Fallacy PowerPoint - Davis School District
advertisement
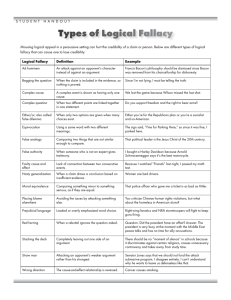
What is a Logical Fallacy? An Introduction to the Types of Reasoning Errors that will DESTROY an Argument! How We DEFINE Logical Fallacy • A logical fallacy is a mistake in reasoning that makes an argument faulty. • Logical Fallacies can be found in speeches, essays, and even advertisements! THEY’RE EVERYWHERE! Types & Examples Ambiguity Ad Hominem • The expression used is confusing to the audience because it is AMBIGUOUS– has more than one meaning. • EX) “Bus Driver Stops En Route to Help Dog Bite Victim.” • A person’s character is being attacked instead of the topic at hand. • EX) “He is so evil, and you have no reason to believe the lies he is telling you.” – Person talking about their opponent instead of the topic at hand – Newspaper Headline Example • Is the bus driver helping the dog bite the victim? Or aiding the wounded, bitten Types & Examples Begging the Question • Circular reasoning is used in a way that offers the argument itself as proof. • Restating the argument in different words • EX) “The product is in high demand because everyone wants one!” Bogus Claims • Promising more than you can deliver • Ex) “I promise to have FREE ICECREAM in the Cafeteria during ALL lunches!” – Student Running for Student Council Types & Examples Card Stacking • Evidence on the opposing side of the issue is ignored • EX) A salesman at a used car dealership is trying to sell you a used car. He tells you how great the car runs and that you will never have any issues with it. However, once you purchase the car, another employee asks if you are interested in purchasing a warranty on the car in case it breaks down. Either-or Fallacy • Only two choices are offered when, really, others exist. • “Deep condition your long, luscious locks with our special Moroccan Oil treatment... Or say goodbye to healthy hair!” Types & Examples False Analogies • Misleading comparisons are made • EX) “Students should only be required to take open-notes tests. After all, lawyers get to use briefs during a trial!” – The situations compared are not similar enough. Lawyers in this situation are not being tested over how much they have learned. Guilt by Association • Attacking the beliefs of a person because of who/what the person is associated with. • EX) Sally must HATE men because she did a research paper on feminism. Types & Examples Jumping on the Bandwagon • Something is right because everyone else does it • “If they jumped off a bridge, would you do it, too?” – Angry mother discussing peer pressure • EX) “Try our new cigars. Everyone is using them!” Hasty Generalization • Stereotyping, making generalizations based on poor evidence • EX) “When visiting a college , my student tour guide was very rude. Therefore, all students at this college are rude.” Types & Examples Irrelevant Argument Loaded Terms • The conclusion made does NOT relate to the premise • EX) “I am on a strict diet, but I decided to order soda at my favorite restaurant, anyways. There were free refills!” • Use of biased diction • Words typically have a strong connotation • EX) Unloaded Term: Plant Loaded Term: Weed – . The argument for ordering a soda has nothing to do with dieting. Types & Examples Misrepresentation • Using or presenting deliberate, outright LIES • EX) Two candidates are running for office. The first states that he wants to increase education spending. The second candidate says that his opponent hates the country because he is going to cut military spending in order to increase spending for the schools. Non Sequitur • Irrelevant evidence is introduced in attempt to support the argument • EX) “Of course you will go to your room! I am your mother!! You WILL do what I tell you to do!” Types & Examples Red Herring • Diverting the issue with topic that is in no way related to the topic at hand • Diverts the attention of the audience from the original issue • EX) In crime shows and mystery novels, we are often led to believe that someone is guilty, when in reality, they are innocent and someone Slippery Slope • Failure to provide evidence that one event will result in a catastrophic chain of events • EX) DIRECTV commercials... – When you have cable, you get bored. When you get bored, you witness something you’re not supposed to... – http://www.youtube.com/wa Types & Examples Self-Contradiction • Arguing two premises that cannot both be true • EX) “You cannot give me this C on my project! This is all wrong. I am always an A student!” Taking Issue out of Context • Issue is distorted when taken out of context • EX) A movie critic originally stated the following: “This movie lacks a strong plot and beautiful character development.” The movie trailer states that the critic said the following: “... Strong plot and beautiful character development.” *Ticket Out The Door* Identify 2 Fallacies Used *Ticket Out The Door* Identify 3 Fallacies Used