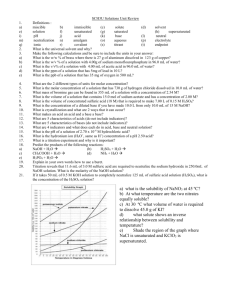
Neutralization Reactions Acid HX(aq) + MOH(aq) → MX(aq) +H 2 O(l)
advertisement

Topic: Neutralization Reaction Do Now: Neutralization Reactions • Acid + Base → Salt + Water HX(aq) + MOH(aq) → MX(aq) +H2O(l) DR rxn Acid-Base Titration • A procedure used in order to determine the unknown molarity of an acid or base • MAVA = MBVB • (molarity of acid)(volume of acid) = (molarity of base)(volume of base) • You will know 3 out of the 4 variable • Standard solution slowly added to unknown solution • As solutions mix: – neutralization reaction occurs • Eventually: – enough standard solution is added to neutralize the unknown solution pH changes during neutralization • Start with an acid pH < 7 • Add a base pH • At neutralization pH = 7 • Start with a base pH > 7 • Add an acid pH • At neutralization pH = 7 • acid-base indicator needed • WHY? • Usually use phenolphalein • WHY? When pH = 7 called equivalence point [H+] = [OH-] Titration • End-point = point at which indicator changes color – if indicator chosen correctly: • end-point very close to equivalence point MH VH = MOH VOH +1 +1 -1 -1 • If you titrate H2SO4 and NaOH 2H+ 1OH+- Titration Problem #1 • In a titration of 40.0 mL of a nitric acid solution, the end point is reached when 35.0mL of 0.100M NaOH is added Calculate the concentration of the nitric acid solution HNO3 + NaOH H2O + NaNO3 Variables • # of H’s = 1 • Ma = ? • Va = 40.0 mL • # of OH’s = 1 • Mb = 0.100 M • Vb = 35.0 mL (1)(X) (40.0 mL) = (0.100 M )(35.0mL)(1) X = 0.875 M HNO3 Titration Problem #2 • What is the concentration of a hydrochloric acid solution if 50.0 mL of a 0.250M KOH solution is needed to neutralize 20.0mL of the HCl solution of unknown concentration? KOH + HCl H2O + KCl (1)(X)(20.0 mL) = (0.250 M) (50.0 mL)(1) X = 0.625 M HCl Titration Problem #3 • What is the concentration of a sulfuric acid solution if 50.0mL of a 0.25 M KOH solution is needed to neutralize 20.0mL of the H2SO4 solution of unknown concentration? H2SO4 + 2 KOH 2 H2O + K2SO4 (2)(X)(20.0ml) = (0.25M)(50.0ml)(1) X = 0.3125 M H2SO4(sulfuric acid)