The Communicative Approach
advertisement

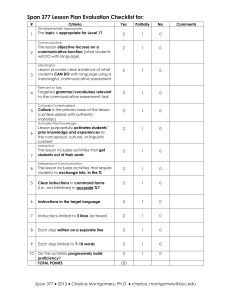
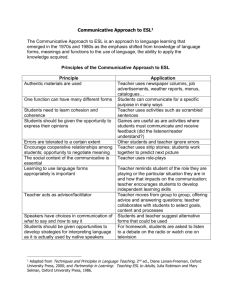
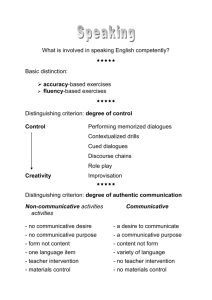
The Communicative Approach What is the communicative approach? The communicative approach is the theory that language is communication. Therefore the final aim of CLT (Communicative Language Teaching) is communicative competence. The Principles of the Communicative Approach: Learners learn through using it to communicate Authentic and meaningful communication should be the goal of classroom activities Fluency is an important dimension of communication Communication involves the integration of different language skills Learning is a process of creative construction and involves trial and error So what is the teacher’s role in this? The teacher has two main roles: • To facilitate the communication process in the classroom • To act as an independent participant within the learningteaching group The teacher is also expected to act as a resource, an organiser of resources, a motivator, a counsellor, a guide, an analyst and a researcher. There are many other minor roles of a teacher, some of these would include being an actor and an entertainer. After all, a good lesson must be interesting or the students will ‘switch off’ and learn nothing. In practical terms, what does that mean? It means that we need to concentrate on the following: Teacher – Student activities Activities Materials Teacher-Student Interaction Since communicative competence is our aim, it is essential that students be given every opportunity to practise communicating. In the communicative classroom teacher talking time (TTT) must be kept to a minimum. This is not to say that the teacher shouldn’t speak at all, but TTT should be controlled and appropriate. The classroom should be learner centred. The teacher’s role is to facilitate student communication which is done through careful selection of materials and activities relevant to the aims of the lesson in which they are used. Communication can be divided into two categories • Input • Output The four communicative skills can be put into these categories Input Reading Listening OUTPUT Speaking Writing Whichever of these skills is being taught the main focus must be on the student and not on the teacher. The interaction should usually be the student to student and should include the teacher only where necessary. During most classroom activities the teacher will monitor and intervene only where necessary. A model for part of a communicative lesson Stage 1 Teacher (T) gives a short presentation of a grammar or vocabulary point. T then gives students (Ss) opportunity to practise the point in a controlled exercise. (Interaction: T›Ss) Stage 2 Ss carry out the controlled exercise while T monitors and intervenes where appropriate. (Interaction: S‹›S) Stage 3 The Ss are asked to take part in an activity designed to get them to produce the vocabulary and grammar they have been taught. T monitors and notes errors and interesting points. T intervenes only when asked or when absolutely necessary. (Interaction: S‹›S) Stage 4 Feedback session, in which T feeds back in a non-threatening way the errors s/he noted during the activity. Ss also have the opportunity to clear up puzzling points. (Interaction: T‹›Ss) The lesson extract follows a method called Presentation-Practice-Production or PPP for short. This was the standard method until a few years ago. Now there are a number of possibilities open to the teacher. You will be introduced to these at a later stage. Activities Classroom activities should, as far as is possible, be carried out in the target language (English). Having said this, there may sometimes be occasions where allowing the students to briefly discuss a point in their native tongue can promote greater understanding and assimilation of new information. This is controversial issue and should not usually be permitted. There are many different types of activities. They provide speaking, listening, writing and reading practice as well as aiding production. A few ideas for activity types Games Role-plays Simulations Information Gaps Where do I find activities? They can be found in books containing supplementary material such as the Reward Resource Packs. Many teachers enjoy creating their own activities, which can be tailored specifically to their classes needs. Activities used in the classroom must be selected carefully as if they are above the level of the students they can destroy self-confidence and if below they can bore the students. Activities usually involve the students working together either in pairs or in small groups. Activities are often used to practise reallife situations involving social interaction and so a high level of social and functional language should be expected. Materials Materials fall into three broad categories: text-based, task-based realia. They can be used as the basis for classroom activities. Once again not only must the activity be appropriate to the level of the students but the materials used must be appropriate too. Text-based materials For example practice exercises, reading passages, gap fills, recordings, etc. can be found in almost any course book as well as in books containing supplementary materials. They form an essential part of most lessons. Task-based materials These include game boards, roleplay cards, materials for drilling, pairwork tasks, etc. They might be used to support 'real life' tasks such as role playing booking into a hotel, or a job interview. Realia This includes such things as magazines, newspapers, fruit and vegetables, axes, maps - things from the real world outside the classroom. They can be used in many activities. For example, fruit and vegetables could be used in a shopping activity, an axe could be used to show the effect of using the present perfect continuous on a short action verb. So what does the communicative approach mean in practical terms? We should now understand that the teacher's job is to get their students to communicate using real language by providing them with instruction, practice, and above all opportunities to produce English in activities which encourage acquisition and fluency. In conclusion CLT should be fun for both teacher and students. Enabling students to communicate successfully is also very rewarding.