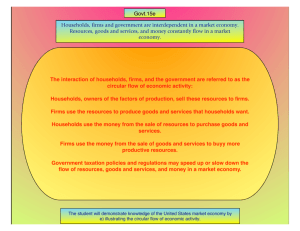
The Market System and the Circular Flow
advertisement

The Market System and the Circular Flow Multiple Choice Questions 1. The market system is an economic system that: A. Produces more consumer goods than capital goods B. Produces more capital goods than consumer goods C. Gives private individuals the right to own resources used in production D. Emphasizes the government's power to control markets and direct economic activity 2. The market system is often also known as: A. Capitalism B. Socialism C. Central planning D. Regulation 3. One element of the command system is: A. Capitalism B. Free markets C. Private ownership D. Central planning 4. The extensive private ownership of property resources in a market system has the following implications, except: A. The market system is also known as capitalism B. Trades that take place in a market system are mutually-agreeable transactions C. Investment, innovation, and maintenance of property are fostered by the market system D. The strong in the society could accumulate property by overpowering the weak 5. Which statement best describes the market system? A. Entrepreneurs direct production activities, and market prices allocate goods and services B. Government policies direct production activities and allocate goods and services C. Government policies direct production activities, while market prices allocate goods and services D. Individuals and markets all function smoothly under the guidance and regulation of the government 6. In a command system: A. Self-interest guides and commands individuals to pursue actions that lead them toward achieving their goals B. The head of each family decides what to do with the family's resources C. The government makes production and allocation decisions D. Market traders command what outputs are produced and how they are allocated 7. Which would be characteristic of a capitalist economy? A. Government ownership of most factors of production B. Competition and unrestricted markets C. Reliance on the market system D. Freedom of enterprise and choice 8. A basic characteristic of a command system is that: A. Wages paid to labor are higher B. Government owns most economic resources C. Free markets are never permitted in a command economy D. Government planners play a limited role in deciding what goods will be produced 9. The economies of Ireland and France are: A. Similar in that they are both basically command systems B. Similar in that they are both basically market systems C. Different in that Ireland has a command system while France has a market system D. Different in that France has a command system while Ireland has a market system 10. The economies of North Korea and South Korea are: A. Similar in that they are both basically command systems B. Similar in that they are both basically market systems C. Different in that North Korea has a command system while South Korea has a market system D. Different in that South Korea has a command system while North Korea has a market system 11. capitalism is characterized by: A. Very limited government role in the economy B. Active government intervention in the economy C. Individuals and firms abiding by a government economic plan D. A very fair distribution of income and wealth 12. By free enterprise, we mean that: A. Products are provided free to those who can't afford to buy them B. Individuals may obtain resources, organize production, and sell the resulting output in any legal way they choose C. Individual producers are free to produce whatever the government decides are needed by the society D. Individuals are free to buy whatever products will satisfy their needs the most 13. Which of the following statements is correct? A. The operation of a market system eventually results in an equal distribution of income B. Producers are "kings" in a market economy because they determine what is produced C. The market system is efficient at allocating resources, but not at distributing products D. Freedom of choice and enterprise are essential elements of the market system 14. In a market system, self-interest is the motivating force that drives the decisions and actions of the following groups, except: A. Workers B. Consumers C. Public officials D. Entrepreneurs 15. How do workers typically express self-interest? A. By minimizing the economic losses of other business firms B. By maximizing the economic profits of other business firms C. By seeking the highest price when purchasing a consumer product D. By seeking jobs with the best combination of wages and benefits 16. In a market economy, entrepreneurs are most concerned with: A. Maximizing utility or satisfaction from limited incomes B. Increasing the wages and salaries of workers C. Maximizing profits or minimizing losses D. The selfish pursuit of money 17. Consumers express self-interest when they: A. Seek the lowest price for a product B. Reduce business losses C. Collect economic profits D. Search for jobs with the highest wages 18. Which of the following statements about the right to private ownership is false? A. It enables individuals to obtain, use, and dispose of land and capital resources as they see fit B. It encourages investment and innovation, and thus fosters economic growth C. It extends to intangibles such as pieces of music and computer programs D. It weakens the incentive to maintain the property that one already owns 19. Competition is more likely to exist when: A. There is easy entry into and exit out of industries B. A government-issued license is required to set up a firm in an industry C. The government purchases most goods and services D. Economic power is concentrated among a few large firms 20. Competition denotes a condition where: A. The diffusion of economic power limits its potential abuse B. A given product can be purchased at a wide range of prices C. There are significant hurdles to entering a market D. A few large sellers are constantly jostling for market share 21. Which statement is correct? A. In a market system, buyers and sellers must be in face-to-face contact with each other B. Prices affect the distribution of goods in a market system but not the allocation of resources C. In a market system, prices serve to ration goods and services to consumers D. The operation of a market system has little, if any, effect on the distribution of income in the economy 22. The construction and use of capital goods to aid in the production of consumer goods illustrates the: A. Division of labor B. Specialization of resources C. Coordinating and regulating function of prices D. Roundabout but more efficient production 23. A characteristic of the market system is: A. Extensive use of direct methods of production B. Extensive use of barter C. Extensive use of capital goods D. Low interest rates 24. All of the following statements describe a market economy : A. Government prescribes the desired prices for goods and services B. Prices serve as a signaling mechanism to buyers and sellers C. The allocation of resources is determined by their prices D. The actions of buyers and sellers establish a product's price 25. The system where workers concentrate on specialized tasks to make a product is referred to as: A. A coincidence of wants B. Roundabout production C. Freedom of enterprise