DENT 1214 Clinical Concepts
advertisement

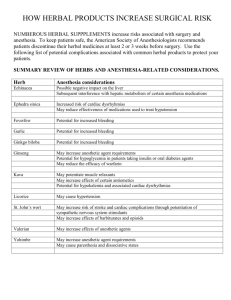
DENT 1160 Pharmacology 1. Define PHARMACOLOGY It is the branch of medicine that conducts research and development in the use and effects of drugs. A drug is a substance used to treat, diagnose or prevent a disease Dentist need to know what the patient is taking because those drugs may effect treatment and interact with the drugs the dentist needs to use. 2. DRUGS Over the counter or Prescription (DEA #) ID a drug by 3 names Chemical acetylsalicylic acid Generic aspirin Brand Bayer, Bufferin 3&4. Physician Desk Reference PDR in text or computer format Tells: use, indications and contraindications, side effects (predictable body reaction) other sourcesUSP, NF, ADT, How to use PDR Obtain any of the following: The name of the drug Turn to the Product Name Index - alphabetical A sample of the drug Look in the Product Identification Section -pictures The prescription container with product name Use the yellow Generic or Chemical Name Section The medical condition the drug is treating Use the blue section -Product Category Index Examples: analgesic anticoagulant diuretic Page numbers will direct you to detailed information, classification, purpose or use, side effects, contraindications 5. Routes of Administration Oral- pill, capsule, liquid Topical- gel or ointment on skin or mucosa (subdermal patch) Inhalation- gas Sublingual- under tongue, absorbed Injection subcutaneous IM IV Prescription Is a written order by Dr or DDS ( with DEA#) to dispense drugs. Keep Rx pads secure!!! Superscription- patient data Inscription- name and amount of drug Subscription- directions for dispensing Signature- directions for use( see list text) Prescriptions DA may call a Rx to pharmacy but CAN NOT PRESCRIBE or dispense OTC without DDS order Controlled Substance Act 1970 Schedule I- no medical use, potential abuse, LSD, heroine, marijuana II- has med use, potential abuse, no call in or refill, opium, cocaine, morphine III- use and less potential abuse, stimulants, depressants, Tylenol with codeine IV- Valium, laibrium, Darvon V- cough meds with codeine 6. Antibiobitics Dentists may prescribe an antibiotic to treat or prevent a bacterial infection. Some common antibiotics are: penicillins PenVee K, Amoxil cephalosporins Keflex, Ceclor erythromycins Zithromax, E-Mycin tetracyclines Minocin,Achromycin clindamycin Clindets, Dalacin Oral Contraceptives????????????????????? 7. AHA Prophylactic Antibiotics When needed? prevent endocarditis Artificial heart valve Shunt Heart murmur mitral valve prolapse Use what? Penicillin or ampicillin (2g) clindamycin (500mg) Take when? One hr before appointment ADA on Premeds http://www.ada.org/public/media/videos/ minute/medi_premedication_broadband. wmv 8&9. Analgesics Also known as pain killers Non narcotic (OTC) relieve mild to moderate pain Acetylsalicylic acid- Aspirin (cause bleeding due to thinning of blood) Acetaminophen- tylenol Ibuprofen- Advil or Motrin 10. Narcotic Analgesics Stronger and may be used for sedation, analgesia and hypnosis morphine codeine meperdine- Demerol Oxycodone- Percodan Propoxyphene- Darvon, Davocet 11. Premed Sedatives Antianxiety agents given to reduce nervousness prior to appointment Diazepam- Valium Chlordiazepoxide-Librium Meprobamate- Miltowm Hydroxyzine- Vistaril Xanax 12. Instructions for Pre Op meds Antibiotic- take as directed 1 hr prior to apt. Sedative- take as instructed, do not drive or drink alcohol 14. Sedation (antianxiety) Inhalation vs IV INHALATION Nitrous oxide Halothane(Fluothane) Methoxyflurane ( Penthrane) IV Pentothal Brevital ADA on Nitrous http://www.ada.org/public/media/videos/ minute/treat_nitrous_broadband.wmv 13. Analgesia vs Anesthetic Analgesic prevent or relieve pain Anesthetic produces a loss of sensation, numbs 15. Topical vs Local anesthesia Topical- gel, ointment, liquid or spray used to numb mucosa. A 5-20% concentration of local anesthetic. Dry area, apply and let set 1-2 min. Local- loss of sensation in area, 2-5% concentration, lidocaine, mepivocaine, xylocaine, lidocaine 16. 3 actions of VASOCONSTRICTOR Constrict BV to prolong the effect Decrease bleeding in the area Reduces the amount of anesthetic needed, safer Epinephrine 1:50,000 or 1:20,000, 1:100.00 17. Contraindication for vasoconstrictor Hypertension Severe cardiovascular disease Hyperthyroid Use nonepinephrine products like: Levophed, Neo-Cobefrin 18. Assistant responsibility You prepare the syringe! 1.Use correct anesthetic (per Dr) cartridge 2. Use correct needle length ( long mand, short max) 3. Place stick shield 4. Engage harpoon 19. Drugs of concern to dental treatment 1. Antabuse- avoid product with high alcohol content like mouthwash 2. Aspirin, Fiorinal, Coumadin (warfarin)bleeding (anticoagulants) 3. NSAID, Naprosyn, indomethacinbeware Diabetics & cause bleeding 4. Albuterol or Ventolin- asthma 5. Insulin- diabetic (food and insulin) 6. Nitrogliceryn- angina 19. Cont drugs of concern 7. Lasix (furosemide)- HBP, restroom use 8. Lanoxin (digoxin)- heart problems 9. Prednisone- immune compromised,cancer 10. Oral Contraceptive- not effective with AB 11. Prozac (fluoxetine)- Do Not use nitrous 12. Zoloft- FATAL with Demeral (meperidine) 13. Dilantin- epilepsy Dilantin for epilepsy ADA on drug side effects http://www.ada.org/public/media/videos/ minute/medi_sideeffects_broadband.wm v The End