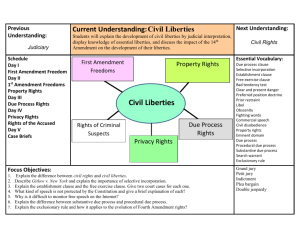
Civil Liberties Amendments
advertisement

Today’s Objectives • Analyze why civil liberties issues involve “politics” as well as “law”. • Evaluate judicial interpretation of various liberties (such as freedom of speech, rights of the accused) & the impact of significant Supreme Court cases on these rights/liberties • Apply key concepts of democratic rule and civil liberties in analyzing current events and pieces of legislation. Civil Liberties The Basis for Any Democracy What Are Civil Liberties? • Civil Liberties: – Basic rights and freedoms that are guaranteed -either in the Bill of Rights/Constitution, or interpreted in Courts • Free Speech, Free Press, Free from Search & Seizure, etc. • Civil Rights: – Basic right to be free from unequal treatment based on certain protected characteristics (race, gender, disability) • What right’s affected? v. Whose rights affected? Bill of Rights: Civil Liberties Amendments • 1st Amendment: – Freedom of Religion, Speech, Press, Petition, Assemble • Establishment Clause: – Congress shall make no law endorsing/ estbl. a religion – Estbl. Separation of Church & State…How closely have we followed this? • Free Exercise Clause – Prevents infringement on people’s right to believe in whatever religion they choose (some religious practices can be restricted however…) – Limits on Free Speech • • • • Clear & Present Danger Doctrine (Schenck v. U.S.) Obscenity (Roth v. U.S.) Libel/Slander (written/spoken defamation) Commercial Speech Regulated by FTC/FCC Bill of Rights: Civil Liberties Amendments • 2nd Amendment: – Right to Bear Arms • “A well regulated Militia, being necessary to the security of a free State, the right of the people to keep and bear Arms, shall not be infringed.” • 3rd Amendment: – Prohibits Quartering of Troops Bill of Rights: Civil Liberties Amendments • Amendments 4-8 – 4th: Protection against illegal search & seizure • Probable Cause/Warrant • Exclusionary Rule (Weeks v. U.S.; Mapp v. Ohio) – Evidence gathered thru illegal search & seizure can’t be submitted in court of law – Deterrent to unlawful police action – 4th Amendment Under Attack – – – – – Terry Frisk Pretext Stops Drug Courier Profiles “Consent Searches” Patriot Act Bill of Rights: Civil Liberties Amendments – 5th: Right to grand jury, no double jeopardy, can’t be forced to testify against self, due process • http://www.comedycentral.com/videoclips/3vk26x/chappelle-s-show-tron-carter-s-law---order – 6th: Speedy/public trial w/ impartial jury; Right to Confront witnesses; Right to counsel; prevents suspension of habeas corpus – 7th: Jury trial in civil cases – 8th: Free from excessive bail; cruel & unusual punishment – Upheld by Gregg v. Georgia Bill of Rights: Civil Liberties Amendments • 9th Amendment: – Protects rights of the people that are not specifically enumerated in the Constitution • Right to Privacy • Explicit? • Griswald v. Connecticut; Roe v. Wade; Planned Parenthood v. Casey • 10th Amendment… • Outlining Federalism/“Reserved Powers” • 14th Amendment: – “No state shall make or enforce any law which shall abridge the privileges or immunities of citizens of the united states nor shall any state deprive person of life, liberty or property without due process of law; nor deny any person within its jurisdiction equal protection of laws” – Incorporation Selective Incorporation: Applying the Bill of Rights to States • Selective Incorporation: – Process by which the courts have gradually applied portions of the U.S. Bill of Rights to the states • Incorporated thru the due process clause/equal protection of the 14th Amendment – Key Court Cases • Barron v. Baltimore (1833) – Said Bill of Rights did NOT apply to states • Gitlow v. New York (1925) – Began process of “Incorporation”…said B.o.R. DID apply to states What is the Main Focus of the Bill of Rights? • Protection of the rights of the accused – Why? • Experiences under Brits • Ex: Syria/China • Big Question: How do you balance need for law enforcement with individual rights? “INJUSTICE ANYWHERE, IS A THREAT TO JUSTICE EVERYWHERE!” MLK JR. Criminal Process 1. Evidence Gathered: – 4th Amendment—forbids unreasonable search & seizure (exclusionary rule) 2. Suspicion Cast/Arrest Made – 6th Guarantee habeas corpus—forbids imprisonment without evidence – 5th Amendment—Right to remain silent; due process “INJUSTICE ANYWHERE, IS A THREAT TO JUSTICE EVERYWHERE!” MLK JR. • Interrogation Held: • 5th Amendment: Forced self-incrimination forbidden • 6th Amendment: Right to Counsel • 8th Amendment: Excessive bail forbidden • Trial Held: • 4th Amendment: Exclusionary Rule (Mapp v. Ohio) • 5th Amendment: No “Double Jeopardy” • 6th Amendment: “Speedy & Public Trial” by an impartial jury ; Right to confront witnesses; Right to counsel • Punishment Imposed: • 8th Amendment: Protection from Cruel & Unusual Punishment Bill of Rights Overview • 1st 10 Amendments added to the Constitution • Bill of Rights – Added to the Constitution to get key states of New York and Virginia to ratify the Constitution – Protects political rights • 1st Amendment: Free speech, press, petition, assemble, religion – Protects the rights of the accused • Protection from illegal search and seizure • Right to a trial by jury, right to an attorney, right to be free from self-incrimination If Your Group Finishes A Station Early… • Define the following terms on a separate sheet: – – – – – – – – – – Due Process Equal Protection Clause Habeas Corpus Amicus Curiae Clear & Present Danger Test Lemon Test Libel Slander Obscenity Miranda Rule Opener: SOPA/PIPA…Another Step Closer to Censorship? Or A Necessary Protection? • Evaluation of SOPA/PIPA • Colbert--SOPA/PIPA • Daily Show--KO Computer