Chalkboard Lesson
advertisement

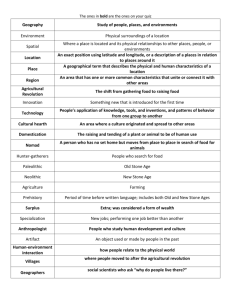
Chalkboard Lesson Era 1 The Beginnings of Human Society Blueprint Skill: History Grade 6 • Recognize major historical time periods (i.e., Early Civilizations, Classical Period, Dark Ages, Middle Ages, and Renaissance). • Era 1 MAIN MENU BACK NEXT Blueprint Skill: History Grade 6 MAIN MENU BACK NEXT Main Menu Agricultural Revolution Humanity’s Story The Stone Age The Peopling of the Earth Ages Humanity’s Story • So far as we know, humanity’s story began in Africa. • For millions of years it was mainly a story of biological change. • Then some hundreds of thousands of years ago our early ancestors began to form and manipulate useful tools. MAIN MENU BACK NEXT Humanity’s Story • Eventually they mastered speech. • Unlike most other species, early humans gained the capacity to learn from one another and transmit knowledge from one generation to the next. MAIN MENU BACK NEXT Humanity’s Story • • The hunter-gatherer society lived in clans and were nomadic Nomadic groups were people who have no fixed home and move according to the seasons from place to place in search of food, water, and grazing land. MAIN MENU BACK NEXT Humanity’s Story • Archaeologists have found the remains of what may have been the first tools used by humans in East Africa. MAIN MENU BACK NEXT Humanity’s Story • Stone tools were the most common tools until about 12,000 years ago. Flint Tools MAIN MENU BACK NEXT The Stone Age • The period of time when people used simple stone tools is called the Old Stone Age or Paleolithic Era. • During the Old Stone Age, people also learned to make fire. MAIN MENU BACK NEXT The New Stone Age • The period of time when people began to settle permanently in one location is called the Neolithic Era, or the New Stone Age. • In the Paleolithic age, men were hunters and gathers. In the Neolithic age, people became scavengers, herders, farmers, or producers. MAIN MENU BACK NEXT The New Stone Age • People were able to live in larger groups. • They learned to domesticate plants and animals. • This meant they also learned which plants provided a higher yield and how to breed animals to better suit their needs. MAIN MENU BACK NEXT Ages • 2.5 million to 8000 BCE Paleolithic - old stone age (cave art, fire, hominids (earlier human like creatures), stone tools, nomads, hunters and gathers) • B.C. - the time period before Jesus was born MAIN MENU BACK NEXT Ages • 8,000 BCE to 3,000 BCE Neolithic new stone age (looms for weaving, domesticate animals, agriculture, people shifted from hunting and gathering to agriculture and herding) • Age of the Earth - 4 to 5 billion years MAIN MENU BACK NEXT Ages • Mesolithic Age - created pottery • Ice Age - long period of cold climate • Stonehenge - archaeological site begun in the Neolithic Age and completed in the Bronze Age • PREHISTORY - time before written history MAIN MENU BACK NEXT The Peopling of the Earth • The first great global event was the peopling of the earth and the astonishing story of how communities of hunters, foragers, or fishers adapted creatively and continually to a variety of contrasting, changing environments in Africa, Eurasia, Australia, and the Americas. MAIN MENU BACK NEXT The Peopling of the Earth • Anthropology - the study of the remains/skeletons/bones of people • Archaeologists - people who study things USED by people who lived a long time ago; eating utensils, houses, tools MAIN MENU BACK NEXT The Peopling of the Earth • Archaeology - the study of things used by people who lived a long time ago; tools, eating utensils, homes • Culture – the ideas, beliefs, and customs of a group of people. MAIN MENU BACK NEXT The Agricultural Revolution • Over a period of several thousand years and as a result of countless small decisions, humans learned how to grow crops, domesticate plants, and raise animals. • The earliest agricultural settlements probably arose in Southwest Asia, but the agricultural revolution spread round the world. MAIN MENU BACK NEXT The Agricultural Revolution • Human population began to soar relative to earlier times. • Communities came into regular contact with one another over longer distances, cultural patterns became far more complex, and opportunities for innovation multiplied. MAIN MENU BACK NEXT The Agricultural Revolution • One reason people migrated from place to place was the search of food. MAIN MENU BACK NEXT The Agricultural Revolution • Early man developed farming and herding because it provided a reliable source of food, man was not as dependent on nature and man was no longer nomadic. MAIN MENU BACK NEXT The Agricultural Revolution • Early man’s crops consisted of wheat, potatoes, rice and maize MAIN MENU BACK NEXT The Agricultural Revolution • The earliest known permanent agricultural community was established in: Mesopotamia near the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. MAIN MENU BACK NEXT The Agricultural Revolution • The development of agriculture took place during the Neolithic Age. MAIN MENU BACK NEXT Resources • World History Standards MAIN MENU BACK NEXT Test your knowledge of Era 1! Chalkboard Challenge Game MAIN MENU BACK NEXT