53.2%, for total, URM and Non-URM populations, by 2015-2016. The university targets for transfer and graduate students are not specifically published, but generally improvement is expected here too. > First-time Freshmen: 6 Year Graduation Rates Academic Programs Industrial/Syst.Engineering Fall 2007 Cohort New UG Transfers: 3 Year Graduation Rates Fall 2010 Cohort Grads : 3 Year Graduation Rates Fall 2010 Cohort Entering % Grad Entering % Grad Entering % Grad Total 2 50.0% 12 25.0% 50 64.0% URM 1 0.0% 8 37.5% 3 33.3% Non-URM 0 0.0% 3 0.0% 23 43.5% Other 1 100.0% 1 0.0% 24 87.5% 7. Headcounts of program majors and new students (per program and degree) Fall 2013 New Students Industrial/Syst Engineering Degree Cont. Students Total 1st Fr. UG Transf New Creds 1st Grads UGs Creds Grads UGs Creds Grads Total 8 11 0 56 101 0 108 120 0 164 BS 8 11 0 0 101 0 0 120 0 0 MS 0 0 0 56 0 0 108 0 0 164 8. SFR and average section size (per program) <The student-to-faculty ratio (SFR) and the average headcount per section can be found at the IEA website at http://www.iea.sjsu.edu/Courses/default.cfm#Prefix under your department name. SFR and average section sizes provide some measure of cost-effectiveness and faculty load. The values can be compared to the college and/or university averages, or a comparable program at another university, if applicable. Any SFR ratios or average section sizes that are either much bigger or smaller than average should be explained and or addressed.> Fall 2013 Course Prefix Course Level ISE - Industrial/Syst Engineer Total Student to Average Faculty Ratio Headcount per (SFR) Section 31.0 30.1 Upper Division 37.4 41.9 Graduate Division 25.3 21.3 9. Percentage of tenured/tenure-track instructional faculty (per department) Fall 2013 Industrial & Systems Engineering % Tenured/Prob Tenured 49.5% 2.885 Probationary Temp Lecturer 2.941 0 Part C 10. Closing the Loop/Recommended Actions Academic year 2013-2014 is an implementation phase of the assessment cycle. We have implemented and/or are implementing the recommendations of the previous phase (assessment data collection, analysis, and recommendation). In Fall 2013 the following actions were taken to improve achievement of program learning outcome j: ISE 102 Course: Depreciation methods and their impact on income taxes were emphasized. Several problems were presented and discussed in the class to improve learning. MACRS depreciation method was particularly emphasized. In Fall 2013 the following actions were taken to improve achievement of program learning outcome k: ISE 167 Course: ProModel model building fundamentals were emphasized and several examples were presented in the class as well as lab to improve student learning in this area. In Spring 2014 the following actions were taken/to be taken to improve achievement of program learning outcomes a and e: ISE 170 Course: Many problems will be solved in the class in the area of Markov chain and throughout the semester the instructor is making a conscious effort to explain with details how to formulate and solve decision making problems using spreadsheet optimizer. In future the instructor plans to video record some lectures to enhance student learning of ISE170. In Spring 2014 the following actions were taken/to be taken to improve achievement of program learning outcome k: ISE 155 Course: The instructor will emphasize mitigating risk in implementation of IT in supply chains to improve student learning. The instructor will give real world examples to show how to avoid risk in IT implementation. 11. Assessment Data Assessment Data Summary – Fall 2012 ABET Performance Criteria Outcome a An ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science, and engineering Course Assessment Method Assessment Result Calculate probability and mean and variance of a probability distribution. (Apply knowledge of mathematics) ISE 130 Test #1 Q5 on finding the mean, variance of a pdf and finding conditional probability and fundamentals of probability 83% of the students scored 70% or above on Q5, Test #1 Solve engineering economic problems (Apply knowledge of mathematics) ISE 102 Test #1 Q1 on use of learning curve in estimating standard time, time value of money, and cash flow 87% of the students scored 70% or above on Q2, Test #1 diagram b An ability to design and conduct experiments, as well as to analyze and interpret data ISE 102 Test #1 Q3 on performing breakeven analysis to determine the best alternative over ranges of production levels and calculating future worth using TVM 82% of the students scored 70% or above on Q3, Test #1 Solve statistical decision making engineering problems (Analyze and interpret data) ISE 130 Graphical and numerical summary of