D. Division of labor 26. How does human specialization contribute to an economy's output? A. It makes use of differences in abilities B. It is a process of creative destruction C. It works like an "invisible hand" D. It decreases derived demand 27. Which of the following is not a reason why specialization and trade are beneficial to society? A. The output of economic goods may be increased even without any increase in resources B. Scarce resources are utilized more efficiently C. Division of labor fosters learning by doing, thus lowering the unit-costs of products D. Firms and workers become less dependent on others for producing goods and services 28. A required element of specialization is: A. A capitalist economy B. Exchange and trade C. Free enterprise D. Competition 29. Which is an example of barter? A. A person trades a desk for a box of tools B. A person buys clothes at a used clothing store C. A gift of tuition money from parents to their children D. The purchase of stock on the New York Stock Exchange 30. An economic system in which money is used is a: A. Planned economy B. Market economy C. Mixed economy D. Barter economy 31. Which of the following is necessary to make a trade in a barter economy? A. Money B. Unlimited wants C. A medium of exchange D. A coincidence of wants 32. Consider a barter system where you have pens, but you want pencils. To satisfy your want there must be: A. Money in the economy B. Easy entry into the market C. Specialization D. Coincidence of wants 33. The use of money for exchange: A. Increases the use of barter B. Encourages more specialization in production C. Reduces consumer sovereignty D. Raises the need for a coincidence of wants 34. Anything that is generally acceptable in trading for goods and services is a: A. Medium of exchange B. Measure of value C. Store of value D. Token money 35. Which is the main problem with the barter system of exchange? A. It encourages self-interest and selfishness B. It fosters specialization and division of labor C. It requires a coincidence of wants D. It undermines the right to bequeath 36. International specialization and trade: A. Has to be done on a barter system B. Often requires the exchange of currencies C. Does not illustrate the division of labor D. Requires active government regulation 37. Why might a company use barter rather than money to make a transaction? A. Barter is generally more efficient than money exchanges B. Barter can enable two firms to trade when their cash flows are limited C. Money requires a coincidence of wants, barter is more direct D. Money is economically efficient for large transactions, but barter is preferred for smaller transactions 38. Which is assumed to be most limited in scope under a market system? A. Entrepreneurship B. Consumer sovereignty C. Competition D. Government 39. If a nation restricts trade with other nations, then the most likely effect is: A. Lower prices of goods and services in the nation B. Increased specialization of production C. Expand the economic wealth of the nation D. Make consumers in the nation worse off 40. Which is one of the five fundamental questions that need to be dealt with in any economic system? A. What makes the rate of unemployment low? B. Who will be the richest group in the economy? C. What goods and services will be produced? D. How high should the prices of goods and services be? 41. All economic systems must answer certain fundamental economic questions. Which is one of these questions? A. Which actions should government take to reduce inflation? B. How will the goods and services be produced? C. How will the economy accommodate change? D. Who is to receive the output? 42. Which is one of the five fundamental questions that an economy must deal with? A. How will the goods and services be produced? B. Why should the goods and services be produced? C. Who is to receive the goods and services produced in the economy? D. In what ways will progress be promoted? 43. Consumer sovereignty and "dollar votes" guide the market system in dealing with which fundamental question? A. What will be produced? B. How is the output to be produced? C. How can the system accommodate change? D. Who is to receive the output? 44. The term means that: A. Government is responsible for protecting consumers' interests B. What is produced is ultimately determined by what consumers buy C. There are no limits on what consumers may buy in a market system D. Producers have a strong influence over what consumers buy 45. The market system is said to be characterized by "consumer sovereignty." This is because: A. A large number of consumer goods are produced B. The prices of consumer goods are regulated by government C. Consumer goods are more profitable than investment goods D. Of the role of consumers in determining what goods are produced 46. The term in a market system means: A. Inflation will occur if consumers don't spend wisely B. Voters may be offered dollars to help elect certain political candidates C. Government is responsible for determining what will be considered legal tender D. Consumers "vote" for certain products to be produced by how they spend their incomes 47. Payments that a firm makes to obtain needed resources comprise its: A. Costs B. Profits C. Capital D. Revenues 48. In a market system, which production techniques will be used by firms to produce their output? A. Those that would allow firms to maximize their prices B. Those that would allow firms to maximize their profits C. Those that would allow firms to maximize their total costs D. Those that would allow firms to minimize their total revenues 49. If the total costs of producing 1,500 units of output is $15,000 and this output sold to consumers for $16,500, then the firm would earn profits of: A. $1,000 B. $16,500 C. $1,500 D. $15,000 50. The production technique that is most efficient is the one that produces a given amount of output: A. using the least amount of labor and capital resources B. at the highest price C. at the lowest total cost D. yielding the maximum total revenues 51. McDonald's introduced the "Big Mac" in 1968 and it turned out to be a hit, but the "Arch Deluxe" introduced in 1996 was not. The success or failure of a product in the market system is determined by: A. Capitalism and entrepreneurship B. Specialization and exchange C. Consumer sovereignty and dollar votes D. Capital goods and roundabout production 52. With an increase in profits in a particular industry, we would expect: A. Firms to leave the industry B. Firms to produce less C. Firms to enter the industry D. People to buy less 53. Firms will tend to leave an industry when: A. Profits in the industry are high B. Demand for the industry's product is decreasing C. Costs of production in the industry are decreasing D. The price of industry's product is rising 54. Within a market economy, some industries may be declining while other industries may be expanding. This indicates that: A. Incomes are declining B. Resources are being reallocated C. Factors of production are scarce D. Producers are not maximizing profits 55. An increase in the demand for a product and a reduction in its costs of production would: A. Decrease profits B. Encourage firms to leave an industry C. Encourage firms to enter an industry D. Cause a shortage of the