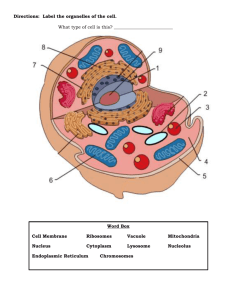
CYTOPLASMIC ORGANELLES
advertisement

CELL STRUCTURE NOTES The following are the main structural components of cells. Fill in the blanks during the PowerPoint slide show. Then learn their names and the function of each of them: CELL MEMBRANE 1. Cell Membrane: a. Found in all cells. b. Composed of two layers of lipid molecules known as the __________ ________________________ Since these molecules don’t mix well with _______________________, they help to control the movement of water in and out of cells. c. Embedded within the lipid bilayer are _________________________. They serve as channels allowing water and other substances to get in and out. d. _______________________________________ molecules are often found near the protein channels and they help to identify substances. They function like chemical _________________________________, so that only certain things are permitted to enter the cell. 2. Cell Wall: a. Found only in ____________________________________________. b. The cell wall gives support to the plant cells. Continued on the back page 1 c. One of the molecules making up the cell wall is _________________. Cellulose is very porous and elastic. Large plants, like trees, have another molecule, ___________________________, in their cell walls. Together, cellulose and lignin give a great deal of support to the tree. d. Finally, __________________ is a sticky substance found on the outside of the cell walls. It acts like a glue, helping to keep the cell walls together. NUCLEUS 1. Nuclear Envelope (Membrane): a. Found only in ________________________ cells (plants and animals) b. This structure acts very much like the cell membrane. It has pores in it that regulates what can enter and leave the nucleus. 2. Nucleolus: a. Also found only in eukaryotic cells. b. The nucleolus assists in manufacturing ________________________, an organelle that makes proteins. Since proteins are the most important group of molecules in your body, controlling the production of ribosomes has the effect of controlling what proteins are made. This in turn controls the function of the entire cell. 3. Chromatin: a. Found in all cells. b. Chromatin, which sometimes condenses into structures called ___________________________________, is made up of _________ and ______________________________. c. DNA carries the genetic code, the set of instructions which tells the cell what to do. 2 d. Chromatin also plays an important part in passing on genetic information to future generations. CYTOPLASM Found in all cells, the cytoplasm is defined as the area between the _____________ and the __________________________________________. Found within the cytoplasm are various organelles: Organelles that Capture and Release Energy: 1. Mitochondria: a. Found in both plant and animal cells. b. Known as the “_______________________________” of the cell. The mitochondria change the chemical energy stored in food particles into a more useful form of energy through a process known as ___________________________________________. c. Mitochondria have two membranes. The inner membrane has many folds to increase its surface area. The more mitochondria a cell contains, the more _____________________________ it can produce. d. Mitochondria contain their own small ____________ molecules, all of which, in humans, was inherited only from your _________________. 2. Chloroplasts: a. Found only in plant and algae cells. b. Similar in structure to the mitochondrion, chloroplasts trap the energy in sunlight and converts it to chemical energy (________________________________). c. Chloroplasts also contain a small amount of ___________________. Organelles that Build Proteins: 3. Ribosomes: a. Found in both plant and animal cells. 3 b. Ribosomes are the structures in which ________________________ are made. c. Some ribosomes are floating free in the cytoplasm, while other ribosomes may be attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. 4. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): a. Found in both plant and animal cells. b. The ER is the organelle where components of the _______________ ___________________________ and some ___________________ are assembled. It also assists with ___________________________ within the cells. c. There are two types of ER: _________________________________. Rough ER has ribosome’s stuck to it. 5. Golgi Apparatus: a. Found in both plant and animal cells. b. Resembling a stack of pancakes, the Golgi Apparatus attaches _____________________________ and _______________________ to _______________________________. This helps to improve the function of these molecules. Organelles that Store, Clean Up, and Support: 6. Lysosomes: a. Found only in _________________________ cells, not in plant cells. b. Lysosomes are responsible for __________________________ ___________________________________________________ c. 7. Produced by the Golgi Apparatus, lysosomes also break down organelles that are no longer functioning or needed. Think of them as the _______________________________________ of the cell! Vacuoles: a. Found in all cells, but particularly large in plant cells. 4 b. Vacuoles are ____________________________________ containers in the cell. They store water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates. c. In many plant cells, a large vacuole, filled with __________________, can be found. This helps to give support to the cell and the plant 8. Plastids (Vesicles): a. Found only in plants. b. Chloroplasts, which were discussed earlier, are one form of plastids. Many plastids store ________________________________________. c. Leukoplasts, found in potatoes, store _________________ molecules. d. Chromoplasts store pigment molecules. The red color found in ____________________________ comes from pigments found in the chromoplasts. 9. Cytoskeleton: a. Found in both plant and animal cells. b. The cytoskeleton is made of a variety of filaments and fibers that supports the cell or helps it to move about. c. There are two main parts of the cytoskeleton: 1. Microtubules: a. These are hollow tubes made of ____________________. They provide support for the cell’s shape and form the centrioles. b. Centrioles are found in animal cells, but not in plant cells. They play an important role in _____________________. c. In some cells, the microtubules form cilia or flagella. ___________________ are short, thread-like structures found around the outside of the cell. They serve like little 5 legs (like on a millipede) that helps the cell move. _________________________________ are longer whip-like structures. They serve like a tail that whips back and forth, moving the cell along. 2. Microfilaments: a. These are long, thin fibers found in the cytoplasm. b. They help ____________________________________ ____________________________________________ 6