Emotion
advertisement

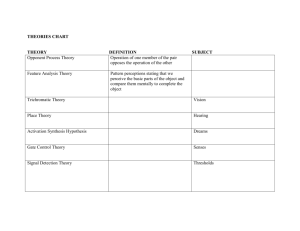
Arousal and Emotion 1 High Arousal Arousal response - pattern of physiological change that helps prepare the body for “fight or flight” muscles tense, heart rate and breathing increase, release of endorphins, focused attention can be helpful or harmful in general, high arousal is beneficial for instinctive, well-practiced or physical tasks and harmful for novel, creative, or careful judgment tasks 2 Some arousal is necessary High arousal is helpful on easy tasks As level of arousal increases, quality of performance decreases with task difficulty Too much arousal is harmful Quality of performance Yerkes-Dodson Law Easy task Moderately difficult task Very difficult task Degree of arousal 3 Concept of Emotion A class of subjective feeling elicited by stimuli that have high significance to an individual stimuli that produce high arousal generally produce strong feelings are rapid and automatic emerged through natural selection to benefit survival and reproduction 4 Theories of Emotion Common-Sense Theory Stimulus Perception Emotion (Tiger) (Interpretation of stimulus-danger) (Fear) Bodily arousal (Pounding heart) Common sense might suggest that the perception of a stimulus elicits emotion which then causes bodily arousal 5 James’s Peripheral Feedback Theory James’s Theory Stimulus (Tiger) Perception (Interpretation of stimulus-danger) Bodily arousal Emotion (Fear) (Pounding heart) perception of a stimulus causes bodily arousal which leads to emotion 6 Schachter’s CognitionPlus-Feedback Theory Schachter’s Theory Stimulus (Tiger) Bodily arousal Perception (Interpretation of stimulus-danger) (Pounding heart) Emotion (Fear) Type Intensity Perception and thought about a stimulus influence the type of emotion felt Degree of bodily arousal influences the intensity of emotion felt 7 Ekman’s Facial Feedback Theory Each basic emotion is associated with a unique facial expression Sensory feedback from the expression contributes to the emotional feeling 8 1.80 1.80 1.60 1.60 Average anger score Average happiness score Ekman’s Facial Feedback Theory 1.40 1.20 1.00 0.80 0.60 0.40 0.20 0.00 1.40 1.20 1.00 0.80 0.60 0.40 0.20 0.00 Frown Smile Facial expression Frown Smile Facial expression Facial expressions have an effect on self-reported anger and happiness 9 Heart rate change (beats per minute) Temperature change (degrees C) Ekman’s Facial Feedback Theory (a) (b) Facial expressions can produce effects on the rest of the body 10 Brain-Based Theory of Emotions Amygdala evaluate the significance of stimuli and generate emotional responses generate hormonal secretions and autonomic reactions that accompany strong emotions damage causes “psychic blindness” and the inability to recognize fear in facial expressions and voice 11 Brain-Based Theory of Emotions Frontal lobes influence people’s conscious emotional feelings and ability to act in planned ways based on feelings (e.g., effects of prefrontal lobotomy) Frontal Parietal Occipital Temporal left frontal lobe may be most involved in processing positive emotions right frontal lobe involved with negative emotions 12