On your map identify the following areas
advertisement

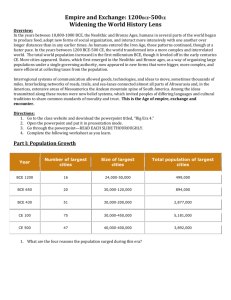
First, the rules of review… THE AP WORLD HISTORY EXAM Basics Multiple Choice Section • 70 Questions • 55 Minutes Essays (Free Response Questions) • 3 Essays (DBQ, Continuity and Change Over Time, Comparative) • 130 Minutes • Part A begins with a mandatory 10-minute reading period for the document-based question. Students should answer the documentbased question in approximately 40 minutes. • In Part B students are asked to answer a question that deals with continuity and change over time (covering at least one of the periods in the concept outline). Students will have 40 minutes to answer this question, 5 minutes of which should be spent planning and/or outlining the answer. • In Part C students are asked to answer a comparative question that will focus on broad issues or themes in world history and deal with at least two societies. Students will have 40 minutes to answer this question, 5 minutes of which should be spent planning and/or outlining the answer. On your map identify the following areas • • • • • • • Mesopotamia Egyptian Empire Indus River Valley Shang Dynasty Zhou Dynasty Olmec Chavin • • • • • • • Persian Empire Maurya Gupta Qin Han Greek City-States Roman Empire Time Periods I and II (8000BCE-600CE) Create A Thesis • Compare the development and interactions of Bronze Age river valley civilizations with those of Classical Period empires in terms of government, economics, and society from the period 2000 BCE to 600 CE. • Keep this question in mind as we speedily go through the River Valley Civilizations & The Classical Period Empire!!! River Valley Civs • Mesopotamia – Tigris, Euphrates = Fertile Crescent – Sumer, Babylon – Unpredictable flooding – Open geography Walk Like an Egyptian Rich soil, gentle flooding •3 Kingdoms •water management, pyramids, astronomy, hieroglyphs, calendar, gold, spices •Polytheistic •Women ruler = Hatshepsut, buy, sell property, inherit, will property, dissolve marriages, still subservient to men • Hierarchy: pharaoh, priest, nobles, merchants, artisans, peasants, slaves Indus Valley: 2500-1500 BCE • Connected with Mespotamia via trade • Harrappa, Mohenjo-Daro 100,000+ each • Master-planned, water system, strong central gov’t, polytheistic, written language (can’t read it) • Pottery, cotton, cloth • Cities abandoned, reason unknown • Aryans arrive 1700 BCE Shang: 1600-1100 BCE • • • • • N. China, walled cities, strong army, chariots Emperor & centralized gov’t Bronze = power Patriarchal, ancestors as advocates w/the gods Character writing; ancestor veneration, Oracle bones It’s Zhou Time • Replaced Shang around 1100 BCE • Ruled 900 years, kept customs, traditions of Shang • Developed political ideology of Mandate of Heaven • Feudal system, nobles gained power, war amongst feudal kingdoms, collapse 256 BCE • Led to the Warring States Period Persian Empire The 1st Empire • • • • • Classical Empires Multi-cultural Empire, Tolerance Run by local governors (satraps/satrapies) By 500 BCE Nile to Turkey/Greece to Afghanistan Great Royal Road, 1700 miles Zoroastrian – links to monotheistic religions (judgment day, God v. Satan set up) • Smaller Civs co-existed – Lydians-coined money – Phoenicians-22-letter alphabet, naval power – Hebrews-Judaism, monotheism Mauryan Empire • Founded by Chandragupta Maurya – Unified smaller Hindu kingdoms • Greatest extent under Ashoka who sponsored BUDDHISM • Big time traders: silk, cotton, elephants to move to the west • Strong military • Ashoka’s Rock & Pillar edicts, Buddhism spread Rise of Gupta • Ashoka dies 232 BCE, Mauryan’s rapidly decline • 400s to 600 CE, revival of empire but REASSERTED HINDUISM as primary religion • Smaller, more decentralized: Golden Age of culture & learning • Arts & Sciences; pi, zero • Hinduism resurgent – spreads to S.E. Asia • Women lost rights b/c of shift away from Buddhism; child marriages common & Sati (widow-burning) encouraged • Collapsed 600 CE (White Huns) Q’in Ups in China 221-209 BCE • strong agri-econ, strong army, iron, expansion…only lasted 15 years • Stuff to know: – GREAT WALL – Strong centralized, brutal gov’t – Qin Shihuangdi emperor – Unified kingdom, standardized weights, measures, laws, written lang, patriarchal – Legalism – Peasant rebellion brings down 209 BCE Han Dynasty 200 BCE-200 CE • • • • • Strength decreases power of pastoralists to interfere Expanded into Central Asia Silk Road to the Mediterranean Buddhism spread at END of Empire Civil Service system, bureaucracies, resulting in stable gov’t. • sundials, calendars, metallurgy • Confucianism = social hierarchy • Mandate of Heaven • Yellow Turban