Eco. 2.2 Free Market
advertisement

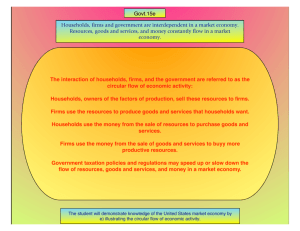
Objectives: 1. Explain why markets exist. 2. Analyze a circular flow model of a free market economy. 3. Understand the self-regulating nature of the marketplace. 4. Identify the advantages of a free market economy. --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*What does a farmers’ market, a sporting goods store, the New York Stock Exchange, and the sign you post on your community bulletin board advertising baby-sitting services have in common? *All are __________________ of ___________________. *A market is an _____________________ that allows ______________ and _____________________ to _________________________________ Why Markets Exist: Markets exist because no one is ___________________________. None of us produces all that we ____________________________________ our needs and wants. We don’t grow many of the things we __________, we buy them at a _________. Markets allow us to exchange the things we __________ for the things we __________. Instead of being self-sufficient, each of us produces just __________________ products. _______________– the concentration of the productive efforts of individuals and firms on a limited number of activities. Specialization makes us more _______________. It is easier to learn one task or a few tasks very well than to learn all the tasks we need. We need markets to sell what we have and to buy what we want. ___________________________: Economic systems that are based on _____________________________ in markets are called ______________________ Individuals and businesses use markets to exchange _________ and _____________. Individuals answer the three key economic questions. This type of economy functions best in a system of ______________________________ governments (like U.S.) We can represent a free market economy in a special kind of drawing called a ______________________________________. A Circular Flow diagrams shows at a glance how individuals and businesses exchange ___________, __________________, and ____________________ in the marketplace. The inner ring of the diagram represents the flow of ____________________________. The outer ring of the diagram represents the flow of _________________. ______________________ – are a person or group of people living in the same residence. Households own the ________________________________ – land, labor, and capital. _____________________ o r ________ – an organization that uses resources to produce a product which it then sells. Firms transfer “____________” or factors of production into “____________” or products. Factor Markets - arena of exchange. _______________ is the financial gain made in a transaction. All businesses want a profit to stay in business. Circular Flow of Economic Activity The Self-Regulating Nature of the Marketplace: How is it that firms and households cooperate to give each other what they want – _________________________ and __________________________. ______________ said competition and our own self-interest is what keeps the marketplace functioning. 1. ________________________ In 1776 – Adam Smith published a book entitled “_______________________” He described how the ___________________________. He observed that an economy is made up of countless individual ____________. In each transaction, the buyer and seller consider only their self-interest or their ____________________________________. Self-interest is the ______________________ in the free world. 2. __________________________ Consumers (households) in pursuit of their self-interest, have the incentive to look for the _______________________. An incentive is the hope of reward or the fear of punishment that encourages a person to behave in a certain way. Smith observed that people respond predictably to both ____________ and __________________ incentives. As for consumers – we expect they will buy more of an item if the price is lower. Vice-Versa, they will buy less of an item if the price is higher. Consumers, pursuing their self-interest will buy the lower priced item most of the time. Economists call this struggle among ___________ for the dollars of consumers – ________________________. 3. __________________________ Self-interest and competition work together to ________________ the _____________________. The overall result is that consumers get the products they want at the _________ that closely affect the cost of producing them. Advantages of a Free Market: 1. 2. 3. 4. Additional Goals Consumers, in essence, decide what gets produced – called ______________________________ REVIEW: 1. How does specialization make us more efficient? 2. What is the difference between the factor market and the product market? 3. What is profit? 4. What are the roles of households and firms in a market economy? 5. How does competition among firms benefit consumers? 6. Explain what Adam Smith meant by “the invisible hand of the marketplace.” 7. What is the connection between incentives and consumer sovereignty in a free market economy?