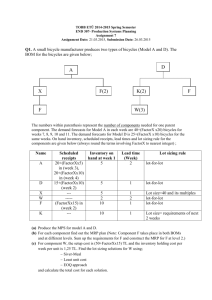
All – Definition of derived demand and MRP, Diagram for
advertisement

Learning objective: Demand for labour what is MRP? Outcomes – All – Definition of derived demand and MRP, Diagram for MRP Most - analysis of diagram-Explain results of experiment Some - Who uses MRP? - Explain Starter – Read article – List factors influencing S&D of labour End Learning objective: Demand for labour what is MRP? Outcomes – All – Definition of derived demand and MRP, Diagram for MRP Most - analysis of diagram-Explain results of experiment Some - Who uses MRP? - Explain Objective – To know - What are the determinants of elasticity of demand for labour Learning objective: What is derived demand and MRP? Outcomes – All – Definition of derived demand and MRP, Diagram for MRP analysis of diagram-Explain Some - Who uses MRP - Explain Learning objective: Demand for labour what is MRP? Outcomes – All – Definition of derived demand and MRP, Diagram for MRP Most - analysis of diagram-Explain results of experiment Some - Who uses MRP? - Explain Past paper Q - June 2002 4. (a) Explain the factors which determine the marginal’s revenue product of labour [10] (b) Discuss the extent to which marginal revenue product is the crucial factor in explaining why top soccer players earn so much more than waiters and waitresses [15] REMEMBER Q’S ARE NOW Q 15 AND 20 MARKS! Learning objective: Demand for labour what is MRP? Outcomes – All – Definition of derived demand and MRP, Diagram for MRP Most - analysis of diagram-Explain results of experiment Some - Who uses MRP? - Explain The demand for labour is a derived demand. Firms only demand employees because of the demand for actual products. We only want you for your output Increase in output Increase in demand for labour Learning objective: Demand for labour what is MRP? Outcomes – All – Definition of derived demand and MRP, Diagram for MRP Most - analysis of diagram-Explain results of experiment Some - Who uses MRP? - Explain People are employed because of the value of their output. This depends on: – The extra output that each extra worker produces (Marginal Product /marginal physical product) MP – The extra revenue this extra worker generates when it is sold (Marginal Revenue) MR the value of the output produced by an extra worker is called the Marginal Revenue Product (MRP) MRP=MPxMR Learning objective: Demand for labour what is MRP? Outcomes – All – Definition of derived demand and MRP, Diagram for MRP Most - analysis of diagram-Explain results of experiment Some - Who uses MRP? - Explain Assumptions: Labour is the only variable factor of production Labour is homogeneous- labour cannot dictate price The labour market is perfectly competitive so no one employer can influence the wage rate The firm operates in a perfectly competitive product market DOES THIS EXIST IN REALITY? Learning objective: Demand for labour what is MRP? Outcomes – All – Definition of derived demand and MRP, Diagram for MRP Most - analysis of diagram-Explain results of experiment Some - Who uses MRP? - Explain MRPWhy does it slope? Learning objective: Demand for labour what is MRP? Outcomes – All – Definition of derived demand and MRP, Diagram for MRP Most - analysis of diagram-Explain results of experiment Some - Who uses MRP? - Explain The demand for labour is downward sloping due to the law of diminishing returns, which states: As successive units of a homogeneous variable factor of production are added to a fixed factor, the increments to total output will rise first and then eventually diminish, ceteris paribus. Learning objective: Demand for labour what is MRP? Outcomes – All – Definition of derived demand and MRP, Diagram for MRP Most - analysis of diagram-Explain results of experiment Some - Who uses MRP? - Explain 1. Get into two/three teams – You will be in charge of making burgers2. Nominate 1 person to cut shapes- no one can help them – the rest of you keep count of productivity 3. To make a burger you have to cut out from the template and then transport and stick up for sale using your blue tack onto the flip chart paper, starting at month 1. 4. You start when told and finish when told (2 mins)-only finished burgers counted Learning objective: Demand for labour what is MRP? Outcomes – All – Definition of derived demand and MRP, Diagram for MRP Most - analysis of diagram-Explain results of experiment Some - Who uses MRP? - Explain Firm sells Number Total of output workers products for £2 Wage rate is 1 constant at £10 2 1. Fill in Gaps 2. How many workers should they employ? 3 4 5 6 Marginal Product MP Marginal revenue MR Marginal Revenue Product MRP Total Revenue Learning objective: Demand for labour what is MRP? Outcomes – All – Definition of derived demand and MRP, Diagram for MRP Most - analysis of diagram-Explain results of experiment Some - Who uses MRP? - Explain Learning objective: Demand for labour what is MRP? Outcomes – All – Definition of derived demand and MRP, Diagram for MRP Most - analysis of diagram-Explain results of experiment Some - Who uses MRP? - Explain Learning objective: Demand for labour what is MRP? Outcomes – All – Definition of derived demand and MRP, Diagram for MRP Most - analysis of diagram-Explain results of experiment Some - Who uses MRP? - Explain Learning objective: Demand for labour what is MRP? Outcomes – All – Definition of derived demand and MRP, Diagram for MRP Most - analysis of diagram-Explain results of experiment Some - Who uses MRP? - Explain Learning objective: Demand for labour what is MRP? Outcomes – All – Definition of derived demand and MRP, Diagram for MRP Most - analysis of diagram-Explain results of experiment Some - Who uses MRP? - Explain Learning objective: Demand for labour what is MRP? Outcomes – All – Definition of derived demand and MRP, Diagram for MRP Most - analysis of diagram-Explain results of experiment Some - Who uses MRP? - Explain Learning objective: Demand for labour what is MRP? Outcomes – All – Definition of derived demand and MRP, Diagram for MRP Most - analysis of diagram-Explain results of experiment Some - Who uses MRP? - Explain Learning objective: Demand for labour what is MRP? Outcomes – All – Definition of derived demand and MRP, Diagram for MRP Most - analysis of diagram-Explain results of experiment Some - Who uses MRP? - Explain 1. Nominate 1 person to cut shapes- no one can help them – the rest of you keep count of productivity 2. To make a burger you have to cut out from the template and then transport and stick up for sale using your blue tack onto the flip chart paper, starting at month 1. 