Rebellion of peasants at end & Wang Mang’s Reforms indicate weakness at end It’s Greek to me! • • • • Impact of geography = Trade, not agriculture Est. colonies Government in a new fashion! • Polis- City-states • UNIFED CULTURAL identity, culture in each but politically DISUNIFIED • Athens – Political, commercial, cultural center • Sparta – militaristic, equality w/o individuality Hierarchy • Citizens-adult males w/ property born in Athens • Free people w/ no political rights • Non-citizens (included slaves 1/3 of the Athenian pop!) • All citizens expected to participate in public life • Was it a true democracy? Religion • Polytheistic • Had human failings: got drunk, cheated on spouses, jealous, angry, took sides, etc. • Greek mythology remains a large part of Western heritage and language War with Persia • Persia invades Greece twice. Despite great odds, Greece survives. • Persia Stated: “No biggie” • Greece controls Aegean • Period of peace and prosperity Golden Age • • • • Athenian culture excels Democracy for all adult males (citizens) Delian League-city-state alliance Socrates, Plato, Aristotle – Truth through rational thought and observation • Math, Science, Architecture, Literature Super-power, super mistake • • • • • Athens dominated the Delian League Peloponnesian War with Sparta (431 BCE) Weakened, Macedonian conquest Philip encouraged Greek culture Followed by son, Alexander, unified Greece, invaded Persia Live fast, die young… • • • • Alexander conquered Persia Pushed to Egypt Did not conquer India Empire divided into three: – Antigonid (Greece/Macedonia) – Ptolemaic (Egypt), – Seleucid (Bactria/Anatolia) Hellenistic Era • Greek Culture and ideas flourished and spread • Alexandria (Egypt) became wealthy, center for learning • After death (323 BCE), empire crumbled • Macedonian focus on the east and Egypt left the door open for… The Romans: 509 BCE-476 CE Rome • Good Geographic position – Protected by mtns in north – Peninsula – Cross-roads in the Mediterranean • Polytheistic, borrowed many Greek gods, mythology still evident in West Social-Political Structure • Patricians (nobles) – Senate, Assembly • Plebians – Non-aristocrats • Representative (as opposed to Direct in Greece) • 12 Tables = importance of Laws (innocent until proven guilty) • Patriarchal/Paterfamilias • Women influential in family, own property, still considered inferior • Slaves (up to 1/3) of Italy’s population Military Domination • • • • • • • • All Directions, all the time Punic Wars 264-146 BCE (Rome vs. Carthage) Gained control of W. Med Defeated Macedonians Gaul Spain Road net, navy, aqueducts Cultural diffusion Republic, no - Imperialism, yes • Increased slavery, displaced plebians, inflation= social unrest • Senate weakened, Triumvirate, J. Caesar, Pompey, Crassus = Civil War • Caesar assassinated 44 BCE • 2nd Triumvirate, civil war (Octavian, Mark Antony, Marcus Aemilius Lepidus) • Octavian, I have a baby attached to my Leg Augustus = Caesar (1st emperor) • Imperial Rome • Pax Romana Peace and Prosperity • Rome, capital of western world • Military expansion • Rule of law, common coinage. Civil service, secure travel for merchants • 200 years of stability • Uniform laws, but traditional cultures in territories survived ie Egyptians, Hebrews • Growth of arts and sciences A New Religion • Christianity competes with polytheism • Christians persecuted • Conversion of Constantine ended persecution 312 CE • Edict of Milan-Christianity official religion of Rome Time Periods I and II (8000BCE-600CE) Create A Thesis • Compare the development and interactions of Bronze Age river valley civilizations with those of Classical Period empires in terms of government, economics, and society from the period 2000 BCE to 600 CE. Time Periods I and II (8000BCE-600CE) Create A Thesis • Compare the development and interactions of Bronze Age river valley civilizations with those of Classical Period empires in terms of government, economics, and society from the period 2000 BCE to 600 CE. • The period between 2000BCE and 600 CE is marked by the growth of increasingly complex and diverse human societies as more and more humans began abandoning pastoral and nomadic lifestyles to take up farming in sedentary villages and as these villages expanded to encompass their neighbors, eventually creating empires. The development and interactions of early civilizations and later empires included increasing centralization of government and an expansion of the distance and amount of trade within economies as river valley civilizations expanded to become the empires of the Iron Age, while both systems relied heavily on inequality in the social hierarchy to retain order.