ch12_stp_as - Doral Academy Preparatory
advertisement

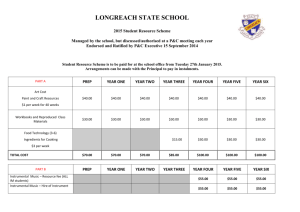
Forces Forces Preview • Understanding Concepts • Reading Skills • Interpreting Graphics Standardized Test Prep Forces Standardized Test Prep Understanding Concepts 1. After a bank customer cashes a check, some of the money received accidentally slips from the customer’s hands. What force causes the bills to hit the ground later than the coins do? A. B. C. D. static friction gravity air resistance magnetism Forces Standardized Test Prep Understanding Concepts 1. After a bank customer cashes a check, some of the money received accidentally slips from the customer’s hands. What force causes the bills to hit the ground later than the coins do? A. B. C. D. static friction gravity air resistance magnetism Forces Standardized Test Prep Understanding Concepts, continued 2. If the nickel and iron at the Earth’s core were suddenly replaced with cotton candy, what would happen to the mass and weight of the objects on the Earth’s surface? F. Their mass and weight both increase. G. Their mass would stay the same and their weight would decrease. H. Their mass would decrease and their weight would increase. I. Neither their mass nor weight change. Forces Standardized Test Prep Understanding Concepts, continued 2. If the nickel and iron at the Earth’s core were suddenly replaced with cotton candy, what would happen to the mass and weight of the objects on the Earth’s surface? F. Their mass and weight both increase. G. Their mass would stay the same and their weight would decrease. H. Their mass would decrease and their weight would increase. I. Neither their mass nor weight change. Forces Standardized Test Prep Understanding Concepts, continued 3. A truck with a mass of 2,000 kg is traveling at a constant velocity of 40 m/s. What is the net force acting upon the truck? A. B. C. D 0.0 N 0.02 N 50 N 800 N Forces Standardized Test Prep Understanding Concepts, continued 3. A truck with a mass of 2,000 kg is traveling at a constant velocity of 40 m/s. What is the net force acting upon the truck? A. B. C. D 0.0 N 0.02 N 50 N 800 N Forces Standardized Test Prep Understanding Concepts, continued 4. A high-altitude balloonist at an altitude of 15,000 m drops an instrument package. When does the package reach terminal velocity? F. G. H. I. as it begins to fall as it matches the speed of the plane as it stops accelerating from air resistance as it impacts the Earth’s surface Forces Standardized Test Prep Understanding Concepts, continued 4. A high-altitude balloonist at an altitude of 15,000 m drops an instrument package. When does the package reach terminal velocity? F. G. H. I. as it begins to fall as it matches the speed of the plane as it stops accelerating from air resistance as it impacts the Earth’s surface Forces Standardized Test Prep Understanding Concepts, continued 5. Explain why the moon does not fly off into space in a straight line nor plummet directly toward the Earth’s surface. Forces Standardized Test Prep Understanding Concepts, continued 5. Explain why the moon does not fly off into space in a straight line nor plummet directly toward the Earth’s surface. Answer: The forward and downward motions combine to produce an orbit. Forces Standardized Test Prep Understanding Concepts, continued 6. A racing motorcycle with a mass of 300 kg accelerates from 0 to 60 m/s in 5 seconds. How much force is acting on the motorcycle? Forces Standardized Test Prep Understanding Concepts, continued 6. A racing motorcycle with a mass of 300 kg accelerates from 0 to 60 m/s in 5 seconds. How much force is acting on the motorcycle? Answer: 3,600 N Forces Standardized Test Prep Reading Skills A REGULAR VISITOR A microgravity environment is one in which the apparent weight of an object is much less than its weight on Earth. The term microgravity is used instead of weightlessness because every object has some weight, though that weight may be so minuscule as to be undetectable. Because every object in the universe exerts a gravitational pull on every other object, every object possesses weight. Microgravity occurs whenever an object is in free fall. Scientists achieve microgravity environments in a number of ways. Drop towers and research aircraft provide it for up to 20 s. The Shuttle and the International Space Station can provide it for