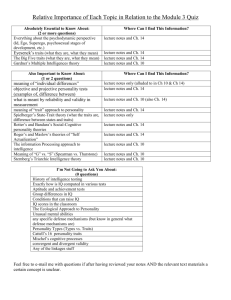
Setting an Education Goal - Public Schools of Robeson County
advertisement

6415 Career Management Unit A 1.02 UNIT:A Personal/Social Development • Competency CM01.00 • Evaluate individual characteristics/traits, interests/preferences, ability levels, skill acquisition, talents/aptitudes, and values in relation to setting and achieving personal, social, lifestyle, educational and career goals. • Objective CM01.02 • Critique individual characteristics/traits, interests/preferences, ability levels, skill acquisition, talents/aptitudes, and values in terms of a variety of personal, social, lifestyle and career goals. 2 9-6-10 Vocabulary List 1.00 Abilities: Natural or acquired skill or talent. Ability: Developed skill. Age Discrimination Act of 1967: Passed to prohibit discrimination against people between forty and seventy years of age. Americans with Disabilities Act: 1992; Gives civil rights projections to those provided on the basis of race, sex, national origin, age, and religion; EOC administers these laws. Aptitudes: Developed abilities; those things that one is good at doing; potential for leaning skills. 3 9-6-10 Vocabulary List 1.00 Assessment: The act of evaluation. Attitude: One’s outlook on life; how one reacts to a situation. Auditory: Relating to the sense of hearing. Career: An occupation or profession followed as a life’s work. Change: To make or become different; to replace with another. COBRA: Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act; law to provide terminated employees or those who lose insurance coverage because of reduced work to be able to buy group insurance for themselves and their families for a limited amount of time. 4 9-6-10 Vocabulary List 1.00 Compassion: To care deeply about other people and their well- being. Divorce: The legal dissolution of a marriage. Dexterity: Proficiency in using the body or hands. Equal Employment Opportunities Commission (EEOC): Enforces laws to prevent unfair treatment on the job due to sex, race, color, religion, national origin, disability, or age. Ethics: The principles of conduct that govern a group or society. 5 9-6-10 Vocabulary List 1.00 Family Medical Leave Act: 1993; Requires employers with 50 or more workers to grant up to 12 weeks of unpaid leave a year to allow workers to take time off to help care for a new baby or an ill family member without fear of losing their jobs. Fair Labor Standards Act: Sets minimum wage, requires over- time pay for time worked over 40 hours, and restricts the employment of minors. Fatigue: Weariness from labor or stress; tired. Formal assessment: Standardized written or performance test of knowledge, aptitude, values, etc. 6 9-6-10 Vocabulary List 1.00 Gender identity: Sexual identify; a person knowing that their sex is permanent and cannot be changed. Generatively: State of human development often referred to as the “working years”; between a person’s late twenties and early sixties, when he or she is productive in the world of work, develops a family and reexamines personal beliefs and values. Hobby: A pursuit or interest engaged in for relaxation. Holland Codes: Codes (career personality types) developed by Dr. John Holland based on the assumption that people can be grouped into six personality types. These codes can be compared to characteristics important to occupations. 7 9-6-10 Vocabulary List 1.00 Individual: Pertaining to one only. Integrity: Following a strict code of conduct or standard of values. Interests: Activities, things, and ideas a person likes and enjoys. Interest Inventory: A periodic survey of a person’s interests. Interpersonal: Relationships between persons. Intrapersonal: Relates to independent action. Inventory: An account of things. 8 9-6-10 Vocabulary List 1.00 Job: To do occasional pieces of work for hire; task. Kinesthetic: Relates to interaction with people and objects in real space. Layoff: An involuntary separation of the employee from the employer for a temporary or indefinite period, through no fault of the employee. Learning Styles: The ways people think and learn. Leisure: Time free from every-day job responsibilities during which a person can pursue personal interests and hobbies. 9 9-6-10 Vocabulary List 1.00 Life Roles: The various parts of one’s life, such as citizen, parent, spouse, worker, etc. Life Stages: Changes that occur as we move through life experiences. Lifestyle: The way a person lives his or her life, including geographic location, type of home, method of transportation, and social situations. Linguistic: Pertaining to the use of language. Logical: Use of reliable inference and reasoning. 10 9-6-10 Vocabulary List 1.00 Marriage: The legal unions of a man and woman as husband and wife. Naturalist: Interested in natural environments. Occupational Changes: Changes in job status. Parenthood: The state or relationship of being a parent. Pink Slip: Notice of termination. Reduction in force: The employment of fewer people. 