Gene Flow
advertisement

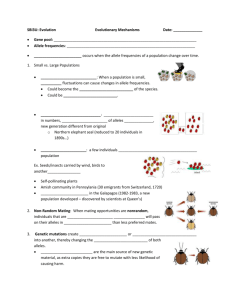
Chapter 11 11.1 & 11.3 Starter Write & Answer 1. Name and graph the three ways natural selection can change the distribution of traits. 2. How might the overfishing of large pink salmon affect salmon size in future generations? Which pathway of natural selection is this? 3. Woodpeckers with extremely large beaks are unable to fit their beaks into small holes and retrieve bugs. Woodpeckers with very small beaks are unable to reach bugs that have crawled to the back of holes and tunnels. What will happen to the woodpecker population? What pathway of natural selection is this? Genetic Variation in Populations • A population shares a common gene pool • gene pool - the combined alleles of all the individuals in a population Genetic Variation increases the probability that some individuals will survive • Genetic variation leads to phenotypic variation • Phenotypic variation is necessary for natural selection • Genetic variation is stored in the population’s gene pool Allele Frequencies measure genetic variation • measures how common an allele is in a population • can be calculated for every allele in a gene pool Genetic variation has several sources: • Mutation (a random change in DNA) – can form a new allele, can be passed on to offspring • Recombination (parents’ alleles recombined in offspring) Natural Selection is not the only mechanism through which populations evolve • Gene Flow : the movement of alleles between populations • Occurs when individuals join other populations and reproduce • Gene flow keeps neighboring populations similar • Low Gene Flow increases the chances that two populations will evolve into different species Genetic Drift • Genetic drift is a change in allele frequency due to chance • Bottleneck Effect: a random/destructive event reduces a population’s size • The Founder Effect: genetic drift that occurs after a small number of individuals colonize a new area Genetic Drift The illustration to the right represents the bottleneck effect. An event reduces the population size, reducing the variation. Here, the “red” alleles are eliminated. The illustration to the left represents the founder effect – a new population of flowers is founded, without the “orange” allele. Genetic Drift has negative effects on populations • less variation, less likely that individuals can adapt • harmful alleles may be more common in the population Sexual Selection • Sexual Selection occurs when certain traits increase mating success • Occurs due to the higher cost of reproduction for females than males • Males produce sperm continuously • Females are more limited in number of potential offspring Two types of Sexual Selection • Intrasexual selection: competition among males • Intersexual selection: males display certain traits to females