Global Warming

Environmental
Problems
Foundations of Science
Natural Cause: The universe behaves in a predictable way under “rules” that can be determined through observation and experimentation.
Uniformity: The “rules” are constant through space and time.
Foundations of Science
Parsimony: All other things being equal, the simplest explanation is the best.
Efficient Cause cause & effect
Objective
Scientific “Method”
Observation
Question
Hypothesize
Test & Observe
Publish
Repeat (as necessary)
Theorize
Publish
Repeat (as necessary)
Environmental Science
interdisciplinary a way of looking at things scientific (& objective) interconnected systems human impact vs naturally occurring
• attempt to assign “responsibility”
What is the Environment?
definitions circumstances or conditions that surround an organism or group of organisms the complex of social or cultural conditions that affect an individual or community for humans - our home - well suited to our existence natural world “man-made”
• plants • sociological
• animals • scientific
• earth
• air
• water
• technological
“Tragedy of the Commons”
common property usually owned by all (or the government) examples
• air
• water
• “air waves”
• public land commons are subject to poor use open, unregulated access benefits of use are focused costs are widely distributed
Common Property
must be carefully managed may privatize cost of use & effects
• internalization of costs
• laws and taxes commons (difficult)
• sale of public land
• sale of right to use
Global Climate Change
Earth’s climate has been changing for over 4.5 billion years wide scale of variability causes of variability
Sun physical Earth life
Research Priorities
What is the scale of the current change?
What are the causes of the current warming?
What are the effects of human activity?
Tools to Study Global
Change
geologic record historical record real time observation mathematical modeling
Energy Balance
almost all energy ultimately from sun earth’s energy cycle incoming energy
• reflected 30%
• absorbed 70% (visible & IR) outgoing energy emitted as IR
• (as much energy as received)
Earth warmed by energy between absorption and emission energy circulated by air and water movement
Earth’s Temperature
atmospheric retention of heat
“greenhouse effect”
H
2
O vapor, CO
2
, CH
4
, CFC’s released by natural & human processes
Earth’s Temperature
historically over last billion years: warmer with ice ages current ice age
• 2MYA to present: cooler with “interglacials”
• last glacial advance ended 10,000 yrs ago
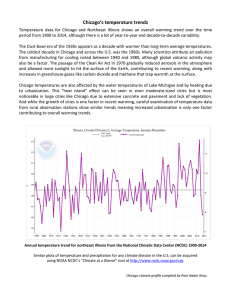
• generally warming since warming rapidly in last 150 years
Earth’s Temperature
CO
2 changes currently: 0.03% of atmosphere recent highs
• “interglacial periods”
• 125K yrs ago and now releasing stored CO
2
• natural from rocks & plants
• humans current increase started in 1800's other “greenhouse” gasses human’s have increased release rate
Potential Effects of Global
Warming
local climate change more rain more violent storms sea level rise change in ocean circulation complex response
Current Research On-line
http://www.globalchange.umich.edu/globalchang e1/current/lectures/samson/climate_patterns/ http://www.giss.nasa.gov/research/ http://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/oa/ncdc.html
http://www.mos.org/cst/article/3369/ http://www.scotese.com/climate.htm
http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/paleo/ei/ei_cover.html
http://www4.nas.edu/onpi/webextra.nsf/web/clim ate?OpenDocument
More research and advocacy on-line
American Petroleum Institute: http://api-ec.api.org/environ/index.cfm
industry site
Natural Resources Defense Council: http://www.nrdc.org/globalwarming/ environmental organization
Global Warming Information Page: http://www.globalwarming.org/
“astroturf” site (no direct supporters listed)
Global Warming Early Warning Signs: http://www.climatehotmap.org/
“environmentalist” site (supporters listed) the Global Simulation Workshop http://www.osearth.com/workshops/ commercial “environmentalist” site
worldwide use of energy
overall oil - 36% coal - 26% natural gas - 23% nuclear - 7% biomass – 6% hydro - 2% geothermal & wind - 1%
U.S. consumes ¼ of worlds energy