PSI AP Chemistry: Chemical Bonding Name Chapter Problems Part
advertisement

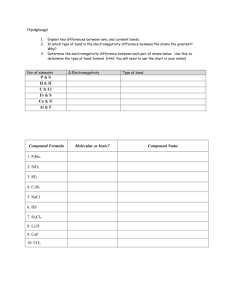
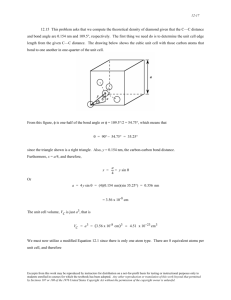
PSI AP Chemistry: Chemical Bonding Chapter Problems Part A Covalent Compounds Name _______________________ 1. The bond between atoms of O and C is referred to as being polar covalent? a. Why is this bond considered covalent and not ionic? b. Why is the bond considered polar covalent instead of nonpolar covalent? c. Which atom in the bond carries the partial positive charge? Explain. d. Provide an element O could bind with to create an ionic bond. Justify your answer. e. Provide an element O could bind with to create a nonpolar covalent bond. Justify your answer. f. What causes the attraction between the atoms in this C-O bond? g. What would happen to the potential energy of the atoms if they got too close to each other? Explain your answer. 2. Explain the following observations: a. The lattice energy of LiF is 1036 kJ/mol while that of LiCl is 897 kJ/mol. b. The N-H bond length is 98 pm while that of P-H is 140 pm. c. The N-H bond length is 98 pm while that of O-H is 94 pm. d. The lattice energy of MgO is higher than that of MgF2. 3. Propose a reason as to CaCl2 may be soluble in water while CaF2 would not be? 4. Examine the figure below: a. What is the approximate bond length for these atoms represented in the diagram? b. What is the approximate bond energy for these atoms in the diagram? c. Why is the potential energy of the atoms higher as the distance between the atoms increases? d. Why does the potential energy of the atoms increase sharply as the inter-nuclear distance becomes very small? e. Is bond formation exothermic or endothermic? Explain your answer. www.njctl.org AP Chemistry Chemical Bonding Answers 1. a. The electronegativity difference is too small for ion formation so electrons are shared instead. b. The electronegativity difference is such that the electrons are shared unequally with the O atom pulling more strongly and possessing the electrons a greater share of the time c. C would, as it has the smaller electronegativity. d. A metal with a small electronegativity like Ca or Rb would be excellent choices, this creates a large enough electronegativity difference to induce ion formation. e. Ideally, itself – as this would create a zero electronegativity difference. f. The shared electrons between the nuclei result in an attraction between them. g. The potential energy would increase as the repulsions between the positive nuclei would increase dramatically. 2. a. The chloride ion has a larger ionic radii than does fluoride resulting in weaker Coulombic attractions and a smaller lattice energy. b. The P atom has a higher atomic radii making the Coulombic attractions weaker and the bond length longer. c. Two reasons. The radii of O is smaller than that of N thereby creating stronger Coulombic attractions but also the bond between O-H is more polar which creates a stronger Coulombic attraction as well. d. The charge density is considerably higher in the oxide ion compared to that of a fluoride ion (-2 to -1) resulting in stronger Coulombic attractions. 5. The lattice energy of CaF2 is considerably higher due to the smaller ionic radii of the fluoride ion. This would make dissociation harder in aqueous solvents. 6. a. 33 pm b. -210 kJ/mol c. The attractions between the atoms diminishes as the distance increases. www.njctl.org AP Chemistry Chemical Bonding d. The repulsions between like charged nuclei increase significantly e. Exothermic, as atoms lower their potential when forming attractions thereby releasing energy to the surroundings. www.njctl.org AP Chemistry Chemical Bonding