Lab 1-2 : Vocabulary
advertisement

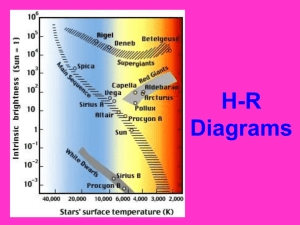
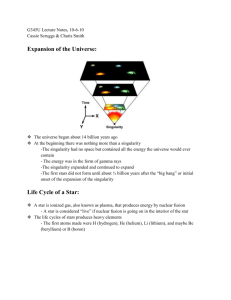
Scientific Method Vocabulary Observation-the act of using the five senses to gather information. Quantitative- analyzing an object using an exact measurement (number). Qualitative- description or distinguishing characteristic about an object Inference/hypothesis- a possible explanation or solution to a problem based on observations. Theory – a well-tested and widely accepted view that explains certain observable facts. • http://vimeo.com/13974273 • http://youtu.be/lhTSfOZUNLo Vocabulary Observation-the act of using the five senses to gather information. Inference- a possible explanation or solution to a problem based on observations. Spectrum – band of various colors of light. Most of what is known about stars comes from spectral studies. There are 3 kinds of visible spectra: Continuous, bright-line and dark-line. Continuous – unbroken band of colors from a source sending out all visible wavelengths. Continuous spectra can come from a (hot) glowing solid, a glowing liquid or a glowing gas (star). Bright-line spectrum – also called an emission spectrum, is a series of unevenly spaced lines of different colors and brightness. Every element has its own unique brightline spectrum, like a fingerprint. Helium emission spectrum Hydrogen emission spectrum Wavelength – the distance between wavecrests (the top of each wave). Frequency – the number of wavelengths in a given distance. Big Bang- theory that all matter and energy in the universe was compressed into an extremely small volume that suddenly began expanding in all directions billions of years ago. Big Bang Briefly http://vimeo.com/5997902 Doppler Effect – apparent shift in the wavelength of energy (sound or light) when emitted by a source moving away from or toward an observer. Stationary Moving Away Moving Toward Lab 3A - Vocabulary H-R diagram (Hertzsprung-Russell); graph showing the temperature and absolute magnitude of a star. Luminosity – the brightness of a star compared to the brightness of the Sun as seen from the same distance. Absolute & Apparent Magnitude • Absolute - the magnitude of a star computed as if viewed from a distance of 32.6 light-years. • Apparent – a star’s brightness as it appears from Earth. The sun APPEARS brighter than the other stars because it is closer to us! H-R Diagram • A chart that shows the relationship between the luminosity and temperature of stars. Characteristics of Stars The temperature of a star is determined by it’s color. BLUE=HOT ; RED=COOL The composition of stars is determined by looking at their emission spectrum. http://sunshine.chpc.utah.edu/labs/star_life/support/HR_animated.swf http://sunshine.chpc.utah.edu/labs/star_life/support/HR_static.swf http://sunshine.chpc.utah.edu/labs/star_life/hr_interactive.html Main Sequence- the 2nd and longest stage in the life cycle of a star. Red Giant–a very large, cool, bright, red star.(3rd stage) White Dwarf – small, hot, dim star. The Life Cycle of Stars THE SUN The Sun Process that generates the sun’s energy: Nuclear Fusion occurs in the Core of the sun. Fusion is the nuclei of hydrogen atoms fusing into helium. This process converts mass into energy. Sunspots- cool, dark areas of gas within the photosphere that are caused by powerful magnetic fields. Solar Flares- a sudden outward eruption of gases. Prominences are huge arches of gas high above the sun’s surface. Auroras (Northern Lights) – magnetic storms in the sky that produce spectacular bands of colored light. Terrestrial Planets – “Earth-like” land/rock planets; 4 planets closest to the sun they are solid, smaller in size and more dense NO LONGER CONSIDERED A PLANET Jovian Planets - like “Jupiter”, 4 outer planets, made of mostly gases, large, and low density • Oblate Spheroid- a slightly flattened sphere • Roundness Ratio- Comparing the polar diameter of a sphere to the equatorial diameter to determine if the object is perfectly round. Zenith -the point on the celestial sphere vertically above a given position or observer