cell organelles power point
advertisement

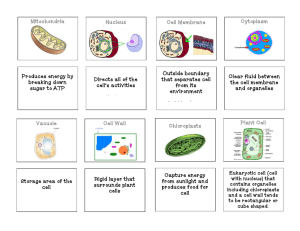
The Cell All organisms are made of cells, the organism’s basic unit of structure and function. Size range of cells The Nucleus Nucleus—control center - enclosed by nuclear envelope - contains most of the genes that control the entire cell - DNA organized with proteins into chromatin - nucleolus-produces ribosomes Mitochondria –powerhouse •energy transformers of cells- produces ATP- energy for cell + double membranes + contain ribosomes/DNA Mitochondrial DNA is only passed on by mom Ribosomes Construction Crew - make proteins - free- float in cytoplasm - bound- attached to endoplasmic reticulum Vacuoles * Cell Closet function in cell maintenance & storage + food vacuole + contractile vacuole- removes excess water + central vacuole (pictured)- in PLANTS Stores water & maintains cell shape Endoplasmic reticulum Endoplasmic reticulumIntercellular highway •Transport cell materials • two distinct regions + rough ER (ribosomes attached) - manufacture proteins for secretion - membrane production + smooth ER - synthesis of lipids - carbohydrate metabolism - detoxify drugs/poisons - stores calcium ions Golgi Apparatus * Packaging & shipping • finishes, sorts, and ships cell products • two poles + cis face + trans face Enzymes in the Golgi modify products of the ER in stages as they move through the Golgi stack from cis to trans face. Lysosomes - clean up crew contain hydrolytic enzymes- Primarily animal cells • digestive compartments + intracellular digestion + recycle cell material + program cell destruction (apoptosis) Apoptosis – programmed cell death http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/disease/ctl_ video.html The Cytoskeleton Cytoskeleton •provides structural support for motility and regulation + network of fibers - microtubules- thick & Hollow (straw) - microfilaments- thin & Solid (toothpick) - intermediate filamentsMedium & solid Cilia & Flagella -Cilia- short, hairlike, numerous. Cover entire cell -Flagella- long, only 1 or 2 on a cell * Both function in movement * Found on outside of ANIMAL cells * Composed of microtubules (cytoskeleton) F C L I A L G I A E L L A Centrosomes • Found in animals primarily • Produce microtubules during cell reproduction • Animal cells contain centrioles which contain 9 sets of 3 microtubules Cell Membrane Plasma Membrane- Bouncer •boundary that separates living cell from its non-living surroundings + 8 nm thick + selectively permeable + unique structure relates to function + phospholipid bilayer Cell Wall Cell Walls (1° & 2°) Plant cells only* - Brick wall •cellulose fibers •Middle lamella Made of pectin (sticky polysaccharide) Cytoplasm/Cytosol --cytosol--Gelatinous fluid that surrounds organelles & holds cellular components (Na+, K+, amino acids, etc) Cytoplasm-everything in Cell EXCEPT nucleus Chloroplasts- site of photosynthesis - Production crew* Only in PLANT cells * Made of thylakoid stacks (grana) where reactions occur * green in color due to chlorophyll Peroxisome Break down large, branched Fatty acid chains •+ contain specialized teams of enzymes - peroxide-producing oxidases and catalase Leucoplast * Basement/Cellar Non-pigmented plastids Bulk storage of starch, commonly in roots Chromoplast * Crayons * * Responsible for pigment synthesis and storage *Commonly found in fruit, flowers, & aging leaves * assist chloroplasts in absorbing suns energy The Endomembrane System Includes: •nuclear envelope •Endoplasmic reticulum •Golgi apparatus •Lysosomes •Vacuoles •Plasma membrane* The organelles of the endomembrane system are related through direct contact or by the transfer of membrane segments as vesicles. Endomembrane System Summary Animal vs. Plant Cell Unique to Plant Cells: - cell wall - large central vacuole - Plastids Unique to Animal Cells: -Centrioles -Lysosomes - flagella and/or cilia A Panoramic View of the Cell Prokaryotic +only in bacteria/archaebacteria Eukaryotic +no true nucleus/nuclear envelope true membrane-bound nucleus +genetic material in nucleoid region genetic material in nucleus +little to no organelles many organelles Protists, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia