TSES 4001 Risk Class schedule 2014 Anne Wiles Topic block 1
advertisement

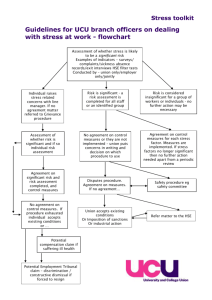
TSES 4001 Risk Class schedule 2014 Anne Wiles Topic block 1: Fundamental concepts and management functions Learning objectives o to understand how we define risk in modern society o to understand how we identify, interpret and respond to risks, as individuals and collectively, in societal norms and institutional expectations o to understand the major elements involved in risk management, including institutional responsibilities, societal considerations, diverse perceptions of risk and the management of uncertainty o to be familiar with main approaches and methods used for assessing risks o to be able to identify and apply key risk concepts, major approaches and methods used in risk assessments and considerations involved in risk management, in an individual book review and in a group evaluation of a risk assessment. Topic block 2: Risk as an organizational and management principle in modern society Learning objectives o To understand ways in which modern society applies risk as a means of interpreting, organizing and managing social functions in a range of sectors o To recognize the influence of risk perceptions and management strategies in risk issues o To be able to apply risk concepts, risk assessment approaches and management considerations in the critical evaluation of a risk issue. Assignments and expectations Book review: 20% of mark. 5-8 page critical review of book with reference to risk concepts. Group assignment: 30% of mark. Consists of written responses to questions on assigned risk issue, presentation of conclusions to class. Take-home exam: 40%. Attendance and class participation:10% split between class attendance and participation in class discussions. Date Topic Sept. 9 Introduction Sept. 16 Basic concepts -hazard; risk bearer; consequence; exposure; probability -risk issues Risk management overview -risk governance, management and assessment -framework elements -policy & technical elements -D-M responsibilities Risk assessment -main types -approaches & methods - considerations and challenges -principles for conduct Risk perception -general patterns: ‘lay’ and ‘experts’ -emotion and values -trust Uncertainty Sept. 23 Sept. 30 Oct. 7 Oct. 14 Oct. 21 Oct. 28 Nov. 4 Nov. 11 Nov. 18 Nov. 25 Dec. 2 Risk decision-making -precaution -tolerability -trade-offs -risk-based management Fall Break Risk communication -uses and misuses -application examples -message comprehension and design class presentations Risk in modern society -social risk management Risk and institutions Complex risk events -case studies -complex dynamics of risk events and issues Review Resources -Aven 2009 -Saner 2010 -Hansson 2010 Activities and Assignments discussion of course objectives and expectations --discussion of group assignment -Jardine et al., 2003 -IRGC Risk Governance Framework -HSE 2001 -NRC 2009 -Rider et al 2009 -Barnett 1998 Krewski and Lemyre 2008 Lupton, 1999 Aven and Steen 2010 Aven, 2011 - Wilson, 2011 -Baltussen and Nessen 2006 MCDA book review due -submit on cuLearn group assignment workshop -Leiss, 2004 -Johnson, 2012 -Lofstedt, 2013 group assignment workshop group assignment due Manthorpe et al. 2010 -Ericson and Doyle, 2003 -MIACC 1994 -Williamson, 2013 References Aven, Terje, 2009. Perspectives on Risk in a decision-making context – review and discussion. Safety Science 47: 798-806. Aven Terje, 2011. On Different Types of Uncertainties in the Context of the Precautionary Principle. Risk Analysis 31(10): 1515-1525. Aven, T. and R. Steen, 2010. The concept of ignorance in a risk assessment and risk management context. Reliability Engineering and System Safety 95: 1117-1122. Ericson, Richard V. and Aaron Doyle (Eds.), 2003. Risk and Morality. University of Toronto Press: Toronto. Hannson, Sven Ole 2005 Seven Myths of Risk Risk Management an International Journal 7(2) 7-17 Hansson, Sven Ole 2010. The Interdisciplinarity of Risk in Oxford Handbook of Interdisciplinarity, Robert Frodeman, Julie Thompson Klein and Carl Mitcham, eds. Chapter 36. Oxford University Press. HSE (Health and Safety Executive), 2001. Reducing Risks, Protecting People: HSE’s decision-making process. Norwich, United Kingdom. http://www.hse.gov.uk/risk/theory/r2p2.pdf Hood, Christopher and Henry Rothstein, 2000 “Business risk Management in Government; Pitfalls and Possibilities” Annex 2, Supporting Innovation: Managing risk in government departments Report by the Comptroller and Auditor General http://www2.lse.ac.uk/researchAndExpertise/units/CARR/pdf/businessriskmanagementingovt.pdf Jardine, Cindy G., Steve Hrudy, John Shortreed, Lorraine Craig, Daniel Krewski, Chris Furgal and Stephen McColl, 2003. Risk Management Frameworks for Human Health and Environmental Risks. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health Part B 6:569-641 Johnson, Brandon B., 2012. Climate Change Communication: A Provocative Inquiry into Motives, Meanings and Means. Risk Analysis. 32(6) Krewski, Daniel, Louise Lemyre, Michelle C. Turnera, Jennifer E.C. Lee, Christine Dallaire, Louise Bouchard, Kevin Branda and Pierre Mercier, 2008. Public perception of population health risks in Canada: Risk perception beliefs. Health Risk & Society Leiss, William, 2004 Effective Risk Communication Practice Toxicology Letters 149: 399-404 Lofstedt, Ragnar, 2013. Communicating Food Risks in an Era of Growing Public Distrust: Three Case Studies Risk Analysis 33(2) Lupton, Deborah, 1999. Risk. London and New York: Routledge. Major Industrial Accidents Council of Canada 1994. Hazardous Substances Risk Assessment: A MiniGuide for Municipalities and Industry .Ottawa, MIACC Manthorpe. Jill, Kalpa Kharicha, Claire Goodman, Danielle Harari, Cameron Swift and Steve Iliffe, 2010. Smarter Working in Social and Health Care: Professional perspectives on a new technology for risk appraisal with older people. British Journal of Social Work 40 1829-1846. National Research Council, 2009. Science and Decisions: Advancing Risk Assessment. Washington: National Academies Press. OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), 2004. The mental models approach to risk research - an rwm perspective http://www.oecd-nea.org/rwm/docs/2003/rwm-fsc2003-7rev1.pdf Rodricks, Joseph V., 2001. Some Attributes of Risk Influencing Decision-making by Public Health and Regulatory Officials American Journal of Epidemiology 154(12) Supplement. Saner, M., 2010. A Primer on Scientific Risk Assessment at Health Canada http://www.hc-sc.gc.ca/srsr/pubs/about-apropos/2010-scientif-ris/index-eng.php Williamson, Lorna, 2013. Challenges in the management of the blood supply. Lancet 381:1866-75. Wilson K., 2011. A Framework for Applying the Precautionary Principle to Transfusion Safety. Transfusion Medicine Reviews 25(3):177‐183