Cell and Cell Membrane(final)
advertisement

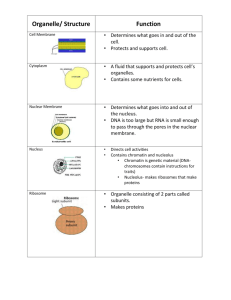
Prof. Dr. Mohammad Ahmed Azmi, Ph.D A BASIC CELL Eukaryotic cell Prokaryotic cell BASIC STRUCTURE OF CELL A typical cell has two main components Cytoplasm Nucleus PROTOPLASM Definition: The fluid living content of the cell. OR The different substances that make up the cells are collectively called as PROTOPLASM. COMPOSITION OF PROTOPLASM The protoplasm is composed of five basic substances: Water Electrolytes Proteins Lipids Carbohydrates Water: Principal fluid medium of the cell. Concentration …….. (65% to 80%). Many cellular chemicals are dissolved in water. Others are suspended in membranous form. ELECTROLYTES The most important electrolytes are: K+ , Mg + + , PO4--, SO4-, HCO3Little amount are: Na+, Ca++, ClProvide in organic chemicals for cellular reactions Important for the transmission of electrochemical impulses in nerve and muscle fibers Intra cellular electrolytes determine the activity of enzyme-catalyzed reactions PROTEINS Complex organic nitrogenous compounds Consisting of polymers of amino acids Constitute 10-20 % of the cell mass Types of proteins Structural proteins Globular proteins Nucleoproteins Structural Proteins Present in the form of long thin filaments o Provide contractile mechanism of all muscles Also organized into microtubules o Provide cytoskeleton of many organelles e.g., cilia, nerve axons, mitotic spindles Extracellularly, fibrillar proteins are found in the form of collagen & elastin fibres of connective tissue, blood vessels, tendons, ligaments e.t.c. Globular proteins Present in the globular form Act as enzymes and participate in chemical reactions e.g. chemical reaction that splits glucose into the cell providing energy for cellular reactions. Nucleoproteins Found in the nucleus in the form of RNA & DNA Lipids Most important are: PHOSPHOLIPIDS CHOLESTEROL Constitute about 2-3 % of cell mass Mainly in soluble in water In addition some cells also contain TRIGLYCERIDES also called neutral fats Carbohydrates Constitutes only about 1% of cell mass Have little structural function in the cell Stored in ECF in the form of glucose Small amount are stored in the form of glycogen (an insoluble polymer of glucose supplying energy to cell Cytoplasm: This is a portion of cytoplasm which surrounds the nucleus It is peripherally covered by a membrane called cell membrane Zones of Cytoplasm: Ectoplasm(Cortex) Endoplasm Ectoplasm (Cortex) Present just beneath the cell membrane. Contains microfilaments mainly composed of ACTIN Endoplasm: Contains clear liquid portion of cytoplasm present between the cortex and nuclear membrane This liquid portion is called CYTOSOL in which inclusions / particles and organelles are present Cell membrane / Plasma membrane Outer covering which envelops the cell Thin and elastic membrane Its structure cannot be seen easily under light microscope About 8-10 nm in thickness Composition of Cell membrane Structure The basic structure is LIPID Lipid molecules form a bi-layer Lipid bi-layer is composed of: PHOSPHOLIPID CHOLESTROL One part of both PL and chol molecule is water soluble……Hydrophilic Other part is fat soluble……Hydrophobic The PO4 radical of PL is hydrophilic & fatty acid radical is hydrophobic . The hydroxyl (OH) radical of cholesterol is hydrophilic The steroid nucleus is hydrophobic The fatty portions (Hydrophobic) occupying the centre of the membrane The hydrophilic portions are directed towards the inner and outer surfaces of the lipid bi-layer Membrane Proteins Integral proteins These protrude all the way through the membrane. Many integral proteins provide structural channels or pores through which water-soluble substances especially ions can diffuse between ECF & ICF. Others act as carrier proteins specially transporting substances in and out of the cell. Peripheral Proteins Do not penetrate the membrane but attached only to the surface on the membrane . These mainly act as enzymes. Membrane Carbohydrate These occur in the form of glyco-lipids and glyco-proteins The entire surface has a loose layer of carbohydrate called GLYCOCALYX . These have several functions. Many are negatively charged that provides over all negative charged surface that repel other negative objects Many cells are attached