Control of heart rate
advertisement

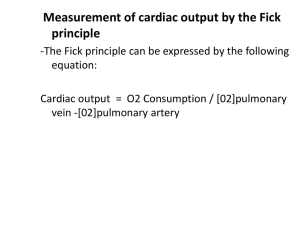
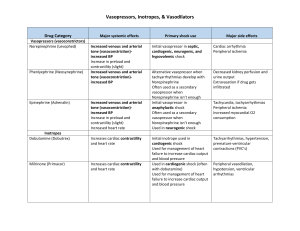
General Schemaatic of HR Control Regulation of Cardiac Cycle Autonomic nerve impulses alter the activities of the S-A and A-V nodes Overview of short-term control mechanisms From: Introduction to Cardiovascular physiology. J.R. Levick. Arnold 4th edition (2003) Heart rate Autonomic regulation (medullary CV center): Receives input from higher brain centers and variety of sensory receptors – Proprioceptors – Chemoreceptors – Baroreceptors • Sympathetic output ↑HR and contractility • Parasympathetic impulses ↓ HR – Little effect on contractility (does not innervate ventricular myocardium) Heart rate • Several factors contribute to regulation of heart rate: – Chemical regulation • Cardiac activity depressed by – Hypoxia – Acidosis – Alkalosis • Hormones – Catecholamines and thyroid hormones increase HR and contractility • Cations – Alterations in balance of K+, Na+ and Ca2+ alter HR and contractility Heart rate • Several other factors contribute to regulation of heart rate: • Age • Gender – Female HR higher • Physical fitness – Resting bradycardia • Body temperature – Increase causes SA node to discharge more rapidly PNS • Vagus nerve (via ACh) ↓ HR by ↓ slow inflow of Na+ and Ca++ and by ↑ the subsequent outflow of potassium (K+). • Acts at SA and AV nodes. • May treat SNS-driven heart attack by gagging or massage of carotid arteries activate vagal reflexes PNS counteracts SNS. The Cardiovascular Stress Response • Get the heart to beat faster: ↑ SNS tone, ↓ PNS tone • Norepinephrine (NE) and epinephrine (Epi) ↑ slow inflow of Na+ and Ca++ increase rate of re-excitation in SA node. • This ↑ Ca++ also increases contractility. • SNS terminals also excite AV node and whole myocardium: enhances contractility everywhere. Summary of long term BP control • Cardiac output and BP depend on renal control of extra-cellular fluid volume via: – Pressure natriuresis, (increased renal filtration) – Changes in: • Vasopressin • Aldosterone • Atrial natiuretic peptide All under the control of altered cardiovascular receptor signaling Vasopressin • Enhances water retention • Causes vasoconstriction • Secretion increased by aortic baroreceptors and atrial sensors http://www.cvphysiology.com/Blood%20Pressure/BP016.htm Baroreceptor reflex Blood pressure falls Sensors Aortic arch Neural integration Nucleus tractus solitarius Vasoconstriction Effectors Carotid sinus Cardiac inhibition Cardiac stimulation Constriction of veins & arterioles Increased stroke volume Increased peripheral resistance Increased heart rate Increased cardiac output Increased blood pressure