product 56. Under what circumstances would you expect economic profits to be zero in a particular industry? A. During a recession B. When there is little competition in the industry C. When the industry is neither expanding nor contracting D. When the demand for the product being produced is increasing 57. As new firms enter an expanding industry: A. Economic profits tend to rise B. Economic profits tend to decline C. Normal profits tend to decline D. Market power in the industry becomes more concentrated 58. Economic efficiency is the primary guide in answering which of the fundamental questions in a market economy? A. What will be produced? B. How is the output to be produced? C. How can the system accommodate change? D. Who is to receive the output? Suppose a firm can produce 70 units of a hypothetical product, Zenia, by combining labor, land, capital, and entrepreneurial ability in each of the four alternative techniques shown in the table below. Assume further that the firm can hire labor at $3 per unit, land at $3 per unit, capital at $6 per unit, and entrepreneurship at $9 per unit. 59. Refer to the above table. Which technique is economically the most efficient way of producing Zenia? A. A B. B C. C D. D 60. Refer to the above table. If each of the 70 Zenias that are produced sells for $1 each, what will be the economic profit for the firm? A. $7 B. $10 C. $13 D. $19 61. Refer to the above table. If the price of labor declines from $3 to $2 per unit, then what is the least costly way of producing Zenias? A. A B. B C. C D. D The following table illustrates alternative production techniques for producing 18 widgets that can be sold for $1 each for a total revenue of $18. 62. Based on the data shown above, the economically most efficient production technique is: A. A B. B C. C D. D 63. Refer to the above table. Using the technique cited in the previous question will result in an: A. Economic loss of $2 B. Economic profit of $1 C. Economic profit of $2 D. Economic profit of $3 64. Refer to the above table. If the price per unit of labor were to increase from $2 to $3, the most efficient production technique would then be: A. A B. B C. C D. D 65. Refer to the above table. At the $3 price for labor the most efficient technique will result in an: A. Economic loss of $2 B. Economic profit of $l C. Economic profit of $2 D. Economic profit of $3 66. Refer to the above table. If the resource prices doubled and the product price doubled from the original amounts, what would be the least costly production technique? A. A B. B C. C D. D 67. Refer to the above table. If the resource prices doubled and the product price doubled from the original amounts, what would be the economic profit? A. $l B. $3 C. $6 D. $9 68. "For whom is a given mix of goods and services to be produced? How, in other words, are the society's outputs to be distributed among its members?" In a market economy, this problem is resolved primarily in the: A. Public sector through the mechanism of central planning B. Business sector through the mechanism of advertising C. Private sector through the earning and spending of income D. Money market through borrowing and saving by households and businesses 69. Issues of the distribution of goods and services and of incomes in a market system are the primary topics of which fundamental question? A. What is to be produced? B. How is the output to be produced? C. How can the system accommodate change? D. Who is to receive the output? 70. In a market economy, the money incomes of individuals depend primarily upon: A. Government policies in setting wages and interest rates B. The values and amounts of productive resources that the individuals possess C. The amount of education that the individuals have D. How hard they are willing to work 71. The market system communicates changes in market conditions and elicits appropriate responses from businesses and resource suppliers through changes in prices. This is known as the: A. Market determination of prices B. Guiding function of prices C. Monetary function of prices D. Circular flow of income 72. Which fundamental economic question does a market system primarily address by focusing on technological advance and capital accumulation? A. What is to be produced? B. How is the output to be produced? C. How will the system promote progress? D. Who is to receive the output? 73. The development of the Internet and e-mail to replace regular mail would be an example of: A. Roundabout production B. Derived demand C. Creative destruction D. Specialization 74. Which of the following does not illustrate the idea of ? A. Digital downloads have shrunk the market for CDs and DVDs B. CDs and DVDs replaced cassette tapes in many homes and offices C. The opening of a new mall reduces the traffic in another mall D. A firm has to destroy some of the expired products in its inventory 75. The idea that the desires of resource suppliers and firms to further their own self-interest will automatically further the public interest is known as: A. Consumer sovereignty B. The invisible hand C. Derived demand D. Profit maximization 76. Which of the following best describes the "invisible hand" concept? A. Ample regulation of business by the government will maximize the public's best interests B. The market system works best when resources are free to move from one use to another C. The problem of scarcity can best be overcome in a system of mixed capitalism D. Self-interest in a market system will automatically promote the public interest as well 77. The highly influential book written by Adam Smith is titled: A. B. C. D. 78. The "invisible hand" concept used to describe the guiding function of prices was developed by: A. Barack Obama B. Adam Smith C. Milton Friedman D. John Kenneth Galbraith 79. The major virtues of the market system include all of the following, except: A. It promotes an efficient allocation of resources B. It leads to equality in the distribution of income C. It provides incentives for greater production and higher incomes D. It emphasizes the freedom to pursue self-interest 80. The market economy is regarded as "efficient" in that: A. It achieves the lowest rate of unemployment B. It leads to the lowest level of poverty in the society C. It directs resources towards products that the society wants most D. It puts the best people in government positions 81. The basic problem in central planning has to do with: A. Determining the production goals for a factory B. Determining the proper geographic location of new firms C. Coordinating production so that production bottlenecks do not develop D. Providing financial resources for increasing the real flows of products 82. The major "success indicator" for business managers in command economies like the Soviet Union and China in the past was: A. The quantity of output B. Product quality C. The amount of profits D. Worker morale 83. A characteristic of centrally planned economies is that: A. The price is relatively unimportant in allocating resources B. Output reflects the pattern of consumer spending C. Income is fairly distributed among individuals D. There are many incentives for innovation and hard work 84. Which is true of an economy which operates entirely through central planning? A. Individual economic incentive is reduced by the