11 9-6-10 Vocabulary List 1.00 Rehabilitation Act of 1973: Extended protection to those with physical or mental handicaps. Resources: Those things that a person can use to help reach goals. Responsibility: A willingness to accept an obligation and be accountable or an action or situation. Retirement: The state of being retired from one’s occupation. Sandwich Generation: Group of people who are caring for both their parents and their children. 12 9-6-10 Vocabulary List 1.00 Self-concept: How people view their own skills, interests, and competence level. Self-esteem: How one views oneself; a feeling of good will with regard to how you feel about yourself; pride; confidence. Skill: Proficiency or ability. Social: Preference to working with others. Spatial: Pertaining to a sense of space. Termination: Dismissal from employment. 13 9-6-10 Vocabulary List 1.00 Time Management: Plan to use time wisely. Transition: The processes of changing from one state, activity, or place to another. Unemployment insurance: A joint state-federal program under which state-administered funds pay a weekly benefit for a limited time to eligible workers when they are involuntarily unemployed. Values: Cherished ideas and beliefs that affect decisions a person makes. 14 9-6-10 Vocabulary List 1.00 Verbal: Expressed in words. Visual: Pertaining to sight. Vocational Rehabilitation Services: Provided free to those who meet the legal eligibility guidelines. Wellness: Good health. Work: Activity directed toward a goal that produces something of value; to exert oneself physically or mentally. 15 9-6-10 Vocabulary List 1.00 Work Ethic: How a person feels about his/her job and the effort he/she puts into it. Work Needs: Those characteristics that employers require for employment (SCANS skills: basic skills, thinking skills, personal qualities, workplace competencies). Work Values: Ideas and beliefs concerning career/work that are important to a person and govern his/her perception of job/occupation/career. Worker’s Compensation: Guarantees financial assistance to workers injured on the job. 16 9-6-10 SCANS Skills-- Review Because the world of work is changing, the U.S. Departments of Labor and Education formed the Secretary's Commission on Achieving Necessary Skills (SCANS) to study the kinds of competencies and skills that workers must have to succeed in today's workplace. The results of the study were published in a document entitled What Work Requires of Schools: A SCANS Report for America 2000. 17 9-6-10 SCANS Skills/Competencies Identifying your current strengths and weaknesses. Create in PowerPoint CM1.02 All About Me! http://www.nccareers.org/ 18 9-6-10 Class Discussion The positive and the negative influence of personal behavior on others. Examples Manners/Etiquette Dress/Appearance Attitude Displays Personal Actions Ethical Choices Habits Peer Pressure 19 9-6-10 Choose Job/Create a Person Handout Available Divide the class into pairs. Each pair will choose a job. Each pair will create a person to fill the job. 1. 20 Write a description of the person that includes name, gender, personality type, special aptitude and skills, career, lifestyle, marital status, number of children, areas of residence, and hobbies. Each team will read its descriptions to the class and discuss why they chose such images. 9-6-10 Ability/Talent Show Each student will present one of their abilities/talents to the class. Teacher will keep a list. Discuss how these abilities/talents can be used in career selection. How can these abilities/talents be used to obtain a career? 2. What are the benefits of making a career choice based on an individual’s abilities/talents? 3. Identify possible career options for each ability/talent presented. Why were these careers selected? 1. 21 9-6-10 Brainstorm Characteristics Brainstorm characteristics of a person who is conceited Brainstorm characteristics of a person with a good self-concept Brainstorm characteristics of a person with a poor self-concept Brainstorm characteristics of a person with a good attitude Brainstorm characteristics of a person with a bad attitude Journal Entry Record characteristics in your Journal (1.02) 22 9-6-10 Journal Entry 1.02 • In your journal, make a list of successful people you know personally. • Choose one • Think about that person’s interests, aptitudes, attitude, and personality. • Homework Assignment 9-9-11 23 Identifying My Personality Traits • Appendix 1.02 (3) Identifying My Personality Traits • Identify traits that describe you by copying and pasting in your CM1.02 All About Me PowerPoint. 