Transport across membranes - SandyBiology1-2
advertisement

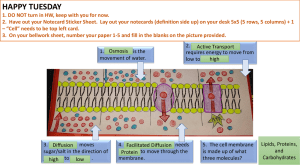
Solutions Solute – The substance that dissolves to form a solution eg salt Solvent – The substance in which a solute dissolves eg water Solution – A mixture of one or more solutes dissolved in a solvent eg sea water Solute Solvent DIFFUSION & OSMOSIS DIFFUSION • Diffusion animation Diffusion is the net movement of particles from a region of higher concentration to a region of relatively lower concentration. No input of energy is required. DIFFUSION & OSMOSIS OSMOSIS • Osmosis animation Osmosis is the net movement of a solvent, usually water, across a differentially permeable membrane. The net movement of water occurs from the side of the membrane where there is a weak solution (high water concentration, low solute concentration) to the side of the membrane where there is a strong solution(low water concentration, high solute concentration). Osmosis does not require energy input. Osmosis Amoeba are small unicellular organisms with a large SA:V Amoeba in action 1 Amoeba in action 2 Some substances can diffuse into /out of these cells very efficiently as a result of the large SA: V ratio Larger food particles can be engulfed: phagoctosis Plasma Membranes Functions of the cell membrane include: 1. It gives a definite shape to the cell. 2. It contains and provides protection to the internal contents of the cell. 3. It is selectively permeable. 4. It can take in solid and liquid materials by in folding. 5. In animal cells, it is involved in the formation of vesicles, cilia, flagella, microvilli, etc. Plasma Membrane overview 5 min Passive diffusion across a membrane Openings both sides eg channels for ion transfer Attach to carbohydrates act as antigens Link cells together Binds hormones and other substances Fluid Mosaic model of plasma membranes Web page including good animation Cell-Membrane-Function Plasmolysis Hemolysis & Crenation Passive v Facillitated Diffusion Cytosis Mitosis