Chapter 4 Vocabulary
advertisement

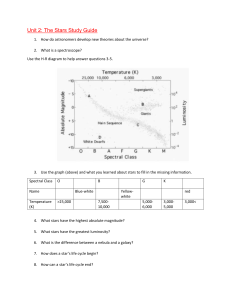
Chapter 4 Vocabulary Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe the moment in time when the universe started to expand out of an extremely hot, dense state big bang the process in which particles of an element collide and combine to form a heavier element fusion a cloud of gas and dust in space, where stars can form nebula the apparent shift in position of an object when viewed from different locations parallax the transfer of energy from place to place by the motion of heated liquid or gas convection a change in the observed frequency of a wave, occurring when the source of the wave or the observer is moving Doppler effect the stage in the life cycle of stars during which stars produce energy by fusing hydrogen and helium main sequence the distance light travels I one year, which is about 9.5 trillion kilometers of 6 trillion miles light-year the outer layer of the Sun’s atmosphere corona the very bright center of a distant galaxy quasar a dense core that may be left behind after a higher-mass star explodes into a supernova neutron star a stream of electrically charged particles that flows out in all directions from the Sun’s corona solar wind a darker, cooler spot on the photosphere sun spot the final stage of an extremely massive star, which is invisible because its gravity prevents any form of radiation from escaping black hole