24 9-6-10 Personality Traits 25 Cooperative Agreeable Stubborn Self-disciplined Friendly Shy Intelligent Thoughtful Impulsive 9-6-10 Personality Traits 26 Energetic Ambitious Generous Greedy aggressive Assertive Independent Dependent Talkative Loyal Honest 9-6-10 Personality Traits Dishonest Pleasant Enthusiastic Outgoing Quiet Confident Happy Sad Funny 27 9-6-10 Personality 28 Witty Boring Dependable Unreliable Tolerant Critical Jealous Capable Lazy Moody Nervous Patient Kind 9-6-10 Personality Religious Polite Respectful Sarcastic Helpful Selfish 29 9-6-10 Attitude/Behavior Connection Appendix 1.02 (4) Attitude/Behavior Connection Complete in CM1.02 All About Me PowerPoint Examine the impact of your behavior and attitude on the job 30 9-6-10 Self Portrait Reflecting upon the information that you discovered about yourself throughout Competency 1.00 use Appendix 1.02 (5) – Self Portrait to put together a brief, written portrait of yourself. Create in CM1.02 ALL ABOUT ME! PowerPoint This information can be used to help you formulate your Letter of Introduction for your CAREER PORTFOLIO. 31 9-6-10 Journal Entry CM1.02 List ten adjectives that describe your personality and match these traits to career interests. 32 9-6-10 Choose an Object Choose an object that represents your perception of your self-concept. (Example: plant – growing; Frosted Flakes – GREAT!) Create a descriptive essay justifying your choice. Use PowerPoint 1.02 ALL ABOUT ME! Object Explanation 33 9-6-10 Work Values It’s important to know exactly what employers look for when hiring full-time employees. In addition to relevant skills, employers seek employees who have the personal values, characteristics, and personality traits that spell success. Good personal values are what makes the foundation for a good employee. 34 9-6-10 Work Values Here is a List of the Top 10 Values Employers Look for in Employees. 1. Strong Work Ethic 2. Dependability and Responsibility 3. Possessing a Positive Attitude 4. Adaptability 5. Honesty and Integrity 6. Self-Motivated 7. Motivated to Grow & Learn 8. Strong Self-Confidence 9. Professionalism 35 10. Loyalty 9-6-10 1. Strong Work Ethic Employers value employees who understand and possess a willingness to 36 work hard. In addition to working hard it is also important to work smart. This means learning the most efficient way to complete tasks and finding ways to save time while completing daily assignments. It’s also important to care about your job and complete all projects while maintaining a positive attitude. Doing more than is expected on the job is a good way to show management that you utilize good time management skills and don’t waste valuable company time attending to personal issues not related to the job. Downsizing in today’s job market is quite common so it’s important to recognize the personal values and attributes employers want to improve your chances of job security should a layoff occur. 9-6-10 2. Dependability and Responsibility . Employers value employees who come to work on time, are there when they are suppose to be, and are responsible for their actions and behavior. It’s important to keep supervisors abreast of changes in your schedule or if you are going to be late for any reason. This also means keeping your supervisor informed on where you are on all projects you have been assigned. Being dependable and responsible as an employee shows your employer that you value your job and that you are responsible in keeping up with projects and keeping them informed of the things that they should know about. 37 9-6-10 3. Possessing a Positive Attitude Employers seek employees who take the initiative and have the motivation to get the job done in a reasonable period of time. A positive attitude gets the work done and motivates others to do the same without dwelling on the challenges that inevitably come up in any job. It is the enthusiastic employee who creates an environment of good will and who provides a positive role model for others. A positive attitude is something that is most valued by supervisors and co-workers and that also makes the job more pleasant and fun to go to each day. . 38 9-6-10 4. Adaptability Employers seek employees who are adaptable and maintain flexibility in completing tasks in an ever changing workplace. Being open to change and improvements provides an opportunity to complete work assignments in a more efficient manner while offering additional benefits to the corporation, the customer, and even the employee. While oftentimes employees complain that changes in the workplace don’t make sense or makes their work harder, oftentimes these complaints are due to a lack of flexibility. 39 9-6-10 Adaptability Adaptability also means adapting to the personality and work habits of co-workers and supervisors. Each person possesses their own set or strengths and adapting personal behaviors to accommodate others is part of what it takes to work effectively as a team. By viewing change as an opportunity to complete work assignments in a more efficient manner, adapting to change can be a positive experience. New strategies, ideas, priorities, and work habits can foster a belief among workers that management and staff are both committed to making the workplace a better place to work. 40 9-6-10 5. Honesty and Integrity Employers value employees who maintain a sense of honesty 41 and integrity above all else. Good relationships are built on trust. When working for an employer they want to know that they can trust what you say and what you do. Successful businesses work to gain the trust of