biogeochemical cycle
advertisement

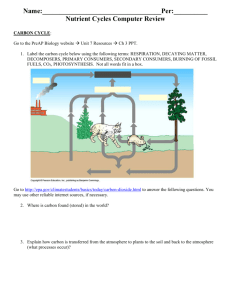
Tuesday September 29th In Notebook: Today’s Learning Targets Agenda: 1. Finish Levels of Organization Poster 2. Show off poster! 3. Start Biogeochemical Cycles What’s a cycle? What is your understanding of a cycle? How have you heard it used in science and in everyday life? Biogeochemical Cycle bio- geo- chemical ything that takes up space and has mass) through the biosphere What is the Carbon Cycle? GOAL: Draw the carbon cycle using the information given to you. • Work with your assigned group to answer the questions on your worksheet. • Rotate to go to each station when told to switch! • On the back of your worksheet draw the carbon cycle using your answers to guide you. • GROUP DISCUSSION, BUT INDIVIDUAL WORK. Station 1 Station 2 Station 4 Station 3 Station 5 8 Wednesday September 30th In Notebook: What is your current understanding of the water cycle? Today’s Learning Targets Agenda: 1. Helpful Notes 2. Finish Carbon Cycle Stations 3. Cycle Notes 4. HEADS UP: OUTSIDE TOMORROW! But first… helpful vocab • Law of Conservation of Mass – matter can be changed from one form into another, but the total amount of mass in universe remains constant • Reservoirs/Sinks - places where matter and nutrients are stored Finish Stations • Go to where you ENDED yesterday. We will rotate to the next one as a class. • 5 minutes at each station. Station 1: Introduction to Carbon Cycle Carbon moves through these processes: 1. Photosynthesis - carbon moves from the environment into living things 2. Respiration - carbon moves from living things back to the atmosphere 3. Decomposition - carbon moves from dead organisms back to the environment 4. Combustion - burning fossil fuels releases carbon back into the atmosphere Station 2: Ocean Carbon Cycle • Additional Info: • Carbon can diffuse back into atmosphere as water warms after upwelling. • Carbon can be brought to deep ocean by decay/decomposition of organisms. Station 3: Soil Carbon Cycle ALL ON THE PINK SHEET Station 4: Terrestrial Carbon Cycle • Woody plants can sequester carbon – pull carbon out of circulation • Plants take in carbon dioxide and give away oxygen. Animals breathe in oxygen and give away carbon dioxide. They depend on eachother! Station 5: Atmospheric Carbon Cycle • Form of carbon in atmosphere: CO2 (carbon dioxide) and CH4 (methane gas) Station 5: Atmospheric Carbon Cycle Time to draw the carbon cycle! Thursday October 1st In Notebook: No Question of the Day. Be ready to go outside after attendance. Today’s Learning Targets Agenda: 1. Ecological Observations in Bunker Hills Regional Park Friday October 2nd In Notebook: Define biogeochemical cycle. What biogeochemical cycles should you be able to label and explain in this class? Today’s Learning Targets Agenda: 1. Finish drawing carbon cycle 2. Notes 3. HOMEWORK?! Time to draw the carbon cycle! Water Cycle Processes of Water Cycle • Evaporation - liquid water becomes a gas • Transpiration - liquid water evaporating off plants • Condensation - water changing from gas to liquid • Precipitation - water falling to Earth from the atmosphere Processes continued… • Run-off - water running over the land that collects in the oceans, lakes, or rivers • Infiltration - water seeping into the ground that provides water for the soil, streams, rivers, and oceans • Ground water - stored in underground caverns and porous rock Nitrogen Cycle Nitrogen Cycle • Nitrogen in the atmosphere is UNUSABLE • Some bacteria can perform nitrogen fixation - capturing nitrogen in atmosphere and converting it into a form that is usable by plants. Animals get nitrogen from eating plants. • Nitrogen is also fixed by the energy in lightning strikes • Nitrogen enters soil when animal urinates/dies • Nitrogen is taken out of soil by plants converting it into proteins or by Denitrification - nitrogen is converted back to gas by some bacteria in the soil Future Nitrogen Cycle • Excess nitrogen can cause eutrophication - nutrient over enrichment in water. Can cause harmful algal blooms, massive fish-kill events, and species shift. • Scientists, farmers, and policymakers are encouraged to decrease fertilizer use while safeguarding agriculture • • Use new farming methods Maintaining wetlands Homework for Monday: • Research the impact that humans have on the carbon cycle, the water cycle, AND the nitrogen cycle. • 2 for each cycle …. 6 TOTAL! • Write them down in your notebook!