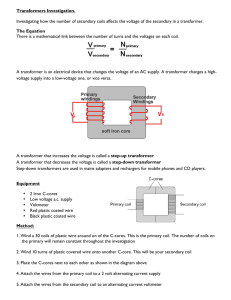
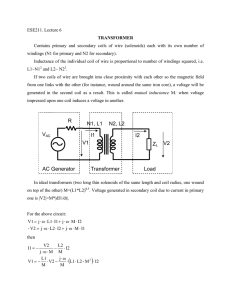
Transformers
advertisement
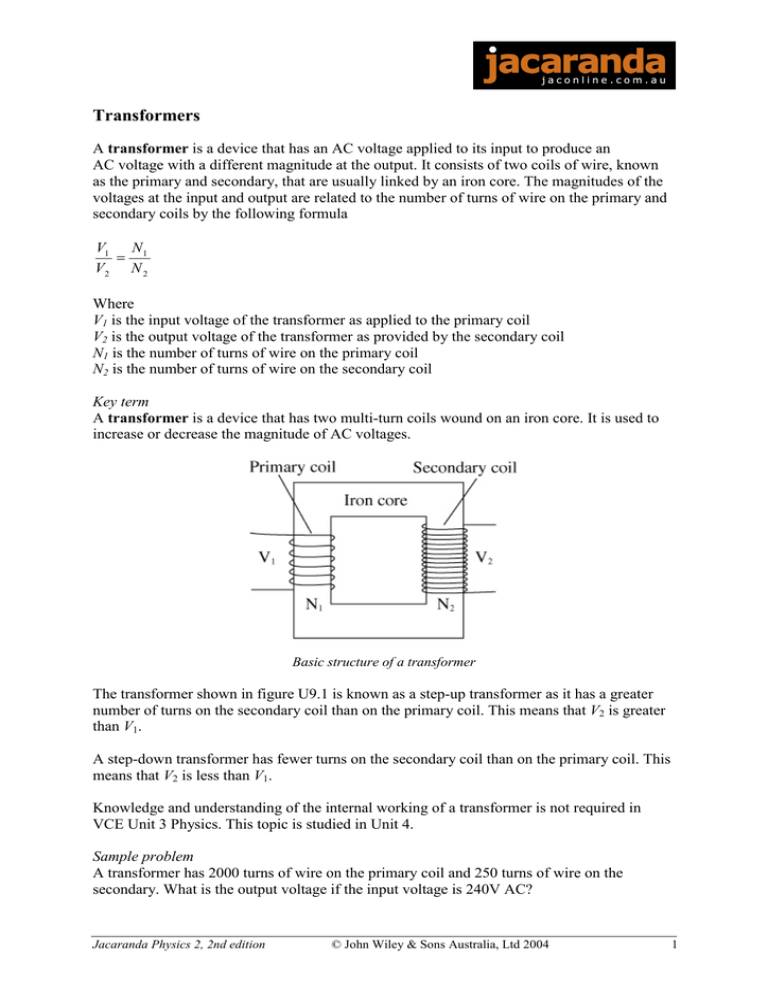
Transformers A transformer is a device that has an AC voltage applied to its input to produce an AC voltage with a different magnitude at the output. It consists of two coils of wire, known as the primary and secondary, that are usually linked by an iron core. The magnitudes of the voltages at the input and output are related to the number of turns of wire on the primary and secondary coils by the following formula V1 N 1 = V2 N 2 Where V1 is the input voltage of the transformer as applied to the primary coil V2 is the output voltage of the transformer as provided by the secondary coil N1 is the number of turns of wire on the primary coil N2 is the number of turns of wire on the secondary coil Key term A transformer is a device that has two multi-turn coils wound on an iron core. It is used to increase or decrease the magnitude of AC voltages. Basic structure of a transformer The transformer shown in figure U9.1 is known as a step-up transformer as it has a greater number of turns on the secondary coil than on the primary coil. This means that V2 is greater than V1. A step-down transformer has fewer turns on the secondary coil than on the primary coil. This means that V2 is less than V1. Knowledge and understanding of the internal working of a transformer is not required in VCE Unit 3 Physics. This topic is studied in Unit 4. Sample problem A transformer has 2000 turns of wire on the primary coil and 250 turns of wire on the secondary. What is the output voltage if the input voltage is 240V AC? Jacaranda Physics 2, 2nd edition © John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd 2004 1 Solution V1 = 240 V V2 = ? N1 = 2000 N2 = 250 V1 N 1 = V2 N 2 V2 = V1 N 2 N1 240 × 250 2000 = 30 = So the output voltage is 30 V Additional questions 1. What is the role of a transformer in an electric circuit? 2. A student wishes to obtain a 12 V AC voltage from a 240 V AC supply. (a) Which type of transformer should he choose; step-up or step-down? (b) Compare the number of turns of wire in the primary coil with the number of turns on the secondary coil in this case. Jacaranda Physics 2, 2nd edition © John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd 2004 2