data, identification of outliers, and dealing with the outliers 73% of the students scored 70% or above on Q2a, Test #2 Design experiments and collect, analyze, and interpret data to solve engineering problems ISE 135 Using factorial experiment to assess the effect of important factors and their interactions on the life of a cutting tool 97% of the students scored 70% or above on Q2a, Test #2 Collect, analyze, and interpret data in simulation studies ISE 167 The assignment for the students was to calculate the “Kanban Size” by part type, and the Producing Process “Batch Size” by part type, that will result in the 85.2% of the students scored 70% or above on final project smallest possible WIP levels that meet/exceed production requirements. They needed to do this for various levels of demand, and various levels of process variability. d An ability to function on multidisciplinary teams Collaboration and conflict management: team development, interpersonal style, conflict management, participation ISE 151 Description of phases of team building 89% of the students scored 70% or above on Quiz #2 Q3 Team Communication: ISE 151 key considerations while providing feedback 89% of the students scored 70% or above on Final Exam Q2 ISE 151 Descriptions of Directive and Achievementoriented decisionmaking 100% of the students scored 100% on Final Exam Q6 Formulate and solve engineering economic analysis problems ISE 102 Estimating present worth of a cost of perpetual life investment alternative 91% of the students scored 70% or above on Q5, Test #2 Understand improvement of process strategies, cycle time, and WIP reduction ISE 140 Final Project: 100% of the students scored 70% or above on the final project Active listening, feedback, influencing others, sharing information Team decision making: Defining a problem, innovation and idea generation, judgment/ using facts, reaching consensus e An ability to identify, formulate, and solve engineering problems f An understanding of professional and ethical responsibility Demonstrates knowledge of professional code of ethics ISE 140 Final exam Q4 93% of the students scored 70% or above on Final Exam Q4 ISE 151, ISE 151: NSPE code of ethics knowledge using Apollo 13 findings and determination s 88% of the students scored 70% or above on Homework #10 Q1 ISE 151 Ethics assignment on Hubble space telescope Optics demonstrating knowledge of professional codes of ethics and ability to make informed ethical choices g An ability communicate effectively to Develop technical writing skills ENGR 100W Demonstrates effective technical presentations and writing senior design report ISE 195A 100% of the students scored 70% or above on ethics assignment X 100% of the students score passing grade Technical presentations on the contemporary ISE topics 95% of the students scored 70% or in technical presentation #1 and 100% of the students scored 70% or above in technical presentation #2. 100% of the students scored 85% or above in the final presentation. When we look at the raw scores of the students for technical presentations #1, #2, and final, there seem to be an improvement trend in the students’ presentation scores h i j Understanding the impact engineering solutions global/societal context of of ISE 140 Experimenting with batch size, priority rule, pull vs push on project 78% of the students scored 70% or above on the relevant portion of the project Learn to use a ProModel, and excel for solving operational problems ISE 140 Using ProModel to successful complete scheduling portion of the project 100% of the students scored 100% on the scheduling portion of the final project ISE 167 Analyze operation of a job shop 91% of the students scored 70% or above on HW #1, Q2. Analyze emergency room operations 64% of the students scored 70% or above on Q5, Test #1 Calculation of depreciation of capital investment using MACRS 66% students scored 70% or above on Q4 of the final exam in Recognition of the need for, and an ability to engage in lifelong learning Knowledge contemporary issue Demonstrate the impact and benefits of moving to a leaner production system of Use of current financial data/parameters to solve engineering decisionmaking problems ISE 102 method income effects k Ability to use the techniques, skills and modern engineering tools necessary for engineering practice Learn to use a simulation software PROMODEL to do the analysis of the existing systems/processes ISE 167 and tax PROMODEL model building fundamentals 64% students scored 70% or above on Q7 of Test #2 Assessment Data Summary - Spring 2013 ABET Outcome a c Performance Criteria Course Assessment Instructor An ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science, and engineering Solve management decision making engineering problems ISE 170 Final Exams. Q1 is on Markov Chain; Q3 is on queueing theory, including formulation and solution. 