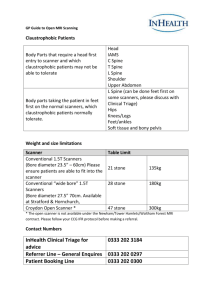
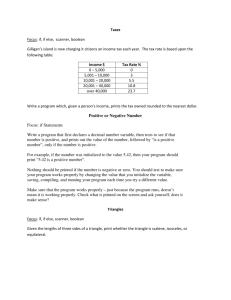
OWASP Plan
advertisement

Introducing the Web Application Security Scanner Evaluation Criteria OWASP Brian Shura Project Leader - WASSEC AppSec Consulting bshura73@gmail.com November 12, 2009 Copyright © The OWASP Foundation Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the OWASP License. The OWASP Foundation http://www.owasp.org Agenda WASSEC Overview Sections of the WASSEC Advice for Conducting a Scanner Evaluation OWASP 2 Definition of a Web Application Security Scanner An automated tool to test web applications for common security problems. Crawls a web application and locates application-layer vulnerabilities by: Manipulating HTTP messages Inspecting HTTP messages for suspicious attributes Scanners are an important part of most application security programs. OWASP 3 WASSEC - Background Web application scanners are a complex class of tools. Many scanners are available, both free and commercial tools. Quality and usefulness varies greatly. Wide variety of strong opinions on which scanners are “best” No formal criteria for conducting a detailed evaluation “Kick the tires a bit and go with your gut feel.” OWASP 4 WASSEC Overview Ongoing project promoted by the Web Application Security Consortium (WASC). Goals Provide scanner users with a reference that can be used to conduct a thorough scanner evaluation and make an informed decision. Provide scanner developers with a list of capabilities to compare their tools against to help them create a roadmap of future enhancements OWASP 5 WASSEC Project Contributors Anurag Agarwal (Whitehat Security) Vijay Agarwal (Foundstone) Robert Auger (WASC) Emilio Casbas (S21sec) Leonardo Cavallari (NSRAV) Matthieu Estrade (Bee Ware) Romain Gaucher (Cigital, Inc.) Jeremiah Grossman (Whitehat Security) Robert Hansen (SecTheory) Amit Klein Chad Loder (Rapid7) Ken Pfeil (WestLB AG) Tyler Reguly (nCircle Network Security) Ivan Ristic (Breach Security) Ory Segal (IBM) Sheeraj Shah (Blueinfy Solutions Pvt. Ltd.) Chris Shiflett (OmniTI) Brian Shura (AppSec Consulting) [Project Leader] Tom Stripling (Security PS) Chris Sullo (CIRT, Inc.) OWASP 6 WASSEC Sections 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Protocol Support Authentication Session Management Crawling Parsing Testing Command and Control Reporting OWASP 7 WASSEC Sections Protocol Support HTTP versions supported, SSL/TLS, proxy support, etc. Authentication Very important section to consider What types of authentication are used by the application you’ll be scanning? HTML form-based HTTP negotiate (NTLM, Kerberos) Single Sign-On Login process that can’t be fully automated (OTP, CAPTCHA) OWASP 8 WASSEC Sections Session Management For dynamic applications, establishing and maintaining a valid session is essential to achieving a thorough scan. Does scanner properly establish a session at beginning of test? Can scanner detect when its session is no longer valid and log back in? What types of session tokens does the scanner support? (cookies, HTTP parameters, URL path) OWASP 9 WASSEC Sections Crawling Scanner must first find the page in order to find the vulnerability! How effectively does the scanner crawl your application? The best scanners have many configuration options for fine-tuning the crawl. Can the scanner automatically submit forms during the crawl? How well does the scanner support redirects? AJAX? Lots of details in this section for developers who would like to improve their scanners! OWASP 10 WASSEC Sections Parsing Closely tied to crawling. Scanner should be able to parse common web content types and extract information such as URLs, forms, parameters, etc. Which content types are used by the applications you’ll be scanning? HTML, Javascript, CSS XML Flash ActiveX Is it possible to customize the parser to handle special situations? http://www.some.site/appEntry?param1^^value1::param2^^value 2...paramN^^valueN OWASP 11 WASSEC Sections Testing Testing capabilities – a long list of security issues that a black-box scanner should be able to test