Unit 05 - Understand the application of electromagnetism in electrical design - Transformers - Learner task (DOC, 2MB)
advertisement

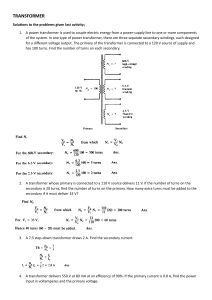
Unit 5: Electrical and electronic design LO2: Understand the application of electromagnetism in electrical design – Transformers Learner activity sheet Transformers have changed little over the last 100 years. They work on the principle of mutual induction – to change the values of alternating voltages and currents. They range in size – from miniature ones used in electronics to large ones used in power distribution. Activity 1 1. Investigate how a transformer works – and explain how it transforms or changes voltage and current. 2. Assuming a no loss transformer – state the formulae, giving the relationship between primary and secondary turns, and primary and secondary current and voltage 3. Explain what is meant by both a ‘step up’ and a ‘step down’ transformer. March 2015 Activity 2 1. An ideal transformer used in a battery charging circuit is connected to a 240 V mains supply, and supplies a 12 V load of 150 W. Calculate the transformer turns ratio, and the current that is taken from the supply. 2. A power distribution transformer has 500 primary turns and 2000 secondary turns. If the primary voltage is 240 V, determine the secondary voltage and whether this is a step-up or step-down transformer. The transformer is ideal. March 2015