3. You start when told and finish when told (2 mins)-only finished burgers counted End Learning objective: Demand for labour what is MRP? Outcomes – All – Definition of derived demand and MRP, Diagram for MRP Most - analysis of diagram-Explain results of experiment Some - Who uses MRP? - Explain How did you get on? What fresources/factors are represented in the game so far?) 1. Total up your sheet then2. Nominate another person – 1 to cut and one to stick shapes no one can help them – the rest of you keep count of productivity 3. You start when told and finish when told (2 mins)-only finished burgers counted End Learning objective: Demand for labour what is MRP? Outcomes – All – Definition of derived demand and MRP, Diagram for MRP Most - analysis of diagram-Explain results of experiment Some - Who uses MRP? - Explain How did you get on? Did you do better? What economic key terms were we proving 1. Total up your sheet then2. Nominate another person (3 now) – 1 to cut and one to stick shapes no one can help them – the rest of you keep count of productivity 3. You start when told and finish when told (2 mins)-only finished burgers counted End Learning objective: Demand for labour what is MRP? Outcomes – All – Definition of derived demand and MRP, Diagram for MRP Most - analysis of diagram-Explain results of experiment Some - Who uses MRP? - Explain How did you get on? Did you do better? Total up your sheet then1. Nominate another person (4 now) – 1 to cut and one to stick shapes no one can help them – the rest of you keep count of productivity 2. You start when told and finish when told (2 mins)-only finished burgers counted End Learning objective: Demand for labour what is MRP? Outcomes – All – Definition of derived demand and MRP, Diagram for MRP Most - analysis of diagram-Explain results of experiment Some - Who uses MRP? - Explain Task How much labour to employ? Draw your data into a graph showing your results Then COMMENT on the diagram using economic terms. Wage Rate W MCL MRP Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Quantity of Labour Learning objective: Demand for labour what is MRP? Outcomes – All – Definition of derived demand and MRP, Diagram for MRP Most - analysis of diagram-Explain results of experiment Some - Who uses MRP? - Explain Profit maximising level of employment occurs where MCf = MRP MCL = Supply of Labour MRP = MPP x P = Demand for Labour Learning objective: Demand for labour what is MRP? Outcomes – All – Definition of derived demand and MRP, Diagram for MRP Most - analysis of diagram-Explain results of experiment Some - Who uses MRP? - Explain How do we measure the productivity of workers in the service sector, eg teacher, supermarket cashier, nurse, secretary? Is there a price that can be put on all workers’ output? MRP theory requires us to assume we can measure the output of each worker. In reality job evaluation is required to set performance targets Learning objective: Demand for labour what is MRP? Outcomes – All – Definition of derived demand and MRP, Diagram for MRP Most - analysis of diagram-Explain results of experiment Some - Who uses MRP? - Explain MRP is difficult to measure as difficult to isolate: Individuals contribution when working in a team Contribution made by labour & Capital Difficult to measure the Marginal Product of some workers in the tertiary sector e.g. surgeons 5 hip replacements vrs 1 heart/lung transplant Learning objective: Demand for labour what is MRP? Outcomes – All – Definition of derived demand and MRP, Diagram for MRP Most - analysis of diagram-Explain results of experiment Some - Who uses MRP? - Explain Knowledge of the MRP curve will let us work out how many workers will be employed but doesn’t tell us how the wage rate is determined. Wage levels depend upon the interaction of demand and supply of labour ONLY WORKS IN PERFECT COMP – I.E. A MODEL! Learning objective: Demand for labour what is MRP? Outcomes – All – Definition of derived demand and MRP, Diagram for MRP Most - analysis of diagram-Explain results of experiment Some - Who uses MRP? - Explain What might cause the demand for labour to shift from DL1 to DL2? 1. Increase in Productivity 2. Increase in demand for the product 3. Increase in the price of the product 4. Increase in the price of capital DL2 DL1 Learning objective: Demand for labour what is MRP? Outcomes – All – Definition of derived demand and MRP, Diagram for MRP Most - analysis of diagram-Explain results of experiment Some - Who uses MRP? - Explain Task 1 - complete exercise 7.1 on Labour market equilibrium – (2 minutes) (Draw diagram showing analysis of the effects on labour market equilibrium if there is a fall in selling price of a firms product Then - “What does it depend on?” Learning objective: Demand for labour what is MRP? Outcomes – All – Definition of derived demand and MRP, Diagram for MRP Most - analysis of diagram-Explain results of experiment Some - Who uses MRP? - Explain Plenary Who uses MRP? What are the factors discussed today? What is most important and WHY?