CELLULAR PHYSIOLOGY
advertisement

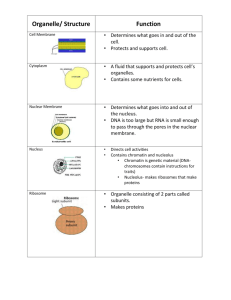
CELLULAR PHYSIOLOGY Ass. Prof. Dr. Emre Hamurtekin EMU Faculty of Pharmacy INTRODUCTION • No cell can be called «typical» of all cells. • Organelles CELL MEMBRANE • Lipids and proteins, semipermeable • Major lipids are phospholipids: phosphatidylcholine phosphotidylserine phosphatidylethanolamine • Head: polar, hydrophilic • Tail: nonpolar, hydrophobic • Glycosphingolipids, Sphingomyelin, cholesterol CELL MEMBRANE • Many different proteins are embedded in the membrane. a) Integral proteins b) Peripheral proteins - CAMs - Pumps - Carriers - Ion channels - Receptors - Enzymes CELL MEMBRANE • Basal lamina • Holds cells together, development, growth www.studydroid.com MITOCHONDRIA • Oxidative phosphorylation!!!.............ATP : ENERGY MITOCHONDRIA • Have their own genome (less DNA compared to nuclear genome) • The enzyme complexes are responsible for oxidative phosphorylation. • Through complex I to complex V (ATP synthase), ATP is generated. • Ineffective DNA repair system mutations = diseases LYSOSOMES • Irregular shaped structures • Surrounded by membrane • Interior is more acidic (proton pump, «H-ATPase») • Contain hydrolytic enzymes (acid hydrolases) pH:5 • Digestion of worn-out cell components, bacteria etc... PEROXISOMES Contain enzymes (oxidases and catalases) Can form by budding of the ER or division Catalize anabolic and catabolic reactions CYTOSKELETON • System of fibres that maintains the structure of the cell + change shape – Microtubules – Intermediate filaments – Microfilaments • Proteins and organelles move along microtubules and microfilaments inside the cell. CYTOSKELETON • Microtubules: – – – – Temperature sensitive Dynamic portion of the cytoskeleton (provide tracks) Form spindles which moves the chromosomes in mitosis. Drugs may affect the microtubules (colchicine, vinblastine, paclitaxel*) CYTOSKELETON • Intermediate filaments: – Connect the nuclear membrane to the cell membrane – Resist external pressure – Cell-type spesific (vimentin: fibroblasts; cytokeratin: epithelial cell) • Microfilaments: – Made up of actin – F-actin: intact microfilaments – G-actin: unpolymerized protein actin subunits – Interact with membrane-bound proteins – Microvilli-intestinal mucosa – Lamellipodia – Focal adhesion complexes - Provide tracks MOLECULAR MOTORS • Move proteins, organelles, cell parts (cargo) inside the cell • ATPases • 3 superfamilies: – Kinesin – Dyneins – Myosin MOLECULAR MOTORS CENTROSOMES • 2 centrioles + surrounding pericentriolar material • Microtubules in groups of three run longitudinally in the walls of each centriole • When a cell divides, they duplicate themselves, pairs move apart to the poles of the mitotic spindle, monitor the steps in cell division CELL ADHESION MOLECULES • Cells are attached to basal lamina and to each other by CAMs. – – – – – – – – Fasten cells to their neighbours Transmit signals Cell movement Embriyonic development Formation of nervous system and other tissues Holding tissues together Inflammation and wound healing Metastasis of tumors • 4 families: – – – – Integrins Adhesion molecules of IgG superfamily Cadherins Selectins INTERCELLULAR CONNECTIONS • Tight junctions (zonula occludens) • Desmosome • Zonula adherens • Hemidesmosomes • Focal adhesions • Gap junction INTERCELLULAR CONNECTIONS • Tight junctions: – Surround the apical margins of the cell – Endothelial barrier function – Permit the passage of some ions and solutes in between adjacent cells • Desmosomes: – Patches characterized by thickenings of the membranes of two adjacent cells – Intermediate filaments attaches to these thickened areas • Zonula adherens: – Major site of attachments for intracellular microfilaments • Hemidesmosomes & Focal adhesions: – Attach cells to underlying basal lamina – Labile structures associated with actin filaments inside the cell – Play an important role in cell movement GAP JUNCTION • Connexons are lined up with one another to form gap junction. NUCLEUS & RELATED STRUCTURES • The nucleus is made up in large part of the chromosomes. • Each chromosome is made up of DNA. • DNA is wrapped around a core of histon protein to form a nucleosome. • The whole complex of DNA and proteins is called chromatin. NUCLEUS & RELATED STRUCTURES • The nucleus of most cells contain nucleolus. • Rich in RNA. • They synthesize the ribosomes. • Nuclear membrane is a double membrane. • Spaces between the two folds are called perinuclear cisterns. ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM • ER is a complex series of tubules in the cytoplasm – Rough (granular) ER: protein synthesis – Smooth (agranular) ER: steroid synthesis & detoxification • Sarcoplasmic reticulum: skeletal and cardiac muscle RIBOSOMES • 60S AND 40S subunits • These are the sites of protein synthesis. • Ribosomes attached to ER synthesize: – all transmembrane proteins – most secreted proteins – most proteins stored in Golgi, lysosomes, endosomes • Free ribosomes synthesize: – Cytoplasmic proteins (i.e. hemoglobin) – proteins found in peroxisomes and mitochondria. GOLGI APPARATUS • Glycosylation of proteins and lipids.