Chapter 11—The East Asian Rimlands - Leleua Loupe
advertisement

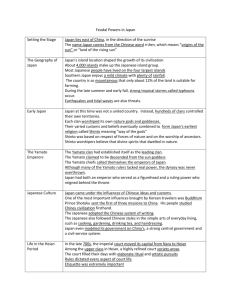
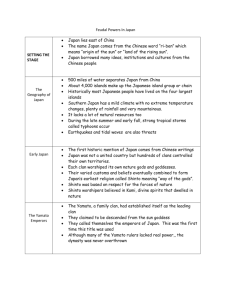
Chapter 11—The East Asian Rimlands: Early Japan, Korea, and Vietnam ESSAY 1. What role did geography play in Japan's early development? How did it influence its social, religious, and political institutions? By comparing and contrasting Great Britain and Japan, can you make any generalizations about the development of insular societies? 2. What is the relationship between the major agricultural regions in Japan and its political development and historical evolution? 3. What were the probable ethnic roots of the Japanese people? What traditional ideas about Japanese origins were devised in Japan to explain its founding? Are the latter compatible with the former? Why or why not? 4. How was the Japanese aristocracy able to suppress the centralization of the Japanese government? How does this contrast with the governmental system of China? What were the advantages and disadvantages of Japan having a governmental system in which the emperor reigns and the shogun rules? 5. "Japan borrowed from China, but only selectively." Discuss with examples. 6. Compare and contrast the Heian era of Japan with the period of the Kamakura shogunate. What changed, and why? 7. What were the possible reasons why Japan failed to adopt the Confucian-based civil service examination system? 8. It can be argued that the symbol of medieval China is the scholar-gentry while in Japan it is the samurai warrior. How do you account for the difference between the two societies? 9. Can the term "feudal" be accurately applied to the medieval Japanese society? How does Japanese "feudalism" compare with that of Europe between 800 and 1500? Compare and contrast the status and function of the medieval Japanese samurai warrior with that of the medieval European knight. 10. Discuss the relationship between Japanese Shinto and Buddhism, regarding the apparent compatibility for many Japanese during the era from 1000 to 1500. 11. What were the major developments in early Japanese literature, art, and architecture? What is meant by the statement "Tea and zen have the same flavor"? 12. Trace the development of government in Korea from the era of the three kingdoms through the establishment of the post-Yuan Yi Dynasty. How did local and Chinese ideas and institutions influence this development? 13. How has Vietnam's resistance to attempted conquest been a primary determinative factor in the development of Vietnamese culture? How has the strong Vietnamese sense of cultural distinctiveness made them resistant to assimilation by China? 14. and con. "China was the paradigm of all East Asian societies." Using examples, discuss, pro IDENTIFICATIONS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. Instructions: Identify the following terms. Hokkaido, Honshu, Kyushu, and Shikoku Pacific Current Asian and Pacific tectonic plates Izanagi and Izanami Amaterasu Nihon Shoki Jomon and Yayoi cultures Jimmu Yamato plain and Yamato clan uji Ainu Shotoku Taishi Taika reforms Fujiwara clan Nara Heian "land of Wa" samurai Bushido shoen Minamoto Yoritomo Kamakura shogunate bakufu shogun kamikaze/"divine wind" Mongol invasions daimyo Kyoto Ashikaga era Onin War genin and eta kami Shinto Pure Land sect/Jodo Zen/Chan satori and zazen haiku No Murasaki Shikibu"s The Tale of Genji bonsai "linked verse" "guardian kings" the tea ceremony Koguryo, Paekche and Silla Koryo dynasty chonmin Yi Song-gye the Trung Sisters Annam and Champa Dai Viet