Foundations Syllabus Marnix Francot
advertisement

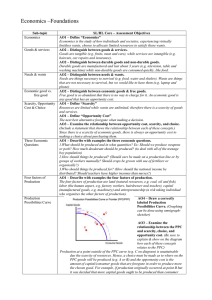
Economics –Foundations Sub-topic Economics Goods & services SL/HL Core – Assessment Objectives AO1 – Define “Economics” Economics is the study of how scare resources are allocated to fulfill the infinite wants of consumers. AO2 – Distinguish between goods & services. Goods are things or objects which can be given out and service is things done in order to give out the goods. AO2 – Distinguish between durable goods and non-durable goods. Durable goods are things that are very strong and non-durable goods are things the are not very sturdy. Needs & wants AO2 – Distinguish between needs & wants. The wants are certain thing that people wish to have, and needs are things that people must have to do their work. Economic good vs. free good AO2 – Distinguish between economic goods & free goods. Free goods are goods which can be given out to people without asking for money and economic goods are goods which can be used to satisfy certain desires or needs. AO1 – Define “Scarcity” Insufficient for the demand. AO1 – Define “Opportunity Cost” The next best alternative forgone when an economic decision is made. AO3 – Examine the relationship between opportunity cost, scarcity, and choice. Scarcity, Opportunity Cost & Choice Three Economic Questions Four factors of Production Utility Margin Production Possibilities Curve AO1 – Describe with examples the three economic questions. AO1 – Describe with examples the four factors of production. Land- natural resources Labor- people making the products Capital- machinery and tools Entrepreneurship- private investors planning the production process AO1 – Define “Utility” Measure of usefulness and pleasure. AO1 – Define the term “Marginal” The extra utility gained from consuming one more unit of that product. AO4 – Draw a correctly labeled Production Possibilities Curve. AO3 – Examine the relationship between the PPC and scarcity, choice, and opportunity cost. AO1 – Define “potential output,” and relate to PPC How much the sector thinks its giving out AO1 – Define “potential growth,” and relate to PPC How much the sectors thinks its growing AO2 – Distinguish between potential output and actual output, and relate to PPC. AO2 – Distinguish between potential growth and actual growth, and relate to Microeconomics vs. Macroeconomics Positive vs. Normative Econ Ceteris Paribus Circular Flow Model PPC. AO2 – Distinguish between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics. Microeconomics is an economy on a small scale and macroeconomics is a economy on large scale AO2 – Distinguish between Positive and Normative Economics with examples. Positive can be checked and normative is an own opinion AO1 – Define “Ceteris Paribus” All other things being held equal. AO1 – Explain the reason Ceteris Paribus is used in economic models. When talking about changing a curve on a graph but leaving everything else the way it is. AO4 – Draw a correctly labeled Circular Flow Model. http://stevenduan.files.wordpres s.com/2010/07/circular-flowmodel1.gif, 20,09,2011 Public vs. Private Sectors Rationing Systems Growth vs. Development AO2 – Explain the Circular Flow Model. Households gives goods and labor to firms and firms gives money to the households. AO3 – Distinguish between the public sector and the private sector with examples. Public means that the company is owned or run by the community and private sector is a private business AO2 – Distinguish between a planned economy and a free-market economy. Planned means that the everything is run by the government and that everything is the same and free-market means that everyone is on their own. AO3 – Compare and contrast the advantages and disadvantages of planned and free-market economies. Planned- everyone has a job, same wages, and same healthcare. Free-market- everyone has their own job own insurance and their own and people have to figure out their own retirement plan AO2 – Distinguish between economic growth and economic development. economic growth is the growth of real output in an economy over time and the econ development is a broad concept of living improvement in standards of living conditions. AO1 – Define “sustainable development” Development that meets the requirement of the present without compromising the ability of future to meet their own needs.