Photosynthesis
advertisement
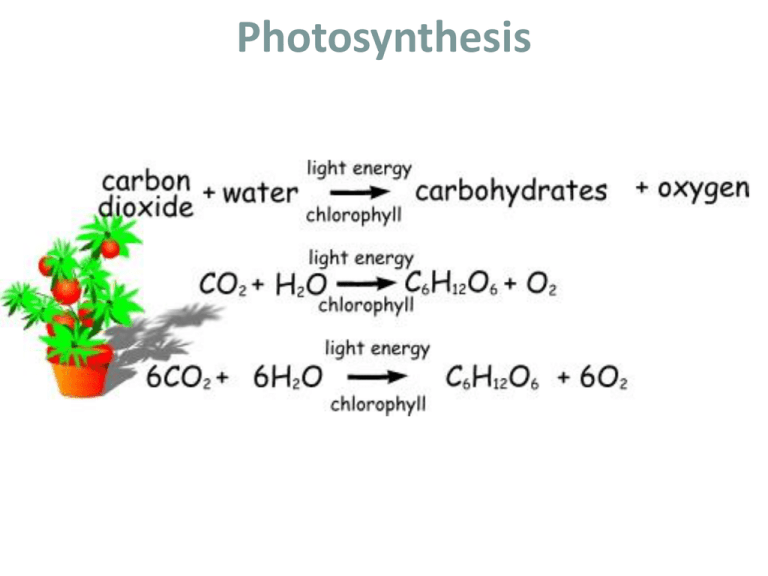
Photosynthesis Pigments of Photosynthesis Pigments are molecules that absorb specific wavelengths (energies) of light and reflect all others. • Chlorophyll is the main molecule in charge of capturing the energy from sunlight. Absorption of Light by Chlorophyll a and Chlorophyll b Chlorophyll b Chlorophyll a V B G YO •Chlorophyll a absorbs …………….. light best. •Chlorophyll b absorbs ……………. light best. •Why do plants look green? •THEY RELFECT GREEN LIGHT!!! R Chloroplast Structure NADP+ – Electron Carrier Molecule • Electron Carrier Molecules – Compound that can accept a pair of high energy electrons and transfer them, along with most of their energy to another molecule – One way the sunlight can be trapped in a chemical form and use it to build glucose for the plant cell – Example: • NADP+ = accepts and holds 2 high energy electrons along with a hydrogen ion (H+) • When NADP+ accepts 2 electrons and a H+ it becomes NADPH Chemical Energy and ATP • ATP – Adenosine triphosphate – Compound that cells use to store and release energy – Made of adenine, 5-carbon sugar (ribose), and 3 phosphate groups • ADP – Adenosine diphosphate – Made of adenine, 5-carbon sugar (ribose), and 2 phosphate groups Chemical Energy and ATP Photosynthesis: Step 1 – Light-Dependent Reaction • Sunlight is used toFigure split water into hydrogen (H) 8-7 Photosynthesis: An andSection oxygen (O). 8-3 • The Oxygen is released to the atmosphere. • Also produces NADPH and ATP for the next step! HO CO • Takes place inLight Thylakoids. Chlo 2 2 Chloroplast NADP+ ADP + P LightDependent Reactions Calvin Cycle ATP NADPH O2 Sugars Photosynthesis: Step 2 – Light-Independent Reaction • This step is also called the Calvin Cycle or Light Independent Reaction because it does not need light. • CO2 combines with the hydrogen (H) released during step 1 to form C6H12O6 (glucose) Figure 8-7 Photosynthesis: A • The NADPH and ATP made in Light Dependent Rxn provides the energy to make Lt. Independent Rxn work. Section 8-3 • Takes place in stroma. Light CO2 C Chloroplast NADP+ ADP + P LightDependent Reactions Calvin Cycle ATP NADPH O2 Sugars H2 O Light Chloroplast CO2 NADP+ ADP + P LightDependent Reactions Calvin Cycle ATP NADPH O2 Sugars What affects the rate of photosynthesis? • Amount of : - sunlight - CO2 - H2O - temperature • All the reactions of photosynthesis are controlled by enzymes. Temperatures above or below the optimum temperature will slow down the chemical reactions.







