click - Uplift Education
advertisement

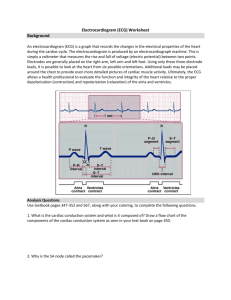
Heart & Blood Vessel Guided Notes Name:__________________________ Do Now Write down 1-3 questions about how your heart works. Cardiovascular System What is the major function of the cardiovascular system? What is the heart’s role in this system, and what are the other major components? Heart Size and Location Describe the heart size, location, and tilt. Heart Layers. Describe the location and function of the three layers. Pericardium – What is pericarditis? Myocardium – Endocardium – Cardiac circulation Cardiac vessels cover the outer surface of the heart and supply the heart muscle itself with blood. Heart disease (___________________________) occurs when the aorta or cardiac arteries Heart Anatomy (Frontal Section) The heart is a double pump • The ____________________ of the heart receives ________________________________________ ________________________________________ and pumps it to the _____________________ ________________________________________ • The ______________________ of the heart receives _________________________________________ _________________________________________ and pumps it to the _____________________ ______________________________________ The heart has four chambers Each side has an ___________________________________________________ and a _____________ ____________________________________________________________ Blood collects in atria while ventricles contract. Then, as ventricles relax, atria contract slightly and ventricles refill. Two sides of heart contract and relax simultaneously. Flow of Blood Use the diagram to determine the flow of blood through the heart and body. Vena cava Vena cava The walls of the ventricles are much thicker than that of the atria? Why? Look at the diagram – how does the left ventricle differ from the right? What is the reason for the difference? Heart valves ensure unidirectional flow of blood valves (tricuspid and mitral) • hang open when the ventricles are filling • forced closed when the ventricles contract • Anchored by ___________________________ Prevent backflow from ____________________ to ______________________________ _________________________________ (pulmonary and aortic) • forced open when ventricles contract • closed when ventricles relax Prevent backflow from ______________________ to _____________________ In what stage of the cardiac cycle is the heart shown above? How do you know? Heart Sounds Normal hearts make the sound: LUB-dup LUB-dup LUB-dup The “LUB” is caused by the closing of the _________________________________. The “dup” is caused by the closing of the _________________________________. Heart murmurs are __________________________heart sounds. • In children, these are often benign. • In adults, they usually indicate a problem – often, the _____________________________________ _______________________________________. Why is it a problem if the valves don’t function properly? ECG and the Heart’s Internal Conduction System Guided Notes Do Now What is an action potential and where do they occur? Intrinsic conduction system _______________ is the heart’s natural pacemaker. ◦ Impulse travels throughout the ____________ and to the ________________ ◦ _______________________________________ _______________________________to allow atria to finish contracting The ______________ (aka bundle of His) transmits the impulse to the _______________________ and ______________________________________. Interestingly, all the cells of the conduction system are _______________________________. That is, all will depolarize at a certain rate. The __________________ has the fastest rate of depolarization, though, so it sets the pace for the entire heart. What is the function of - AV node - Gap junctions Travels cell-to-cell through __________ _________________ in intercalated discs – another unique feature of cardiac muscle ◦ Quick Review – Intrinsic Conduction System It depolarizes ~75 times / min, to start each heartbeat. ◦ These bundles and fibers speed the transmission of the impulse throughout the ventricles, to coordinate ventricular contraction - SA node - Purkinje fibers Name 3 differences between cardiac and skeletal muscle contraction & explain why each is important to cardiac function. ECG An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) records the electrical current through the heart. A normal ECG has three distinct waves: ◦ P wave – atrial depolarization ◦ QRS complex – ventricular depolarization AND atrial repolarization ◦ T wave – ventricular repolarization ECG Questions What is responsible for the delay between P wave and QRS complex? What is responsible for the delay between T wave and next P wave? Examine this normal ECG. When would the ventricles be in systole? When would they be in diastole? When would the heart sounds occur, and what do the heart sounds correspond to? ECG abnormalities Examine these ECG readouts, and identify how they differ from a normal ECG. a) b) c) d) Descriptors – Name AV block Atrial fibrillation Tachycardia Bradycardia Characteristic ECG In severe cases, there is NO relationship between P waves and QRS complex. QRS still occurs due autorhythmic cells in AV node, but at a slower rate. Wavy baseline, no regular p waves QRS normal shape but occurs randomly Looks messy Heart beats faster than normal (more than 100 bpm) Heart beats slower than normal (less than 60 bpm) Cause(s) Damage to AV node, such as from reduced blood flow (ischemia) or fibrosis. Treatment: dual chamber artificial pacemaker- one that ‘listens’ to the SA node and sends a signal to the AV node Heart is doing uncoordinated, ineffective contraction due to lack of blood, excess alcohol, or infection Exercise, drugs Many conditions, including heart damage, medications, etc, Regulation of Heart Rate Earlier, we said that the SA node depolarizes at a rate of ~75 beats per minute, and that this acts as a pace maker for heart contraction. Does this mean our hearts always beat at ~75 bpm? What are the two branches of the autonomic nervous system, and how do they affect heart rate? Other factors that influence heart rate Age (fastest in fetus, young children) Gender (faster in females) Temperature (faster in heat) Exercise (faster with exercise) Ions imbalances & medicines (faster or slower) Weak / damaged heart (can be either faster / slower) Blood Vessels Types of Blood Vessels Draw a cycle that shows how blood flows through the heart and blood vessels. Blood Vessel Tunics All vessels except capillaries have three layers, or tunics Capillaries have a single layer of epithelial cells Different vessels differ in the thickness and adaptations of each tunic. Comparison of the blood vessels Explain the function of each special feature Blood vessel micrograph Which is which? How can you tell? How does blood return to the heart? Muscular pump Respiratory Pump How does the muscular pump work? How does the respiratory pump work? Capillary Bed What is the difference between the vascular shunt and a true capillary? What is the function of the precapillary sphincters?