absence of the profit motive B. There is relative ease in matching resource allocation to consumer demand C. Producers receive market information through the price mechanism D. The system adapts easily to technological change 85. A major problem with state ownership of resources is that it does not: A. Allow for the full use of central economic planning B. Let state enterprises buy resources used to make products C. Let state enterprises sell products produced with those resources D. Give incentives for individuals to make the best use of those resources 86. The centrally planned system used by the former Soviet Union and pre-reform China lacked: A. Entrepreneurship B. Production targets C. Allocation by directive D. Government price setting 87. In the circular flow model, households: A. Buy products and resources B. Sell products and resources C. Buy products and sell resources D. Sell products and buy resources 88. The circular flow model: A. Assumes that central planning is taking place B. Illustrates how natural resources are created C. Illustrates how money is created by the banking system D. Illustrates the interdependence of businesses and consumers 89. The simple circular flow model shows that workers and capital-owners offer their services to firms through the: A. Product markets B. Resource markets C. Employment agencies D. Government agencies 90. In the circular flow model, households earn their incomes in the: A. Resource markets B. Product markets C. Capitalist markets D. Money markets 91. In product markets: A. Households earn revenues from businesses B. Business incur their consumption expenditures to households C. Businesses acquire their inputs from households D. Businesses earn their revenues from households 92. The money income of households consists of the sum of: A. Wages plus salaries plus profits B. Consumption expenditures plus profits C. Wages plus rents plus interest plus profits D. Revenues plus profits plus wages 93. Which of the following would be primarily determined in the resource market? A. The price of compact discs B. The wage rates for electricians C. The number of automobiles produced D. The amount of money in circulation 94. Refer to the above figure. If box A represents households, B the product market, and C businesses, and if flow (3) represents revenues, then flow (1) would represent: A. Costs B. Money income C. Consumption expenditures D. Resources 95. Refer to the above figure. If box A represents households, D the resource market, and C businesses, then flow (8) would represent ___ while flow (6) would represent ___. A. Revenues; costs B. Consumption expenditures; money income C. Resources; money income D. Money income; costs 96. Refer to the above figure. If box A represents households, B the product market, and C businesses, and if flow (3) represents revenues, then (4) would represent ___ while flow (5) would represent ____. A. Resources; goods and services B. Goods and services; resources C. Costs; resources D. Goods and services; costs 97. In the circular flow diagram, households: A. Make consumption expenditures and pay for land, labor, and capital B. Make consumption expenditures and receive goods and services C. Buy resources and receive goods and services D. Receive revenue and supply resources 98. What, according to economist Donald Boudreaux in the "Last Word" section of the chapter, best explains why the decentralized market system is a random, chaotic mess? A. There is active cooperation among private property owners and government officials to correct the excesses of a market economy B. The roundabout methods of production allocate resources from consumers to producers in an orderly fashion C. Government planning limits the chaos and government controls direct economic activity to create stability in the market D. People choose the course of action that promises the highest reward, and in the process promoting efficiency and growth in the society True / False Questions 99. A market system is characterized by the private ownership of resources and the use of markets and prices to coordinate economic activity. True False 100. The economy of the United States can best be described as capitalism. True False 101. Property rights have a positive effect in a market economy because they encourage owners to maintain their property. True False 102. Property rights are the right of the government to own, use, and dispose of resources in an economy. True False 103. Selfishness and self-interest are identical concepts. True False 104. An important part of the market system is that producers and consumers consider the public interest in making production and consumption decisions. True False 105. If people tried to produce as much of what they need on their own, then this would lead to a more efficient use of the economy's resources. True False 106. A division of labor enhances a society's total output by permitting people to take advantage of existing differences in their abilities and skills. True False 107. Exchange by barter is just as efficient as trading with money. True False 108. One of the most important economic resources is money. True False 109. Maximizing profits always means the same thing as maximizing revenues. True False 110. If economic profits exist in an industry, resource suppliers will be enticed into expanding the industry. True False 111. The concept of consumer sovereignty refers to the situation where consumers have the right to vote for the board of directors of large corporations. True False 112. Firms will choose the production techniques that will give them the maximum price and revenues. True False 113. Economic efficiency entails producing a certain output with the minimum number of units of inputs. True False 114. The choice of the most efficient production technique is not affected by how much buyers want to buy the product. True False 115. In the market system, prices tend to guide resources from less important to more important uses as the market system accommodates change. True False 116. In a competitive market economy, firms and resource suppliers will seek to further their own self-interest and at the same time, as if guided by an "invisible hand," they will promote the public interest. True False 117. The problems of central planning become more complex as an economy grows over time. True False 118. Profit, but not price, is the primary success indicator in a centrally planned economy. True False 119. Quantitative measures of managerial success, such as production targets or quotas, are highly foolproof and are thus ideal to use. True False 120. In the circular flow model, households function as buyers in both the product and resource markets. True False 121. In a market system, entrepreneurs start up businesses in order to earn a high salary. True False 122. In a market system, the income earned by owners of natural resources is called interest income. True False 123. A corporation is a type of business firm where the debt of the firm is fully its owners' debt as well. True False 124. According to the circular flow model of the market system, firms get their ability to pay for their costs of production from the revenues that they receive for their products. True False 125. According to the circular flow model of the market