to each other by these carbohydrate moieties Many act as receptor substances for binding hormones Some are involved in immune system Presence of Channels and Pumps Na+ - K+ leak channel The cell membrane contains protein channels, called leak channels They allow Na+ or K+ to leak down their concentration gradients INTO or OUT OF the cell. Cell membranes are considerably more permeable to K+ than to Na+ because they have many more K+ leak channels than Na+ leak channels. Na+ - K+ Electrogenic Pump The Na+/K+ Pump creates a concentration gradient by moving 3 Na+ out of the cell and 2 K+ into the cell. The movement of ions occur against concentration gradient. This pump requires energy in the form of ATP during the movement of ions. Gating of Protein Channels Voltage gated - Na+ channel At – 90mv the gate remain closed from outside. When potential changes from -90 to +35mv, conformational changes suddenly occurs and the gate opens During this time large amount of Na enters in to the cell. This causes depolarization Voltage gated – K+ channel At-90mv the gate remain closed from inside of the cell. When potential changes from -90 to +35mv, the gate opens slowly to cause the out flux of K+ to the exterior of the cell. Carrier Protein Channel A substance cannot pass through the membrane whiteout specific binding with the receptor site. After binding conformational changes occur and the channel open and the substances in to the cell Ligand Gated Channel Channels open by binding of an other molecule with the protein. Conformational changes occur in the protein molecule that opens or closes the gate. This is called ligand gating substance that binds with the protein is called ligand Best example is the effect of acetylcholine also called acetylcholine channel. Plays an important role in the transmission of signals from : nerve cell …………………………………… nerve cell nerve cell …………………………………… muscle cell Ca++ Pump Calcium ions play a crucial role in the metabolism and physiology of eukaryotes. Normally maintained at very low concentration in the intra cellular cytosol Two calcium pumps are involved Present in the cell membrane …………….. Pumps calcium to the out side of the cell Pumps calcium into one or more intra vesicular organelles of the cell In both cases carrier protein penetrates the membrane It acts as ATP-ase that transports ions across the membranes using energy obtained from the hydrolysis of ATP. Cell Organelles Prof. Dr. Mohammad Ahmed Azmi, Ph.D. Membranous Organelles Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) • Network of tubular and vesicular structures which are interconnected with each other •It is covered by limiting membrane composed of protein & lipid bi-layer •Lumen of ER contains a fluid called endoplasmic matrix •ER forms a link between nucleus and cell membrane •OR •Forms connection of cell membrane with the nuclear membrane •Granular or Rough A granular or Smooth ER Granular or Rough ER A granular or Smooth ER • Ribosomes are attached on the surface of ER • Donot have ribosomes •Synthesis of proteins •Synthesize lipids, steroid hormones •Role in the degradation of worn out cytoplasmic •Also involved in the detoxification of some organelles like mitochondria drugs Mitochondria • rod-shaped or oval shaped •Covered by lipid bi-layer membrane •Outer membrane is irregular & folded forming shelves – cristae •Inner space of cristae – called mitochondrial matrix •Matrix contains many enzymes and protein molecules for involved in respiration & formation of ATP Power house of cell Golgi Apparatus • Consists of 5 to 8 membranous sacs usually flattened in structure called cisternae •Situated near the nucleus •Present in all cells but larger in those that synthesize & export proteins. •Proteins move from rough ER to the gogli apparatus where they are packaged into secretory vesicles called secretory granules •The seceretory vesicles are stored & when proteins are needed they move to the cell membrane & so proteins are exported. Lysosomes • They are oval or spherical membrane bound vesicular organelle •Found throughout the cytoplasm •Enzymes formed in rough ER are processed and packed in the form of small vesicles in the golgi apparatus •These vesicles are then moved out from golgi apparatus and become the lysosomes. Lysosomes