BLOWIN' IN THE WIND
advertisement

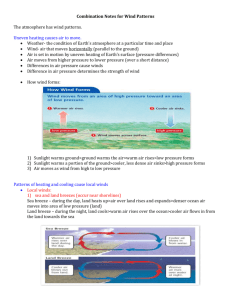
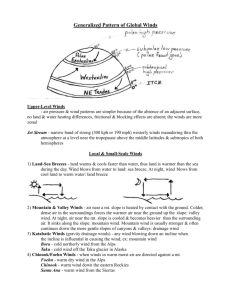
BLOWIN' IN THE WIND temperature differences cause pressure differences which cause the movement of air, wind USA wind map http://hint.fm/wind/ Earth wind map http://earth.nullschool.net/#current/wind/isobaric/10hPa/ortho graphic=-74.14,2.58,303 a wind’s job is to distribute the unequal heating of the earth warm air creates lower pressure cool air creates higher pressure air moves from higher pressure to lower pressure winds are named for the direction in which they come from there are 3 categories of winds: local/regional, global, & episodic (storms) there are 4 types of local/regional winds: land/sea breeze, monsoon, mountain/valley wind, & foehn LAND/SEA BREEZES diurnal wind change on the coast land breeze: at night the land cools down faster, creating a higher pressure and cool winds coming from the land sea breeze: in the day the water heats up slower, creating a higher pressure and cool winds coming from the water MONSOONS seasonal change in wind, Arabic word meaning season in the winter the land cools down faster, creating a higher pressure and dry winds coming from the land in the summer the water heats up slower, creating a higher pressure and wet winds coming from the water MOUNTAIN/VALLEY WINDS diurnal wind change in the mountains due to density differences mountain wind: at night the cooler, more dense air of the mountain falls into the valley valley wind: during the day the air in the valley warms up (low pressure) and rises into the mountains FOEHN extremely warm and dry air that comes down the leeward side of a mountain can evaporate 2 feet of snow and raise the temperature 50 °F in 12 hours chinook “snow eater”, is the local name for a foehn in the Rocky Mountains HW: Read pages 366-373 Answer # 1-3 on page 373 Read page 376 Answer # 5 on page 377 Answer # 21-25 page 387 Read 427-429 Answer # 3, 4 page 429