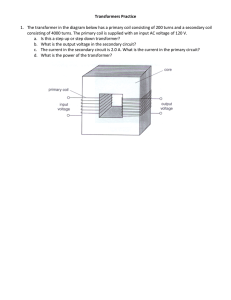
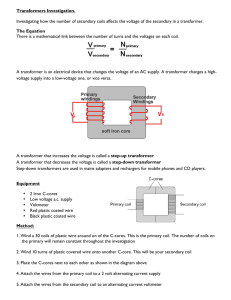
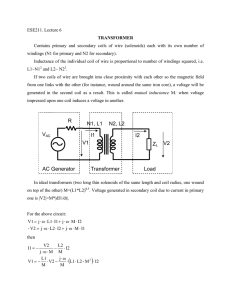
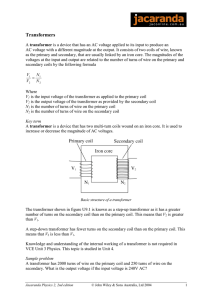
Transformer
advertisement

Transformer Gao Yan Gabriel Leow Zihui What is a transformer? • A transformer is an electrical device that takes electricity of one voltage and changes it into another voltage. How does a transformer work • First, in an electric circuit, there is magnetism around it. • Second, Faraday’s Law, whenever a magnetic field changes (by moving or by changing strength) a voltage is made. Construction • The construction of a transformer includes a ferromagnetic core around which multiple coils, or windings, of wire are wrapped. The input line connects to the 'primary' coil, while the output lines connect to 'secondary' coils. Working principle • The voltage outgoing is directly related to the number of turns in secondary coil over primary coil. • The voltage at the secondary coils is directly related to the primary voltage by the turns ratio, or the number of turns in the primary coil divided by the number turns in the secondary coil Applications • Electrical Grid • Firstly, a transformer converts the voltage from a power plant to very high usually 155,000 to 765,000 volts so that it can travel a long distance. • Secondly, after the current reached our houses. transformer is required to transfer the voltage to 230 volts so that it can power our home appliances. Reference • http://www.energyquest.ca.gov/how_it_work s/transformer • http://www.physlink.com/education/askexper ts/ae427.cfm.html • http://hyperphysics.phyastr.gsu.edu/hbase/magnetic/transf.html • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transformer#Ap plications