Primary lysosomes Secondary lysosomes Inactive in nature containing Active containing lysosomal enzymes Hydrolytic enzyme proteases, lipases amylases Formed from Golgi apparatus nucleases Peroxisomes • Are microvesicular structures like lysosomes. • They are pinched off from ER & not from golgi apparatus. • Contain some oxidative enzymes in the phagocytosis of foreign particles Centrosome and Centrioles • Membranous bound cellular organelle, cylindrical in shape •Situated in the centre of cell and close to nucleus •Responsible for the movement of chromosomes during cell division. Non-membranous Organelles Ribosomes • Non-limiting cellular organelle •Granular and small dot-like structure •Made up of proteins (35%) and RNA (65%) •RNA present in ribosomes are called r-RNA •Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis Attached to ER Protein formation Free ribosome in the cytoplasm Responsible for protein of Hb, peroxisome & mitochondria Cytoskeleton: Consists of: -Microtubules -Microfilaments •Cell organelles that determine the shape of cell & support •Also responsible for cellular movement and response of cell to external stimuli Microtubuls •Spindle fibers •Cilia •Flagella •Actin & myosin Cell Organelles Prof. Dr. Mohammad Ahmed Azmi, Ph.D. Membranous Organelles Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) • Network of tubular and vesicular structures which are interconnected with each other •It is covered by limiting membrane composed of protein & lipid bi-layer •Lumen of ER contains a fluid called endoplasmic matrix •ER forms a link between nucleus and cell membrane •OR •Forms connection of cell membrane with the nuclear membrane •Granular or Rough A granular or Smooth ER Granular or Rough ER A granular or Smooth ER • Ribosomes are attached on the surface of ER • Donot have ribosomes •Synthesis of proteins •Synthesize lipids, steroid hormones •Role in the degradation of worn out cytoplasmic •Also involved in the detoxification of some organelles like mitochondria drugs Mitochondria • rod-shaped or oval shaped •Covered by lipid bi-layer membrane •Outer membrane is irregular & folded forming shelves – cristae •Inner space of cristae – called mitochondrial matrix •Matrix contains many enzymes and protein molecules for involved in respiration & formation of ATP Power house of cell Golgi Apparatus • Consists of 5 to 8 membranous sacs usually flattened in structure called cisternae •Situated near the nucleus •Present in all cells but larger in those that synthesize & export proteins. •Proteins move from rough ER to the gogli apparatus where they are packaged into secretory vesicles called secretory granules •The seceretory vesicles are stored & when proteins are needed they move to the cell membrane & so proteins are exported. Lysosomes • They are oval or spherical membrane bound vesicular organelle •Found throughout the cytoplasm •Enzymes formed in rough ER are processed and packed in the form of small vesicles in the golgi apparatus •These vesicles are then moved out from golgi apparatus and become the lysosomes. Lysosomes Primary lysosomes Secondary lysosomes Inactive in nature containing Active containing lysosomal enzymes Hydrolytic enzyme proteases, lipases amylases Formed from Golgi apparatus nucleases Peroxisomes • Are microvesicular structures like lysosomes. • They are pinched off from ER & not from golgi apparatus. • Contain some oxidative enzymes in the phagocytosis of foreign particles Centrosome and Centrioles • Membranous bound cellular organelle, cylindrical in shape •Situated in the centre of cell and close to nucleus •Responsible for the movement of chromosomes during cell division. Non-membranous Organelles Ribosomes • Non-limiting cellular organelle •Granular and small dot-like structure •Made up of proteins (35%) and RNA (65%) •RNA present in ribosomes are called r-RNA •Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis Attached to ER Protein formation Free ribosome in the cytoplasm Responsible for protein of Hb, peroxisome & mitochondria Cytoskeleton: Consists of: -Microtubules -Microfilaments •Cell organelles that determine the shape of cell & support •Also responsible for cellular movement and response of cell to external stimuli Microtubuls •Spindle fibers •Cilia •Flagella •Actin & myosin Thanks