system, when resource-owners' money income is rising, then the costs to business firms must be falling. True False Chapter 02 The Market System and the Circular Flow Answer Key Multiple Choice Questions 1. The market system is an economic system that: A. Produces more consumer goods than capital goods B. Produces more capital goods than consumer goods C. Gives private individuals the right to own resources used in production D. Emphasizes the government's power to control markets and direct economic activity 2. The market system is often also known as: A. Capitalism B. Socialism C. Central planning D. Regulation 3. One element of the command system is: A. Capitalism B. Free markets C. Private ownership D. Central planning 4. The extensive private ownership of property resources in a market system has the following implications, except: A. The market system is also known as capitalism B. Trades that take place in a market system are mutually-agreeable transactions C. Investment, innovation, and maintenance of property are fostered by the market system D. The strong in the society could accumulate property by overpowering the weak 5. Which statement best describes the market system? A. Entrepreneurs direct production activities, and market prices allocate goods and services B. Government policies direct production activities and allocate goods and services C. Government policies direct production activities, while market prices allocate goods and services D. Individuals and markets all function smoothly under the guidance and regulation of the government 6. In a command system: A. Self-interest guides and commands individuals to pursue actions that lead them toward achieving their goals B. The head of each family decides what to do with the family's resources C. The government makes production and allocation decisions D. Market traders command what outputs are produced and how they are allocated 7. Which would be characteristic of a capitalist economy? A. Government ownership of most factors of production B. Competition and unrestricted markets C. Reliance on the market system D. Freedom of enterprise and choice 8. A basic characteristic of a command system is that: A. Wages paid to labor are higher B. Government owns most economic resources C. Free markets are never permitted in a command economy D. Government planners play a limited role in deciding what goods will be produced 9. The economies of Ireland and France are: A. Similar in that they are both basically command systems B. Similar in that they are both basically market systems C. Different in that Ireland has a command system while France has a market system D. Different in that France has a command system while Ireland has a market system 10. The economies of North Korea and South Korea are: A. Similar in that they are both basically command systems B. Similar in that they are both basically market systems C. Different in that North Korea has a command system while South Korea has a market system D. Different in that South Korea has a command system while North Korea has a market system 11. capitalism is characterized by: A. Very limited government role in the economy B. Active government intervention in the economy C. Individuals and firms abiding by a government economic plan D. A very fair distribution of income and wealth 12. By free enterprise, we mean that: A. Products are provided free to those who can't afford to buy them B. Individuals may obtain resources, organize production, and sell the resulting output in any legal way they choose C. Individual producers are free to produce whatever the government decides are needed by the society D. Individuals are free to buy whatever products will satisfy their needs the most 13. Which of the following statements is correct? A. The operation of a market system eventually results in an equal distribution of income B. Producers are "kings" in a market economy because they determine what is produced C. The market system is efficient at allocating resources, but not at distributing products D. Freedom of choice and enterprise are essential elements of the market system 14. In a market system, self-interest is the motivating force that drives the decisions and actions of the following groups, except: A. Workers B. Consumers C. Public officials D. Entrepreneurs 15. How do workers typically express self-interest? A. By minimizing the economic losses of other business firms B. By maximizing the economic profits of other business firms C. By seeking the highest price when purchasing a consumer product D. By seeking jobs with the best combination of wages and benefits 16. In a market economy, entrepreneurs are most concerned with: A. Maximizing utility or satisfaction from limited incomes B. Increasing the wages and salaries of workers C. Maximizing profits or minimizing losses D. The selfish pursuit of money 17. Consumers express self-interest when they: A. Seek the lowest price for a product B. Reduce business losses C. Collect economic profits D. Search for jobs with the highest wages 18. Which of the following statements about the right to private ownership is false? A. It enables individuals to obtain, use, and dispose of land and capital resources as they see fit B. It encourages investment and innovation, and thus fosters economic growth C. It extends to intangibles such as pieces of music and computer programs D. It weakens the incentive to maintain the property that one already owns 19. Competition is more likely to exist when: A. There is easy entry into and exit out of industries B. A government-issued license is required to set up a firm in an industry C. The government purchases most goods and services D. Economic power is concentrated among a few large firms 20. Competition denotes a condition where: A. The diffusion of economic power limits its potential abuse B. A given product can be purchased at a wide range of prices C. There are significant hurdles to entering a market D. A few large sellers are constantly jostling for market share 21. Which statement is correct? A. In a market system, buyers and sellers must be in face-to-face contact with each other B. Prices affect the distribution of goods in a market system but not the allocation of resources C. In a market system, prices serve to ration goods and services to consumers D. The operation of a market system has little, if any, effect on the distribution of income in the economy 22. The construction and use of capital goods to aid in the production of consumer goods illustrates the: A. Division of labor B. Specialization of resources C. Coordinating and regulating function of prices D. Roundabout but more efficient production 23. A characteristic of the market system is: A. Extensive use of direct methods of production B. Extensive use of barter C. Extensive use of capital goods D. Low interest rates 24. All of the following statements describe a market economy : A. Government prescribes the desired prices for goods and services B. Prices serve as a signaling mechanism to buyers and sellers C. The allocation of resources is determined by their prices D. The actions of buyers and sellers establish a product's price 25. The system where workers concentrate on specialized tasks to make a product is referred to as: A. A coincidence of wants B. Roundabout