ME240/107S: Product Dissection
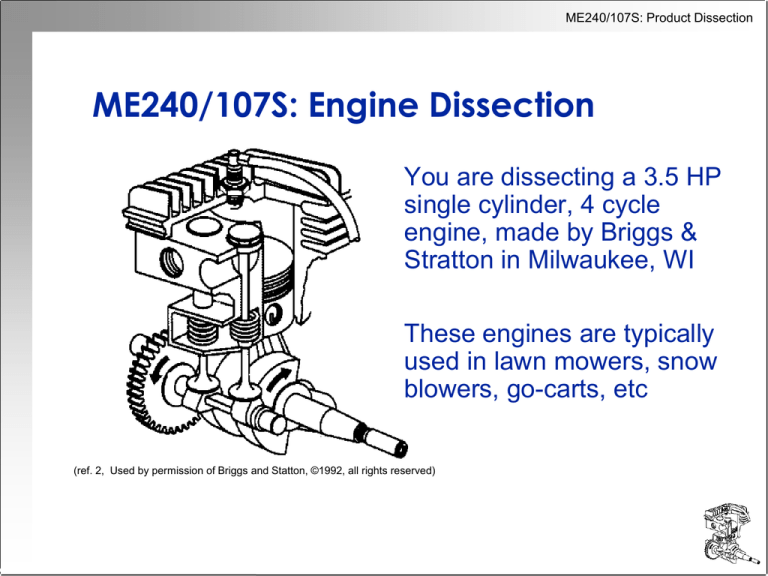
ME240/107S: Engine Dissection
You are dissecting a 3.5 HP
single cylinder, 4 cycle
engine, made by Briggs &
Stratton in Milwaukee, WI
These engines are typically
used in lawn mowers, snow
blowers, go-carts, etc
(ref. 2, Used by permission of Briggs and Statton, ©1992, all rights reserved)
ME240/107S: Product Dissection
Lecture 2
Carburetor
Ignition System
Drivetrain Components
ME240/107S: Product Dissection
Session 1: Carburetor and Ignition
In small groups, discuss your answers to the
following questions from Session 1
Carburetor:
What
are the components of the Pulsa-Jet
Carburetor and how do they work?
How
many jets are used? What is their function?
ME240/107S: Product Dissection
Session 1: Carburetor and Ignition
Ignition:
What
is the purpose of the starter clutch?
Why
is the flywheel comprised of different
materials? What are those materials?
How
does the ignition system work?
How
is ignition timing achieved in the engine?
ME240/107S: Product Dissection
Carburetor
Purpose of the carburetor is to produce a
mixture of fuel and air on which the engine
can operate
Uses a venturi nozzle to
reduce air pressure in
the carburetor to create
suction to “pull” fuel into air
ME240/107S: Product Dissection
Pulsa-Jet Carburetor
Incorporates a diaphragm type fuel pump
and a constant level fuel chamber
ME240/107S: Product Dissection
Pulsa-Jet Carburetor Operation
Intake stroke of piston
creates a vacuum in
carburetor elbow
Pulls cap A and pump
diaphragm B inward and
compresses spring
Vacuum thus created on
“cover side” of diaphragm
pulls fuel up suction pipe S
into intake valve D
ME240/107S: Product Dissection
Pulsa-Jet Carburetor Operation
When engine intake stroke
is complete, spring C
pushes plunger A outward
Gasoline in pocket above
diaphragm to close inlet
valve D and open
discharge valve E
Fuel is then pumped into
fuel cup F
ME240/107S: Product Dissection
Pulsa-Jet Carburetor Operation
Venturi in carburetor is
connected to intake pipe
I which draws gasoline
from fuel cup F
Process is repeated on
the next stroke, keeping
the fuel cup full
Since fuel cup level is
constant, engine gets
constant air-fuel ratio
ME240/107S: Product Dissection
Ignition System
Consists of:
Spark
plug
Armature
Coil
(primary and
secondary)
Flywheel
Magnet
ME240/107S: Product Dissection
Ignition System - Electric Circuit
Uses a changing
magnetic field to
generate current in
primary and
secondary circuits
ME240/107S: Product Dissection
Ignition System - Magnetic Flux
As magnet approaches,
induces magnetic flux in
armature
Breaker points close
and current dissipates
through primary circuit
ME240/107S: Product Dissection
Ignition System - Spark Fires
After magnet rotates past
armature flux reverses
direction, and the breaker
points open
Change in magnetic flux
produces 170 volts in
primary circuit
Induces 10,000 volts in
secondary circuit, firing
spark plug
ME240/107S: Product Dissection
Ignition System - Breaker Point
Crankshaft rotation
causes mechanical
actuation of breaker
ME240/107S: Product Dissection
Ignition System - Magneto System
In Magnetron ignition
system, magnetic flux
induced by flywheel
magnet also actuates
primary circuit and
spark timing
Capacitor helps
regulate current (i.e.,
serves as condenser)
ME240/107S: Product Dissection
The Drivetrain
As a group, brainstorm as many drivetrain
components as you can. You have 3 min.
ME240/107S: Product Dissection
Drivetrain
Provide power via
rotating crankshaft
ME240/107S: Product Dissection
Drivetrain: Piston-Rod Assembly
Piston is connected
to the crankshaft by
the connecting rod
Vertical motion of
piston rotates the
crankshaft
What is purpose of
compression rings?
ME240/107S: Product Dissection
Drivetrain: Valves
Valves regulate air-fuel
flow mixture into and out
of piston cylinder
ME240/107S: Product Dissection
Drivetrain: L-Valve Actuation
Camshaft drives
actuation and
timing of intake
and exhaust
valves in L-head
configuration
ME240/107S: Product Dissection
Drivetrain: Valve Actuation
In overhead or I-head,
camshaft actuates a
tappet (lifter) which
forces a push rod
upward, causing the
rocker arm to rotate to
actuate the valves
What is the purpose
of the valve spring?
Rocker arm
Push rod
Tappet
ME240/107S: Product Dissection
4 Stroke Cycle
1
Intake Valve
Intake
Manifold
Cylinder
2
Exhaust Valve
Exhaust
Manifold
3
4
Spark
Plug
Piston
Connecting
Rod
Intake Stroke
Intake valve opens,
admitting fuel and air.
Exhaust valve closed
for most of stroke
Crank
Crankcase
Compression Stroke
Both valves closed,
Fuel/air mixture is
compressed by rising
piston. Spark ignites
mixture near end of
stroke.
Power Stroke
Fuel-air mixture burns,
increasing temperature
and pressure, expansion
of combustion gases
drives piston down. Both
valves closed - exhaust
valve opens near end
of stroke
Exhaust Stroke
Exhaust valve open,
exhaust products are
displaced from cylinder.
Intake valve opens
near end of stroke.
ME240/107S: Product Dissection
Parts of an
IC Engine
Name as many
parts as you can
Your name:_________________
CROSS SECTION OF OVERHEAD VALVE FOUR CYCLE SI ENGINE