for Test configuration - it is often important to exclude certain pages, parameters, file extensions, etc. from testing. Can test policies be created to run a subset of available tests against your application? What type of support does the scanner provide for creating custom tests? OWASP 12 WASSEC Sections Command and Control Does scanner allow you to view the real-time status of running scans? Can scans be paused and resumed? Can multiple scans be run simultaneously? Does scanner support multiple users? What type of control interfaces are provided? CLI, client application with GUI, web-based interface… Does the scanner have an API and the ability to integrate with common bug-tracking systems? OWASP 13 WASSEC Sections Reporting What types of reports are available? How useful is the information provided for each vulnerability? Severity rating, CVSS score, remediation advice, etc. Can reports be customized? For example: Adding custom notes to vulnerabilities Modifying severity levels Marking issues as false positives Adding company logo to report footer or header OWASP 14 Advice for Conducting a Scanner Evaluation Go through the WASSEC and choose which criteria are important to you. In most cases you won’t care about every feature described in the WASSEC. Add the relevant criteria to your evaluation spreadsheet and assign them weights. If certain criteria are “must have”, mark them as such! OWASP 15 Advice for Conducting a Scanner Evaluation Factor in non-technical criteria such as: Purchase cost Ongoing support cost Ease of use Quality of documentation Quality of technical support Availability of training Frequency of updates Licensing restrictions Usefulness of results OWASP 16 Advice for Conducting a Scanner Evaluation Decide which scanners will be in-scope for evaluation. A thorough evaluation is a great learning experience but can be time-consuming. Eliminate scanners that don’t meet your “must have” criteria. OWASP 17 Advice for Conducting a Scanner Evaluation Obtain latest version of each scanner that is inscope for hands-on evaluation For commercial scanners, contact vendor for free trial. Don’t download old versions off of PirateBay! OWASP 18 Advice for Conducting a Scanner Evaluation Decide which applications will be scanned during evaluation. Some advice: Avoid well-known vulnerable apps like WebGoat or HackMe Bank. Chose a variety of technologies that represent what you’ll be scanning. Java, ASP.Net, AJAX or Flash-heavy applications, etc. Choose complex applications that will allow you to learn more. Large # of dynamic pages, single sign-on, spanning multiple hostnames, multi-step sequences, multiple user roles, etc. OWASP 19 Advice for Conducting a Scanner Evaluation Prepare the applications for scanning Best to use a non-Production environment If scanning Production: Back up the database first Notify Production Support personnel of your plans If you intend to publish your results, document the application setup so others can repeat it. OWASP 20 Advice for Conducting a Scanner Evaluation Multiple scans may be necessary using a variety of scan configurations. “Point and shoot” Login credentials and form-training Monitor running scan to ensure it’s not just “spinning its wheels”. For example, getting a 401 or “Session Timeout” response to every test… Running scan through a proxy can help if you need to closely analyze activity, determine whether scanner is logging in successfully, etc. Target Website Scanner HTTP Proxy OWASP 21 Advice for Conducting a Scanner Evaluation Score each of the scanners on the criteria you’ve selected and add up the weighted scores. For results, focus the amount of useful, actionable information provided by scanner, not just quantity. Tally up the scores. You can now make an informed decision on which scanner to use, purchase, or recommend. OWASP 22 Advice for Conducting a Scanner Evaluation OWASP 23 For More Information View the WASSEC: http://webappsec.org/projects/wassec Join the project mailing list: wasc-wassec-subscribe@webappsec.org Contact project leader: bshura73@gmail.com OWASP 24