customers and maintain the attitude that “the customer is always right”. It is the responsibility of each person to use their own individual sense of moral and ethical behavior when working with and serving others within the scope of their job. 9-6-10 6. Self–Motivated Employers look for employees who require little supervision and 42 direction to get the work done in a timely and professional manner. Supervisors who hire self-motivated employees do themselves an immense favor. For self-motivated employees require very little direction from their supervisors. Once a self-motivated employee understands his/her responsibility on the job, they will do it without any prodding from others. Employers can do their part by offering a safe, supportive, work environment that offers employees an opportunity to learn and grow. Working in a supportive work environment and taking the inititiative to be self-directive will provide employees with a better sense of accomplishment and increased self-esteem. 9-6-10 7. Motivated to Grow & Learn In an ever changing workplace, employers seek employees who are interested in keeping up with new developments and knowledge in the field. It has been noted that one of the top reasons employees leave their employers is the lack of opportunity for career development within the organization. Learning new skills, techniques, methods, and/or theories through professional development helps keep the organization at the top of its field and makes the employee's job more interesting and exciting. Keeping up with current changes in the field is vital for success and increased job security. 43 9-6-10 8. Strong Self–Confidence Self-confidence has been recognized as the key ingredient between someone who is successful and someone who is not. A self – confident person is someone who inspires others. A self-confident person is not afraid to ask questions on topics where they feel they need more knowledge. They feel little need to have to impress others with what they know since they feel comfortable with themselves and don’t feel they need to know everything. 44 9-6-10 Strong Self–Confidence The self-confident person does what he/she feels is right and is willing to take risks. Self- confident people can also admit their mistakes. They recognize their strengths as well as their weaknesses and are willing to work on the latter. Self-confident people have faith in themselves and their abilities which is manifested in their positive attitude and outlook on life. 45 9-6-10 9. Professionalism Employers value employees who exhibit professional behavior at all times. Professional behavior includes learning every aspect of a job and doing it to the best of one’s ability. Professionals look, speak, and dress accordingly to maintain an image of someone who takes pride in their behavior and appearance. Professionals complete projects as soon as possible and avoid letting uncompleted projects pile up. 46 9-6-10 Professionalism Professionals complete high quality work and are detail oriented. Professional behavior includes all of the behavior above in addition to providing a positive role model for others. Professionals are enthusiastic about their work and optimistic about the organization and its future. To become a professional you must feel like a professional and following these tips is a great start to getting to where you want to go. 47 9-6-10 10. Loyalty Employers value employees they can trust and who exhibit their loyalty to the company. Loyalty in the workforce has taken on a new meaning. Gone are the days when employees plan on starting out and retiring with the same company. It is said that most people will hold between 8 – 12 jobs throughout their career. What does this mean in terms of loyalty in today’s workforce? 48 9-6-10 Loyalty Companies offering employee growth and opportunity will ultimately gain a sense of loyalty from their employees. Employees today want to feel a sense of satisfaction in their jobs and will do a good job when they feel that the employer is fair and wants to see them succeed. Although this may mean only staying for five or ten years in a position, employees can offer loyalty and make an important contribution during their time with the company 49 9-6-10 Loyalty More companies today encourage employee feedback and offer employees an opportunity to lead in their area of expertise. This gives employees a greater sense of satisfaction and a sense of control over their job. Empowerment encourages employees to do their best work since companies are displaying a trust and expectation that they believe in their employees to do a good job. 50 9-6-10 Loyalty Offering jobs that encourage learning and the development of new skills also gives employees a sense of empowerment in the workplace. Aligning an employees values with the goals of the organization will foster loyalty and a bond between employer and employee. Fostering good relationships within an organization and offering constructive ways to handle conflict provides a win – win situation for both employer and employee. 