The Solution Process of Simple Ionic and Covalent Compounds
advertisement
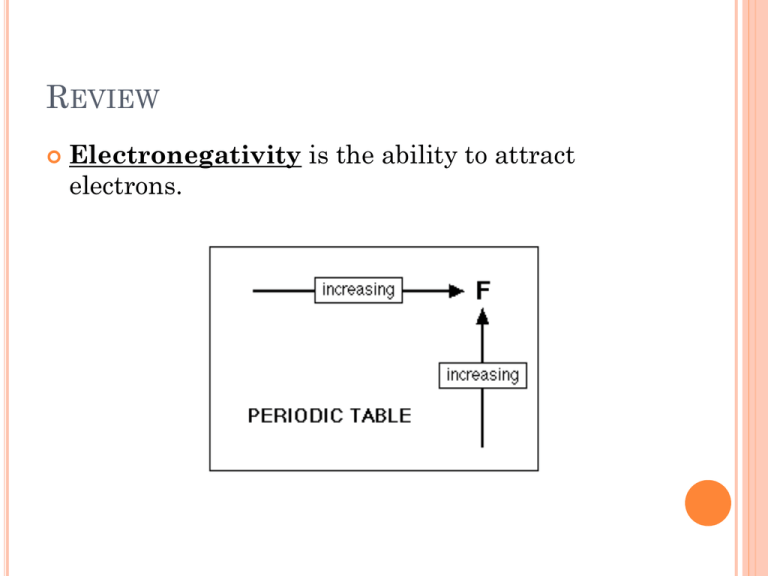
REVIEW Electronegativity is the ability to attract electrons. REVIEW Polar molecules: Bonds between two atoms with different electronegativities. REVIEW Non Polar molecules: Bonds between two atoms with similar electronegativities. QUESTION Which of the following will be polar molecules? Include a diagram and justify your answer. HCl F2 I2 CH3Cl THE SOLUTION PROCESS OF SIMPLE IONIC AND COVALENT COMPOUNDS REVIEW Ionic bond - transfer of electrons between a metal (cation) and non-metal (anion) Covalent bond- sharing of electrons between two non-metals (anions) Covalent bonds can be polar or non-polar. IONIC COMPOUNDS When a solute is placed into a solvent, the solvent particles completely surround the surface of the solute particles. The polar water molecules orientate themselves around each exposed ion on the surface of the solid. IONIC COMPOUNDS IONIC COMPOUNDS If the solute is soluble, the attraction between the solvent solute increases to the point where it finally exceeds the forces holding the crystal lattice. The separation of an ionic compound into ions is called dissociation IONIC COMPOUNDS Solvation is the process of the solvent surrounding the solute ions. IONIC COMPOUNDS If the solvent is water than the process of solvation can be called hydration and the solute particles are hydrated. IONIC COMPOUNDS http://programs.northlandcollege.edu/biology/Biol ogy1111/animations/dissolve.html IONIC COMPOUNDS Dissociation: NaCl(s) → Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq) KF(s) → K+(aq) + F-(aq) NH4NO3(s) → COVALENT COMPOUNDS An entire molecule is pulled away from the solid structure and is surrounded by the solvent. C12H22O11(s) C12H22O11(aq) QUESTIONS 1. Explain the process of CaCl2 dissolving in water. Include a diagram in your explanation. 2. Compare and contrast dissolving ionic compounds and covalent compounds. 3. Use your knowledge of dissociation and solvation to explain why stirring powdered hot chocolate and water dissolves the crystals faster.




