Economic Policy

and the AD/AS Model
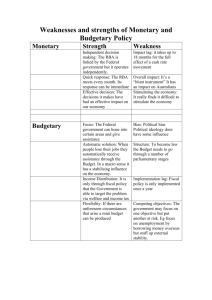
Most economists believe that it takes the economy a decade or longer to self-correct
Economists like Keynes believe in active stabilization , use of government policy to reduce the severity and length of recessions or to rein in excessive expansions
Stabilization Policy: the use of government policy to reduce the severity of recessions and rein in excessively strong expansions.
Negative Demand Shock causes a Recessionary Gap o
Fall in demand is easiest to correct through policy o
Unfortunately, policy measures to increase AD can increase deficits
& may hinder long-run growth
Positive Demand Shock causes an Inflationary Gap o
Government tries to offset positive shocks too, as inflationary gaps have significant costs in the long-run
In both of these situations, the governments goal is to shorten the duration of a recession or inflationary period.
No easy remedy for these, as they result from changes in production costs
A negative supply shock leads to rising prices and decreasing output (& employment)
Policy to fix one of these problems makes the other worse
What if we tackled a negative supply shock by trying to influence AD ?
The government plays a sizable role in the circular flow diagram.
1.
2.
Government Spending o
Like households, the government spends money on goods and services.
o
Can you list some examples?
• Local: police cars in your city
• State: a system of State Parks
• Federal: the military o o
Transfer Payments
The government can also provide transfer payments to some households
Can you list some examples?
• Social Security, Medicare, Medicaid, VA benefits, food stamps, etc.
3 . Tax Collection o o
Like households, the government must collect money in order to pay for this spending, and therefore, must collect taxes.
Can you list some examples?
• Sales tax, income tax, property tax, vehicle registration tax, gas (or liquor or tobacco) excise taxes, tax on corporate profits…
And like households, the government can borrow to make up for a shortfall in tax revenue that does not pay for all of the spending. (Government borrowing will be covered later in the course.)
Government directly controls G, but also indirectly influences C and I through fiscal policy o o
C is based on disposable income, which is directly related to transfers and taxes
• The government can indirectly increase C if it can increase Y d
• How can it increase Y d ?
• By cutting taxes or by increasing transfers
I is influenced by business regulation and tax policy
In a Recessionary Gap, fiscal policy should try to shift AD to the right
Expansionary fiscal policy normally takes one of three forms: o
Increase government purchases of goods and services o o
Increase transfers
Cut taxes
In a Inflationary Gap, fiscal policy should try to shift AD to the left.
Contractionary fiscal policy normally takes one of three forms: o
Reduce government purchases o o
Reduce transfers
Raise taxes
Many economists argue against extremely active stabilization policies
One caution for fiscal policy are time lags
1.
2.
3.
Recognition Lag: the government has to realize that the recessionary gap exists.
Decision Lag: the government has to develop a spending plan.
Implementation Lag: It takes time to spend money.
*After all of these time lags, the economy might have already begun self-correcting back to Y p