51 9-6-10 Loyalty Creating an organization that values loyalty within the organization can also work to its benefit by using the same techniques and strategies to establish loyalty with customers; and loyalty from customers ultimately makes for a successful business. 52 9-6-10 Work Values – Appendix 1.02 (6) WorkValues Rank work values in order of importance to you 53 9-6-10 Work Values Class Activity Collect data regarding each individual’s results What are the 3 most important work values to the class? What are the 3 least important? 54 9-6-10 General Job Inventory Appendix 1.02 (7) Complete as a Class Activity **Line up, If student’s answer is strong – step forward. 55 9-6-10 General Job Skills 56 Meeting deadlines Organizing projects Planning Taking risks Public speaking Self-control Budgeting/money management Self-motivation Supervision Detail oriented Instructing others Computer skills/knowledge Accepting responsibility Explaining things to others Managing people Problem-solving Meeting the public Writing Teamwork Math 9-6-10 Working with Things Dexterity Assembling things Building things Constructing/repairing 57 buildings Making things Observing/inspecting things Driving/operating vehicles Using equipment 9-6-10 Working with Data Analyzing facts Auditing records Investigating Using the Internet Sending and receiving electronic 58 communication Researching and locating information Calculating, computing Classifying data Counting/Inventory Observing 9-6-10 Working with People 59 Patient Sensitive Outgoing Tactful Teaching Interviewing Listening Tolerant Understanding Kind Diplomatic/Fair Counseling Trusting Firmness 9-6-10 Using Words and Ideas Logical Public speaking Designing Editing Remembering information Writing clearly Correspondence Creativity 60 9-6-10 Using Leadership Ability Arranging social functions Competitive Motivating others Decisive Running meetings Delegating Working out agreements Planning 61 9-6-10 Creativity/Artistic Ability Dancing/Movement Drawing Performing/Acting Playing musical instruments Presenting artistic ideas Music appreciation Expressive 62 9-6-10 Setting an Education Goal Education goals enable individuals to prepare for future success in the workplace. They also can be both short-term and long-term goals. Taking specific classes, getting good grades, and participating in extra curricular activities are three examples of how individuals can better prepare for future careers. Education goals prepare individuals to achieve higher education thus preparing them with greater opportunities to earn a higher income. Write an education goal for yourself by following the five elements of educational goal setting. (see next slide) 63 9-6-10 Setting an Educational Goal 1. Specific To be specific, state exactly what is to be done in your academics to reach a goal. For example: I plan to raise my grade in advanced algebra. What guidelines will you set to help you determine that this goal has been met? 64 9-6-10 Setting an Education Goal 2. Measurable To make a goal measurable, write the letter grade or final outcome for the goal. For example: I plan to raise my grade from a B- to a B+ in advanced algebra. What specific item are you striving to achieve? 65 9-6-10 Setting an Education Goal 3. Attainable To make a goal attainable, determine how the goal can be reached, which is often determined by an individual’s current academics. For example: I plan to raise my grade from a B- to a B+ in advanced algebra by staying after school on Monday and Wednesday nights for math tutoring. How are you going to reach this goal? 66 9-6-10 Setting an Education Goal 4. Realistic Be realistic. Do not set the goal for something unattainable or unrealistic. Is the goal realistic? Why or Why not? 67 9-6-10 Setting an Education Goal 5. Time Bound To make the goal time bound, specifically state when the goal needs to be reached. This is influenced by how attainable the goal is. Realistically, a person cannot raise their math grade in one academic week. When will you reach your goal? 68 9-6-10 Setting an Education Goal What is your final goal statement. --put in CM1.02 All About Me! PowerPoint 69 9-6-10 Character Traits – Appendix 1.02 (9) Identify two different ways that you demonstrate the following character traits at home, school, community and work. 70 Positive Attitude Loyalty Dependability Open-Mindedness Friendliness Self-Confidence Honesty Self-Control Initiative Sense of Humor 9-6-10 Rating Your Personal Traits Appendix 1.02 (10) Rating Your Personal Traits Rate your personal characteristics by placing a check mark in the appropriate box. For each trait that you checked a rating of poor or very poor, develop a strategy to improve your rating. 71 9-6-10 Self-Improvement Plan Appendix 1.02 (11) Self-Improvement Plan Choose one personal trait you wish to improve. Complete MAKE A PLAN. Will you need to spend more time trying to correct bad habits? 72 9-6-10 What did you learn from CM1.02? Must be at least 5 sentences. Explain your statements. 9-6-10 73