Nombre Periodo ______ Fecha Nacionalidad Los Apuntes de la
advertisement

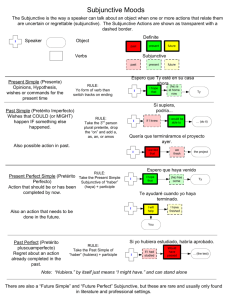
Nombre ________________________________________ Fecha __________________________________________ Periodo ___________ Nacionalidad ____________________ Los Apuntes de la Unidad 2 Etapa 2 I. The Present Subjunctive of the Regular Verbs (pg 136) Remember when you learned to tell someone not to do something using the negative command forms? The same endings are used when you want to express your opinion or point of view using the subjunctive. Modelo: Es importante que uses el transporte público. (It’s important that you use public transportation.) Write the present subjunctive endings below: -ar -er/-ir Remember that you must use the yo form of the verb and drop the –o and then add the subjunctive endings. Also some verbs change the spelling to keep the pronunciation the same. -car verbs __________________ -gar verbs __________________ -zar verbs __________________ -ger verbs __________________ buscar busque pagar pague cruzar cruce recoger recoja II. The present subjunctive of Irregular Verbs (pg 138) You have already learned to form the subjunctive of regular verbs to express your opinion or point of view. Some verbs have irregular forms in the subjunctive. Fill out your t-charts for each verb below. Dar Estar Ir Saber Ser Verbs with yo forms that end in –go or zco in the present indiciative use the same irregular stem in the subjunctive. Decir Digo Conocer Conozco Other verbs like these are: caer, hacer, oír, salir, venir, tener, traer, ofrecer III. The Present subjunctive of stem-changing verbs (pg 139) When you use the present subjunctive of –ar and –er stem changing verbs, remember to make the same stem changes as in the present indiciative. Notice that –ir verbs change their stems differently. The stem change of an e ie stem changer is changed to ie in the boot, but outside the boot it changes to i. The stem change of an o ue stem changer is changed to ue in the boot, but outside the boot it changes to u. If it is an e i stem change, it changes to an i in all forms. IV. The Present Perfect Subjunctive (pg. 141) You have already learned how to form the present perfect in the indicative. Remember it is the present tense of haber + the past participle of the verb which is the –ado or –ido form of the verb. The subjunctive also has a present perfect. To form it you use the present subjunctive of haber + past participle. Present Subjunctive of Haber To form the past participle drop the –ar and put ado and for –er/-ir verbs put ido. You use the present perfect subjunctive to indicate that the action of the subordinate clause took place in the past. Compare the following sentences. Present Subjunctive: Es possible que Juan visite Mitla. (It’s possible that Juan is visiting/will visit Mitla.) Present Perfect Subjunctive: Es possible que Juan haya visitado Mitla. (It’s possible that Juan has visited Mitla.) Present Subjunctive: Es bueno que hagas eso. (It’s good that you’re doing/ will do that.) Present Perfect Subjunctive: Es bueno que hayas hecho eso. (It’s good that you’ve done/ you did that.) Notice how the meanings of two subjunctives contrast with each other