months. Forces Standardized Test Prep Reading Skills, continued A REGULAR VISITOR, continued A rocket ship that is accelerating by firing its rockets cannot provide microgravity. Even if the rocket is accelerating uniformly, force is applied to the rocket by the gas escaping out the back. This force must be transferred to each part of the ship through either pressure or tension, and thus weightlessness is not experienced. Forces Standardized Test Prep Reading Skills, continued 7. When the Shuttle is orbiting, it is in constant motion around the Earth. Why isn’t this motion experienced as weight? A. There is no net force acting on the Shuttle. B. The Shuttle’s mass is not large enough to exert a measurable gravitational pull. C. The Earth is exerting the same pull on both the Shuttle and its passengers. D. The Earth is too far away to have a measurable gravitational effect. Forces Standardized Test Prep Reading Skills, continued 7. When the Shuttle is orbiting, it is in constant motion around the Earth. Why isn’t this motion experienced as weight? A. There is no net force acting on the Shuttle. B. The Shuttle’s mass is not large enough to exert a measurable gravitational pull. C. The Earth is exerting the same pull on both the Shuttle and its passengers. D. The Earth is too far away to have a measurable gravitational effect. Forces Standardized Test Prep Reading Skills, continued 8. Why can the Shuttle provide microgravity only after it achieves orbit? Forces Standardized Test Prep Reading Skills, continued 8. Why can the Shuttle provide microgravity only after it achieves orbit? Answer: Because before that point and after it takes off, the Shuttle is accelerating, so there is a net force on it that is also experienced by the objects within it. Forces Standardized Test Prep Interpreting Graphics The following graph charts the speeds of three objects in motion. Use this graph to answer questions 9 and 10. Forces Standardized Test Prep Interpreting Graphics, continued 9. At the 1 s mark, which objects have equal momentum? A. the bicycle and the rock B. the rock and the bowling ball C. the bowling ball and the bicycle D. All three objects have the same momentum. Forces Standardized Test Prep Interpreting Graphics, continued 9. At the 1 s mark, which objects have equal momentum? A. the bicycle and the rock B. the rock and the bowling ball C. the bowling ball and the bicycle D. All three objects have the same momentum. Forces Standardized Test Prep Interpreting Graphics, continued 10. At the 3 s mark, which object or objects have a net force acting on them? F. H. G. I. the bicycle the bowling ball the rock the bicycle and the bowling ball Forces Standardized Test Prep Interpreting Graphics, continued 10. At the 3 s mark, which object or objects have a net force acting on them? F. H. G. I. the bicycle the bowling ball the rock the bicycle and the bowling ball Forces Standardized Test Prep Interpreting Graphics, continued The following graphic shows a long jumper making a jump from west to east. Use this graphic to answer questions 11 and 12. Forces Standardized Test Prep Interpreting Graphics, continued 11. In what direction or directions is the net force acting on the jumper between 0.5 s and 2 s? A. first up and to the east, then down and to the west B. first up and to the east, then down and to the east C. up and to the east D. down and to the west Forces Standardized Test Prep Interpreting Graphics, continued 11. In what direction or directions is the net force acting on the jumper between 0.5 s and 2 s? A. first up and to the east, then down and to the west B. first up and to the east, then down and to the east C. up and to the east D. down and to the west Forces Standardized Test Prep Interpreting Graphics, continued 12. When the long jumper jumps, Earth exerts a force that moves him up and to the east. Since there is a reaction force exerted on Earth, why doesn’t Earth move the same distance down and to the west? Forces Standardized Test Prep Interpreting Graphics, continued 12. When the long jumper jumps, Earth exerts a force that moves him up and to the east. Since there is a reaction force exerted on Earth, why doesn’t Earth move the same distance down and to the west? Answer: The acceleration of Earth is force divided by mass, and since Earth’s mass is so large, the resulting acceleration of Earth is very small.