File 5_themes_of_geography
advertisement

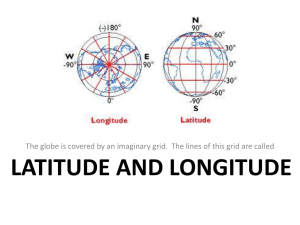
5 Themes of Geography Warmup WHY ARE MAPS IMPORTANT? What are some different types of maps? Geography Geo- Greek word for Earth Graphe- Greek word that means “to talk about” Put together- “to talk about the Earth” (The study of the Earth) Location Tells us where something is located Answers the question- Where is it? Location •“Where is it?” 1. Absolute location Longitude (Vertical) -Latitude (Horizontal) Meridians Parallels Prime Meridian- runs Equator, through Greenwich, England Tropic of Capricorn, Tropic of Cancer The Tropics mark the area of the earth’s surface that receives the most heat from the sun. Equator Prime Meridian Lines of Longitude Lines of Latitude Use the map and write absolute location. Remember latitude first and then longitude. 1. What is the approximate latitude and longitude for Brunswick, GA? 2. What are the approximate coordinates for Miami, Florida? 3. Name the state whose southern border is latitude 35 degrees N. 4. Is the location 35 degrees N latitude, 75 degrees W longitude in the Atlantic or Pacific Ocean? 5. The location 26 degrees N, 105 degrees W is in what country? 2 Types of Location Absolute- the exact place where something is located (we get this by using longitude and latitude or can use the address) Ex.- 34 N/ 128 W or 1234 Lanier Blvd. Relative- where a place is in relation to something else Ex.- McDonalds is next to Popeyes Place “What is it like there?” •Physical features Land, water, plants, animals •Human features –Activities – hunting, farming, shopping –Culture – religion, language Place Physical features and human features that make a location special or unique the climate physical features- mountains, beach human features- cities, man-made structures (Summer Waves, Statue of Liberty) Home on the Range http://www.kididdles.com/lyrics/h020.html http://www.traditionalmusic.co.uk/folk-songlyrics/Home_on_the_Range.htm How does the song capture a sense of place for the prairie? Do you know what state adopted it as the state song? Human-Environment Interaction How people have changed the land and how the land has changed people What have people done to the place where they live (cut down trees, built cities) Has the land made people want to live there. (is there farmland) Has the land made it hard for people to survive. (is there enough water, is the climate too harsh) Human/Environment Interaction “What is the relationship between people and their environment?” Attraction for people – Lake, river, ocean, soil, warmth How people adapt and change – Hot weather – light clothing Problems created for environment – Pollution Movement How and why people and their stuff get from one place to another Why do people move around? (jobs, family) How do people move around? (car, plane, bus, boat) Movement “How are people and places connected?” Reasons for movement – better land, religious freedom How they move – cars, subway, buses Interdependent Not just people--ideas and goods, too Look at the tag in each article of clothing: Where was your clothing made? What part of the world is that country located in. How is that place different than the US? How do you think your clothing made it to your possession (transportation)? Region What does a certain place have that makes it different from another place? What kind of things are found in one area? Ex.- urban regions have lots of people mountainous regions have lots of mountains *Regions help us understand the differences between places. Region Based on similar physical or human characteristics 2 types of regions – Uniform region – has a uniform characteristic (farming, cattle) – Functional region – Area with central point (Chicago, Atlanta metro area) Lots of People Have Moved Round Location Place Human – Environment Interaction Movement Region