lec
advertisement
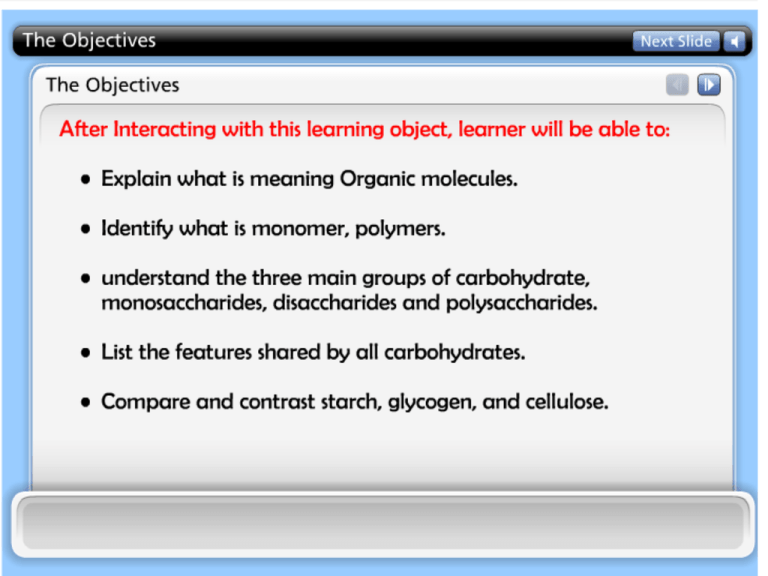
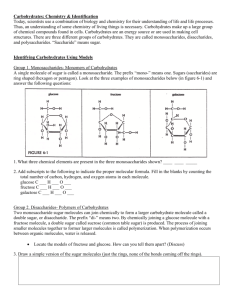
II- Organic molecules • Organic molecules are those that: 1) formed by the actions of living things. 2) have a carbon backbone. • Each organic molecule group has small molecules (monomers) that are linked to form a larger organic molecule (macromolecule). • Monomers can be joined together to form polymers that are the large macromolecules made of three to millions of monomer subunits. (Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins and nucleic acids) Mono-mer Di-mer Poly-mer Polymer is a long molecule consists of a chain of similar building molecules (monomers) covalently bounded together. Polymer can be built up by linking its monomers by dehydration (removing H2O). Polymer can be broken down to its monomers by hydrolysis (adding H2O). 1- Carbohydrates Fuel and Building Material 1.Sugars, the smallest carbohydrates, are fuel and carbon sources. 2.Polysaccharides, the polymers of sugars, have storage and structural functions 1- Carbohydrates Fuel and Building Material • Monosaccharides, are the simplest carbohydrates (simple sugars). • Disaccharides, double sugars, consist of two monosaccharides joined by dehydration. • Polysaccharides, are polymers of many monosaccharides. 1- Monosaccharides Hexose Sugar Pentose Sugar Triose Sugar H O H O C H H H C OH H C OH H Glyceraldehyde H H C OH C OH C C OH OH H Ribose OH C C H H C O OH C H H C OH H C OH H C OH H Fructose 2- Disaccharides 1- Maltose 2(C6H12O6) 2 Glucose C12H22O11 Maltose + H2O 2- Lactose (milk sugar): consists of Glucose + Galactose. 3- Sucrose (table sugar): consists of Glucose + Fructose. 3- Polysaccharides • Consisted of few hundreds to few thousands of monosaccharides. They are two types: 1- Storage: Provide sugar for cell by hydrolysis. 2- Structural : Serve as building materials for the organism. A)- Storage Polysaccharides I- Starch (in plants) A storage polysaccharide of plants (within plastids).• It is consisted of thousands of glucose molecules.• Potatoes and grains are the major source of starch. • II- Glycogen (in animals) Stored in animal cells (e.g. liver and muscle cells in Human).• It is consisted of thousands of glucose molecules.• B)- Structural Polysaccharides I- Cellulose • It is the building material of plants (cell wall). • It is consisted of thousands of β glucose molecules. • Human cannot digest it, but some bacteria and protozoa can (e.g. in Termites and Cows stomach). II- Chitin • It is the building material of the cuticle in insects. • It is consisted of thousands of glucose molecules with a N atom in one end. • It is used to manufacture the surgical threads. The Summary Carbohydrates No. of C atoms Triose (3C) Glyceraldehyde Pentose (5C) Ribose Monosaccharides Glucose & Fructose No. of sugar molecules Hexose (6C) Glucose Disaccharides Maltose & Sucrose Storage Starch (in plants) & Glycogen (in animals) Polysaccharides Structural Cellulose (in plants) & Chitin (in insects)