Ocean Circulation
advertisement

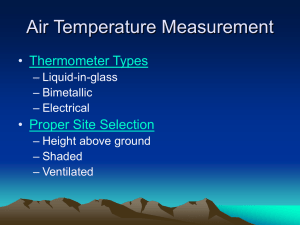
Ocean Circulation Currents Currents • Horizontally • Vertically The Forces That Drive Currents • Primary forces – Starts water movement and determine its velocity • Stress of wind • Secondary forces – Influence the direction and nature of flow • • • • Coriolis effect gravity friction shape of ocean basins Surface currents • Wind • Surface currents – rapid with well defined boundaries – slow and diffuse – horizontal or vertical • Gyre Bottom Currents • Driven by the force of gravity - dense water sinks and less dense water rises Flow within a Gyre • North Atlantic gyre – Four inter connected currents • Eckman spiral • Eckman transport Geostrophic Gyres • Geostrophic Gyre – 5 Geostrophic gyre • North Atlantic gyre • South Atlantic gyre • North Pacific gyre • South Pacific gyre • Indian Ocean gyre – Geostrophic gyres independent of each other in each hemisphere • Geostrophic currents • 6 current circuits in the world ocean – 2 in Northern hemisphere 4 in southern hemisphere Currents within Gyres • Western boundary Currents • Eastern Boundary Currents • Transverse currents Western Boundary Currents • Fastest and deepest • Found at the western boundaries of the Ocean basins • Narrow • Move warm water poleward in each gyre Western boundary currents • Five western boundary currents – – – – – Gulf stream Japan or Kuroshio current Brazil current Agulhas current East Australian current • Sverdrup • Eddies – Cold core eddies – Warm core eddies Eastern Boundary Currents • • • • • The Canary Current The Benguela Current California Current West Australian Current The Peru or Humboldt Current Eastern Boundary Currents • • • • Carry cold water equatorward Shallow and broad Boundaries not well defined Eddies tend not to form Westward Intensification • The converging flow of the trade winds on either side of equator • The rotation of the earth Transverse Currents • Currents that flow from east to west – Linking the eastern and western boundary currents • Counter Currents • Under Currents Exceptional Surface Currents • Monsoon Currents • High Latitude Currents Effects of Surface Currents on Climate • Distribute tropical heat • Influences climate and weather Wind-Induced Vertical Circulation • Upwelling – Equatorial upwelling – Coastal upwelling • Downwelling Langmuir Circulation (page 222 fig 9.16) • Langmuir Circulation El Nino Thermohaline Circulation • Density driven Water Masses • Five common water masses – – – – – Surface water Central water Intermediate water Deep water Bottom water Formation and downwelling of Deep water • Antarctic bottom water • North Atlantic deep water Thermohaline Circulation Patterns • Low and mid latitudes • Caballing • Contour currents Studying Currents • Float method • Flow method • Acoustical Tomography