production C. Freedom of enterprise D. Division of labor 26. How does human specialization contribute to an economy's output? A. It makes use of differences in abilities B. It is a process of creative destruction C. It works like an "invisible hand" D. It decreases derived demand 27. Which of the following is not a reason why specialization and trade are beneficial to society? A. The output of economic goods may be increased even without any increase in resources B. Scarce resources are utilized more efficiently C. Division of labor fosters learning by doing, thus lowering the unit-costs of products D. Firms and workers become less dependent on others for producing goods and services 28. A required element of specialization is: A. A capitalist economy B. Exchange and trade C. Free enterprise D. Competition 29. Which is an example of barter? A. A person trades a desk for a box of tools B. A person buys clothes at a used clothing store C. A gift of tuition money from parents to their children D. The purchase of stock on the New York Stock Exchange 30. An economic system in which money is used is a: A. Planned economy B. Market economy C. Mixed economy D. Barter economy 31. Which of the following is necessary to make a trade in a barter economy? A. Money B. Unlimited wants C. A medium of exchange D. A coincidence of wants 32. Consider a barter system where you have pens, but you want pencils. To satisfy your want there must be: A. Money in the economy B. Easy entry into the market C. Specialization D. Coincidence of wants 33. The use of money for exchange: A. Increases the use of barter B. Encourages more specialization in production C. Reduces consumer sovereignty D. Raises the need for a coincidence of wants 34. Anything that is generally acceptable in trading for goods and services is a: A. Medium of exchange B. Measure of value C. Store of value D. Token money 35. Which is the main problem with the barter system of exchange? A. It encourages self-interest and selfishness B. It fosters specialization and division of labor C. It requires a coincidence of wants D. It undermines the right to bequeath 36. International specialization and trade: A. Has to be done on a barter system B. Often requires the exchange of currencies C. Does not illustrate the division of labor D. Requires active government regulation 37. Why might a company use barter rather than money to make a transaction? A. Barter is generally more efficient than money exchanges B. Barter can enable two firms to trade when their cash flows are limited C. Money requires a coincidence of wants, barter is more direct D. Money is economically efficient for large transactions, but barter is preferred for smaller transactions 38. Which is assumed to be most limited in scope under a market system? A. Entrepreneurship B. Consumer sovereignty C. Competition D. Government 39. If a nation restricts trade with other nations, then the most likely effect is: A. Lower prices of goods and services in the nation B. Increased specialization of production C. Expand the economic wealth of the nation D. Make consumers in the nation worse off 40. Which is one of the five fundamental questions that need to be dealt with in any economic system? A. What makes the rate of unemployment low? B. Who will be the richest group in the economy? C. What goods and services will be produced? D. How high should the prices of goods and services be? 41. All economic systems must answer certain fundamental economic questions. Which is one of these questions? A. Which actions should government take to reduce inflation? B. How will the goods and services be produced? C. How will the economy accommodate change? D. Who is to receive the output? 42. Which is one of the five fundamental questions that an economy must deal with? A. How will the goods and services be produced? B. Why should the goods and services be produced? C. Who is to receive the goods and services produced in the economy? D. In what ways will progress be promoted? 43. Consumer sovereignty and "dollar votes" guide the market system in dealing with which fundamental question? A. What will be produced? B. How is the output to be produced? C. How can the system accommodate change? D. Who is to receive the output? 44. The term means that: A. Government is responsible for protecting consumers' interests B. What is produced is ultimately determined by what consumers buy C. There are no limits on what consumers may buy in a market system D. Producers have a strong influence over what consumers buy 45. The market system is said to be characterized by "consumer sovereignty." This is because: A. A large number of consumer goods are produced B. The prices of consumer goods are regulated by government C. Consumer goods are more profitable than investment goods D. Of the role of consumers in determining what goods are produced 46. The term in a market system means: A. Inflation will occur if consumers don't spend wisely B. Voters may be offered dollars to help elect certain political candidates C. Government is responsible for determining what will be considered legal tender D. Consumers "vote" for certain products to be produced by how they spend their incomes 47. Payments that a firm makes to obtain needed resources comprise its: A. Costs B. Profits C. Capital D. Revenues 48. In a market system, which production techniques will be used by firms to produce their output? A. Those that would allow firms to maximize their prices B. Those that would allow firms to maximize their profits C. Those that would allow firms to maximize their total costs D. Those that would allow firms to minimize their total revenues 49. If the total costs of producing 1,500 units of output is $15,000 and this output sold to consumers for $16,500, then the firm would earn profits of: A. $1,000 B. $16,500 C. $1,500 D. $15,000 50. The production technique that is most efficient is the one that produces a given amount of output: A. using the least amount of labor and capital resources B. at the highest price C. at the lowest total cost D. yielding the maximum total revenues 51. McDonald's introduced the "Big Mac" in 1968 and it turned out to be a hit, but the "Arch Deluxe" introduced in 1996 was not. The success or failure of a product in the market system is determined by: A. Capitalism and entrepreneurship B. Specialization and exchange C. Consumer sovereignty and dollar votes D. Capital goods and roundabout production 52. With an increase in profits in a particular industry, we would expect: A. Firms to leave the industry B. Firms to produce less C. Firms to enter the industry D. People to buy less 53. Firms will tend to leave an industry when: A. Profits in the industry are high B. Demand for the industry's product is decreasing C. Costs of production in the industry are decreasing D. The price of industry's product is rising 54. Within a market economy, some industries may be declining while other industries may be expanding. This indicates that: A. Incomes are declining B. Resources are being reallocated C. Factors of production are scarce D. Producers are not maximizing profits 55. An increase in the demand for a product and a reduction in its costs of production would: A. Decrease profits B. Encourage firms to leave an industry C. Encourage firms to enter an