Signal Transduction Pathways Lecture Outline
advertisement
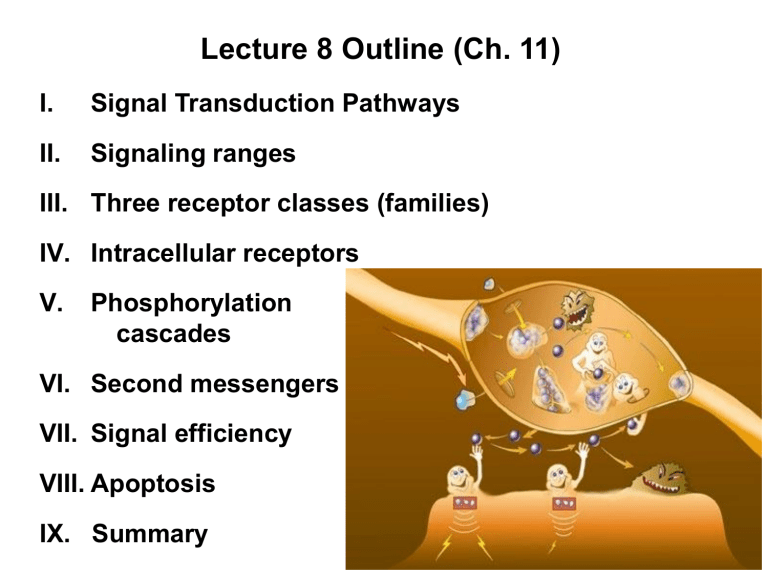
Lecture 8 Outline (Ch. 11) I. Signal Transduction Pathways II. Signaling ranges III. Three receptor classes (families) IV. Intracellular receptors V. Phosphorylation cascades VI. Second messengers VII. Signal efficiency VIII. Apoptosis IX. Summary Cell Signaling = Signal Transduction Signal Transduction – receiving a signal & relaying the response Signal Transduction Cell phone rings 1 Reception You listen to your friend 2 Transduction You drive somewhere 3 Response Receptor Relay molecules Activation of cellular response Signaling molecule Response variable – examples: mate, organize, divide, die, grow, send another signal, etc… Sending the Signal – direct contact Sending the Signal Three methods of cell signaling over distances: Signal Transduction Signal called a ligand Signaling-molecule binding site The receptor is a protein that detects the signal Segment that sends signal inside cell G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) A 7-pass transmembrane receptor Links via a G-protein….binds GTP/GDP Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs) Transmembrane receptor – dimerizes when activated Auto-phosphorylates when active to rely signal Ligand-gated ion channels Open when the ligand is bound Close when signal is not present Signal Transduction for hydrophobic molecules Hormone (testosterone) EXTRACELLULAR FLUID Plasma membrane Receptor protein Hormone (testosterone) EXTRACELLULAR FLUID Plasma membrane Receptor protein Hormonereceptor complex Hormonereceptor complex DNA DNA • hydrophobic signals - Receptor moves to DNA NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM Transduction – relay the signal • Phosphorylation: adding a phosphate group • Used to activate proteins already in the cell Transduction hydrophilic signals – relay the signal • Dephosphorylation = removing a phosphate group Signal Transduction for hydrophilic molecules • hydrophilic signals Signaling molecule Receptor alerts molecules inside the cell = phosphorylation Receptor Activated relay molecule Inactive protein kinase 1 Active protein kinase 1 Inactive protein kinase 2 ATP ADP Pi P Active protein kinase 2 PP Inactive protein kinase 3 ATP ADP Pi Active protein kinase 3 PP Inactive protein P ATP P ADP Pi PP Active protein Cellular response Signal Transduction for hydrophilic molecules First messenger G protein G protein-coupled receptor Adenylyl cyclase = small molecules inside cell to relay message GTP ATP • example second messengers: GTP, cAMP, ATP, Ca++ • Or use second messengers Second cAMP messenger Protein kinase A Cellular responses Specificity of cell signaling Scaffold proteins increase signal efficiency • Scaffold protein – larger protein for binding and bringing together several other signal proteins Response – cell does something 1 mm Interdigital tissue Response – ex. No death signal, cell lives protein (active) Inhibits activity Mitochondrion Receptor for deathsignaling molecule Inactive proteins (a) No death signal Apoptosis – programmed cell death - membrane inverts - biomolecules degraded - organelles break down Response – ex. Death signal, cell undergoes apoptosis Cell forms blebs (inactive) Deathsignaling molecule Active Active Other proteases Caspases Nucleases (b) Death signal Activation cascade Signal transduction = reception, transduction, response Growth factor Reception Receptor Phosphorylation cascade Transduction CYTOPLASM Inactive transcription factor Active transcription factor P Response DNA Gene NUCLEUS mRNA