Photosynthesis II PPT
advertisement

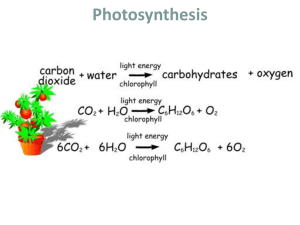
Photosynthesis Photosynthesis -Primarily in chloroplasts of plants -Reactions occur inside structures within the chloroplasts called thylakoids and the stroma. Chloroplast Granum Single thylakoid Stroma Overall Reaction of Photosynthesis Reactants: carbon dioxide, water, and energy (sun) Products: glucose and oxygen 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 Light Reactions Function: -Energy from the sun is absorbed by chlorophyll located inside the thylakoids. -The light energy is transferred from the chlorophyll to NADP+ to form NADPH. This occurs in a series of reactions called the electron transport chain (ETC) across the thylakoid membrane. -ATP is formed from ADP by chemiosmosis across the thylakoid membrane. (ADP adds a P group with the help of the protein ATP Synthase.) Location: chlorophyll & thylakoid membrane Reactants: H2O, energy (sun) ADP, and NADP+. Products: oxygen, ATP, and NADPH. Photosynthesis H2O CO2 Light NADP+ ADP + P Lightdependent reactions O2 Calvin cycle Sugars Calvin Cycle (Dark Reactions) Function: -No sunlight is needed. -Plants use the energy within ATP and NADPH to build organic compounds (glucose) which are sources of nutrients for the plant. Location: stroma of the chloroplast Reactants: CO2 (from air), ATP and NADPH Products: Organic Compounds (Glucose) Photosynthesis H2O CO2 Light NADP+ ADP + P Lightdependent reactions O2 Calvin cycle Sugars Photosynthesis • The two sets of photosynthetic reactions work together. – The light-dependent reactions trap sunlight energy in chemical form. – The light-independent reactions use that chemical energy to produce stable, high-energy sugars from carbon dioxide and water. Alternative Biochemical Pathways • C4 Pathway – Plants in hot, dry climates. Try to prevent water loss. Water loss occurs through the stomata. (Passageway for O2 & CO2 entering and leaving the plant.) • CAM Pathway – open stomata only at night. • C3 , C4 & CAM pathway plants also differ by the initial product of carbon fixation. Factors affecting the Rate of Photosynthesis: • Light Intensity • Amount of CO2 • Temperature