industry D. Cause a shortage of the product 56. Under what circumstances would you expect economic profits to be zero in a particular industry? A. During a recession B. When there is little competition in the industry C. When the industry is neither expanding nor contracting D. When the demand for the product being produced is increasing 57. As new firms enter an expanding industry: A. Economic profits tend to rise B. Economic profits tend to decline C. Normal profits tend to decline D. Market power in the industry becomes more concentrated 58. Economic efficiency is the primary guide in answering which of the fundamental questions in a market economy? A. What will be produced? B. How is the output to be produced? C. How can the system accommodate change? D. Who is to receive the output? Suppose a firm can produce 70 units of a hypothetical product, Zenia, by combining labor, land, capital, and entrepreneurial ability in each of the four alternative techniques shown in the table below. Assume further that the firm can hire labor at $3 per unit, land at $3 per unit, capital at $6 per unit, and entrepreneurship at $9 per unit. 59. Refer to the above table. Which technique is economically the most efficient way of producing Zenia? A. A B. B C. C D. D 60. Refer to the above table. If each of the 70 Zenias that are produced sells for $1 each, what will be the economic profit for the firm? A. $7 B. $10 C. $13 D. $19 61. Refer to the above table. If the price of labor declines from $3 to $2 per unit, then what is the least costly way of producing Zenias? A. A B. B C. C D. D The following table illustrates alternative production techniques for producing 18 widgets that can be sold for $1 each for a total revenue of $18. 62. Based on the data shown above, the economically most efficient production technique is: A. A B. B C. C D. D 63. Refer to the above table. Using the technique cited in the previous question will result in an: A. Economic loss of $2 B. Economic profit of $1 C. Economic profit of $2 D. Economic profit of $3 64. Refer to the above table. If the price per unit of labor were to increase from $2 to $3, the most efficient production technique would then be: A. A B. B C. C D. D 65. Refer to the above table. At the $3 price for labor the most efficient technique will result in an: A. Economic loss of $2 B. Economic profit of $l C. Economic profit of $2 D. Economic profit of $3 66. Refer to the above table. If the resource prices doubled and the product price doubled from the original amounts, what would be the least costly production technique? A. A B. B C. C D. D 67. Refer to the above table. If the resource prices doubled and the product price doubled from the original amounts, what would be the economic profit? A. $l B. $3 C. $6 D. $9 68. "For whom is a given mix of goods and services to be produced? How, in other words, are the society's outputs to be distributed among its members?" In a market economy, this problem is resolved primarily in the: A. Public sector through the mechanism of central planning B. Business sector through the mechanism of advertising C. Private sector through the earning and spending of income D. Money market through borrowing and saving by households and businesses 69. Issues of the distribution of goods and services and of incomes in a market system are the primary topics of which fundamental question? A. What is to be produced? B. How is the output to be produced? C. How can the system accommodate change? D. Who is to receive the output? 70. In a market economy, the money incomes of individuals depend primarily upon: A. Government policies in setting wages and interest rates B. The values and amounts of productive resources that the individuals possess C. The amount of education that the individuals have D. How hard they are willing to work 71. The market system communicates changes in market conditions and elicits appropriate responses from businesses and resource suppliers through changes in prices. This is known as the: A. Market determination of prices B. Guiding function of prices C. Monetary function of prices D. Circular flow of income 72. Which fundamental economic question does a market system primarily address by focusing on technological advance and capital accumulation? A. What is to be produced? B. How is the output to be produced? C. How will the system promote progress? D. Who is to receive the output? 73. The development of the Internet and e-mail to replace regular mail would be an example of: A. Roundabout production B. Derived demand C. Creative destruction D. Specialization 74. Which of the following does not illustrate the idea of ? A. Digital downloads have shrunk the market for CDs and DVDs B. CDs and DVDs replaced cassette tapes in many homes and offices C. The opening of a new mall reduces the traffic in another mall D. A firm has to destroy some of the expired products in its inventory 75. The idea that the desires of resource suppliers and firms to further their own self-interest will automatically further the public interest is known as: A. Consumer sovereignty B. The invisible hand C. Derived demand D. Profit maximization 76. Which of the following best describes the "invisible hand" concept? A. Ample regulation of business by the government will maximize the public's best interests B. The market system works best when resources are free to move from one use to another C. The problem of scarcity can best be overcome in a system of mixed capitalism D. Self-interest in a market system will automatically promote the public interest as well 77. The highly influential book written by Adam Smith is titled: A. B. C. D. 78. The "invisible hand" concept used to describe the guiding function of prices was developed by: A. Barack Obama B. Adam Smith C. Milton Friedman D. John Kenneth Galbraith 79. The major virtues of the market system include all of the following, except: A. It promotes an efficient allocation of resources B. It leads to equality in the distribution of income C. It provides incentives for greater production and higher incomes D. It emphasizes the freedom to pursue self-interest 80. The market economy is regarded as "efficient" in that: A. It achieves the lowest rate of unemployment B. It leads to the lowest level of poverty in the society C. It directs resources towards products that the society wants most D. It puts the best people in government positions 81. The basic problem in central planning has to do with: A. Determining the production goals for a factory B. Determining the proper geographic location of new firms C. Coordinating production so that production bottlenecks do not develop D. Providing financial resources for increasing the real flows of products 82. The major "success indicator" for business managers in command economies like the Soviet Union and China in the past was: A. The quantity of output B. Product quality C. The amount of profits D. Worker morale 83. A characteristic of centrally planned economies is that: A. The price is relatively unimportant in allocating resources B. Output reflects the pattern of consumer spending C. Income is fairly distributed among individuals D. There are many incentives for innovation and hard work 84. Which is true of an economy which operates entirely through central planning? A. Individual