DNA replication: mitosis & meiosis
advertisement

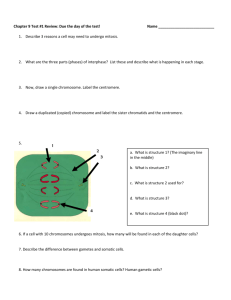
DNA REPLICATION: MITOSIS & MEIOSIS 3A3B Biology DNA REPLICATION Keywords Mitosis Meiosis DNA replication Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Keywords Chromatin Chromatids Chromosomes Centromere Centriole Spindle fibres Cytokinesis GENETIC INFORMATION Each species has a specific number of chromosomes, composed of a particular kind of DNA Example: Humans have 46 chromosomes Dogs have 78 chromosomes Dandelions have 16 chromosomes Strawberries have 14 chromosomes MITOSIS Cell division is responsible for growth, replacement and repair. The activities of a cell are controlled by the nucleus Mitosis is the division of the nucleus. This process ensures that genetic information is accurately copied and passed on The result of mitosis is the formation of two genetically identical cells – the parent cell divides to form 2 identical daughter cells STAGES OF MITOSIS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Mitosis can be divided into 5 stages: Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Interphase is a period when the cell functions as normal, but is also preparing for cell division. The chromosomes are strung out in long chromatin threads within the nucleus. Each chromatin thread is replicated over a period of time. All the various organelles are also being replicated at this time. PROPHASE Centrioles become visible in the cytoplasm Chromatin condenses into chromosomes Each chromosome consists of 2 identical strands called chromatids These are attached to each other at a point call the centromere Nuclear membrane disappears centrioles chromosome – consisting of 2 chromatids 6 METAPHASE spindle fibres During metaphase the chromatids line up at the equator of the cell. The centromere of each pair is attached to a spindle fibre chromosomes – spindle fibre attached at the centromere centrioles 7 ANAPHASE During anaphase each pair of chromatids separate at the centromere The chromatids are pulled apart towards the opposite poles of the cell by the spindle fibres spindle fibre chromatid centriole 8 TELOPHASE During telophase the 2 sets of chromosomes form tight groups at each pole The spindle disappears Nuclear membranes and nuclei form Centrioles divide Chromosomes uncoil and disappear Cytokinesis occurs during this phase Cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm https://www.youtube.com/w atch?v=P4KCaGkh8v0 centriole cytokinesis group of chromosomes 9 STAGES OF MITOSIS MEIOSIS There is another form of cell division called meiosis Meiosis does not produce identical daughter cells that are copies of the original parent cell Instead, cell division involving meiosis produces the gametes (sex cells) After meiosis, each gamete ends up with only half the number of chromosomes MEIOSIS The process of meiosis involves two nuclear divisions, but the chromosomes duplicate only once The first division of meiosis is similar to mitosis but during metaphase I the chromosomes pair off, rather than all of them lining up singly. The members of each pair of chromosomes are identical in size and shape and are called homologous pairs Meiosis Mitosis Metaphase I Metaphase Homologous pair of chromosomes Metaphase II MEIOSIS – WHAT HAPPENS IN THE NUCLEUS Crossing over occurs during the first prophase. This ensures genetic diversity in offspring. MEIOSIS I & MEIOSIS II DIPLOID VS HAPLOID CELLS Term Definition Diploid The number of chromosomes present in the body (or somatic) cells of an individual (2n) Haploid The number of chromosomes present in the gametes (n) Mitosis (Amoeba Sisters) 8 min https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gwcwSZIfKlM Meiosis (Amoeba Sisters) 8 min https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=toWK0fIyFlY