60% of the students scored 70% or above for Q1; 80% of the students scored 70% or above for Q3. An ability to design a system, component, or process to meet desired needs within realistic constraints such as economic, environmental, social, political, ethical, health and safety, manufacturability, and sustainability Design and plan process, facilities ISE 195B ISE 195B 100% of the projects scored 70% or above in the design and plan process facilities section of the report Develop a strategic and management plans ISE 195B ISE 195B 100% of the projects scored 70% or above in strategic and management plans of the report (Apply knowledge of math, science, and engineering) e An ability to identify, formulate, and solve engineering problems Formulate and solve operations research/management decision making problems ISE 170 Questions 3, 4 & 5 of the Final Exam. 80% of the students scored 70% or above on Question 3; 44% of the students scored 70% or above on Question 4; 32% of the students scored 70% or above on Question 5.. f An understanding of professional and ethical responsibility Demonstrates knowledge of professional code of ethics ISE 195A ISE 195A 100% of the students scored 70% or above in the ethics assignment g An ability to communicate effectively Communicate in small teams, writing and in variety of other ways ISE 120 projects are to be real world workplace evaluations incorporating 100% of the students scored 70% or above in the written portion of the report and 100% of the students scored 70% or above in the oral presentation of their reported work Operation Process Charts, work measuremen t and ergonomics Develop technical writing skills h Understanding of the impact of engineering solutions in global/societal context ENGR 100W ENGR 100W Demonstrates effective technical presentations and writing senior design report ISE 195A and ISE 195B ISE 195A and ISE 195B 100% of the students scored 70% or above in the technical presentations of both courses Evaluate society context of poor quality ISE 131 Multiple choice questions 9, 10, 14, 18 on final exam 79% of the students scored 70% or above i j Recognition of the need for, and an ability to engage in lifelong learning Knowledge of contemporary issue Demonstrate approaches to improve quality ISE 131 ISE 131 final project 100% of the students scored 70% or above Develop green system solutions ISE 195B ISE 195B Learn about Sustainability as applied to life cycle engineering ISE 103 Homework on sustainability Learn to use MINITAB and Microsoft Excel to for solving statistical quality problems ISE 131 ISE 131 Final Project 100% of the students scored 70% or above in the final project Research and analyze new IE topics ISE 195A ISE 195A 100% of the groups scored 70% or above in researching and analyzing new IE topics Develop an understanding of the "state of the art" of service management thinking ISE 142 A question on mid-term two exam on using exponential smoothing in forecasting teller services 79% of the students scored 70% or above Remember/recognize the benefits of a well-defined and integrated supply chain and the technical benefits and impact of an ERP system ISE 155 HW #6 assignment on Dell Supply Chain Case Study 100% of the students scored 70% or above HW #9 assignment on Green logistics 89% of the students scored 70% or above Final exam Q4: Risk inherent in implementing IT system and Q7: Risk in 63% of the students scored 70% or above 100% of the groups scored 70% or above in addressing green system solutions 100% of the students scored 70% or above 100% scored 70% or outsourcing k Ability to use the techniques, skills and modern engineering tools necessary for engineering practice above Research and present contemporary topics ISE 195A ISE 195A 100% of the groups scored 70% or above in researching and presenting on contemporary IE topics Learn to use spreadsheet optimizers software to do sensitivity analysis ISE 170 All of HW 8 questions involved solution by Excel LP Solver; some of other HW sets also involved Excel LP Solver. 69% of the students scored 70% or above for HW 8; 65% of the students scored 90% or above for HW 8; 46% of the students scored 100% for HW 8. 12. Analysis Based upon the data collected in fall 2012 and spring 2013, outcomes a, e, j and k were partially achieved. Some of the performance measures of each outcome were achieved and some were not achieved. During summer of 2014, the senior exit written and oral exam data collected during the last two years will be analyzed. 13. Proposed changes and goals (if any) None