economic incentive is reduced by the absence of the profit motive B. There is relative ease in matching resource allocation to consumer demand C. Producers receive market information through the price mechanism D. The system adapts easily to technological change 85. A major problem with state ownership of resources is that it does not: A. Allow for the full use of central economic planning B. Let state enterprises buy resources used to make products C. Let state enterprises sell products produced with those resources D. Give incentives for individuals to make the best use of those resources 86. The centrally planned system used by the former Soviet Union and pre-reform China lacked: A. Entrepreneurship B. Production targets C. Allocation by directive D. Government price setting 87. In the circular flow model, households: A. Buy products and resources B. Sell products and resources C. Buy products and sell resources D. Sell products and buy resources 88. The circular flow model: A. Assumes that central planning is taking place B. Illustrates how natural resources are created C. Illustrates how money is created by the banking system D. Illustrates the interdependence of businesses and consumers 89. The simple circular flow model shows that workers and capital-owners offer their services to firms through the: A. Product markets B. Resource markets C. Employment agencies D. Government agencies 90. In the circular flow model, households earn their incomes in the: A. Resource markets B. Product markets C. Capitalist markets D. Money markets 91. In product markets: A. Households earn revenues from businesses B. Business incur their consumption expenditures to households C. Businesses acquire their inputs from households D. Businesses earn their revenues from households 92. The money income of households consists of the sum of: A. Wages plus salaries plus profits B. Consumption expenditures plus profits C. Wages plus rents plus interest plus profits D. Revenues plus profits plus wages 93. Which of the following would be primarily determined in the resource market? A. The price of compact discs B. The wage rates for electricians C. The number of automobiles produced D. The amount of money in circulation 94. Refer to the above figure. If box A represents households, B the product market, and C businesses, and if flow (3) represents revenues, then flow (1) would represent: A. Costs B. Money income C. Consumption expenditures D. Resources 95. Refer to the above figure. If box A represents households, D the resource market, and C businesses, then flow (8) would represent ___ while flow (6) would represent ___. A. Revenues; costs B. Consumption expenditures; money income C. Resources; money income D. Money income; costs 96. Refer to the above figure. If box A represents households, B the product market, and C businesses, and if flow (3) represents revenues, then (4) would represent ___ while flow (5) would represent ____. A. Resources; goods and services B. Goods and services; resources C. Costs; resources D. Goods and services; costs 97. In the circular flow diagram, households: A. Make consumption expenditures and pay for land, labor, and capital B. Make consumption expenditures and receive goods and services C. Buy resources and receive goods and services D. Receive revenue and supply resources 98. What, according to economist Donald Boudreaux in the "Last Word" section of the chapter, best explains why the decentralized market system is a random, chaotic mess? A. There is active cooperation among private property owners and government officials to correct the excesses of a market economy B. The roundabout methods of production allocate resources from consumers to producers in an orderly fashion C. Government planning limits the chaos and government controls direct economic activity to create stability in the market D. People choose the course of action that promises the highest reward, and in the process promoting efficiency and growth in the society True / False Questions 99. A market system is characterized by the private ownership of resources and the use of markets and prices to coordinate economic activity. TRUE 100. The economy of the United States can best be described as capitalism. FALSE 101. Property rights have a positive effect in a market economy because they encourage owners to maintain their property. TRUE 102. Property rights are the right of the government to own, use, and dispose of resources in an economy. FALSE 103. Selfishness and self-interest are identical concepts. FALSE 104. An important part of the market system is that producers and consumers consider the public interest in making production and consumption decisions. FALSE 105. If people tried to produce as much of what they need on their own, then this would lead to a more efficient use of the economy's resources. FALSE 106. A division of labor enhances a society's total output by permitting people to take advantage of existing differences in their abilities and skills. TRUE 107. Exchange by barter is just as efficient as trading with money. FALSE 108. One of the most important economic resources is money. FALSE 109. Maximizing profits always means the same thing as maximizing revenues. FALSE 110. If economic profits exist in an industry, resource suppliers will be enticed into expanding the industry. TRUE 111. The concept of consumer sovereignty refers to the situation where consumers have the right to vote for the board of directors of large corporations. FALSE 112. Firms will choose the production techniques that will give them the maximum price and revenues. FALSE 113. Economic efficiency entails producing a certain output with the minimum number of units of inputs. FALSE 114. The choice of the most efficient production technique is not affected by how much buyers want to buy the product. TRUE 115. In the market system, prices tend to guide resources from less important to more important uses as the market system accommodates change. TRUE 116. In a competitive market economy, firms and resource suppliers will seek to further their own self-interest and at the same time, as if guided by an "invisible hand," they will promote the public interest. TRUE 117. The problems of central planning become more complex as an economy grows over time. TRUE 118. Profit, but not price, is the primary success indicator in a centrally planned economy. FALSE 119. Quantitative measures of managerial success, such as production targets or quotas, are highly foolproof and are thus ideal to use. FALSE 120. In the circular flow model, households function as buyers in both the product and resource markets. FALSE 121. In a market system, entrepreneurs start up businesses in order to earn a high salary. FALSE 122. In a market system, the income earned by owners of natural resources is called interest income. FALSE 123. A corporation is a type of business firm where the debt of the firm is fully its owners' debt as well. FALSE 124. According to the circular flow model of the market system, firms get their ability to pay for their costs of production from the revenues that they receive for their products. TRUE 125. According to the circular flow model of the market system, when resource-owners' money income is rising, then the costs to business firms must be falling. FALSE